Author:
Charles Brown
Date Of Creation:
4 February 2021
Update Date:
2 July 2024

Content
- To step
- Method 1 of 2: Testing the ignition coil with a spark test
- Method 2 of 2: Test the ignition coil by measuring its resistance
- Tips
- Necessities
The ignition coil, or ignition coil, is an important part of a car's ignition system. The ignition coil supplies electricity to the spark plugs. Maybe there is something wrong with the ignition coil if the car does not start, if the car does not run properly, or if the engine frequently cuts out. Fortunately, it is very easy to test whether the ignition coil is functioning properly. Based on the results, you can determine whether or not you should take the car to the garage.
To step
Method 1 of 2: Testing the ignition coil with a spark test
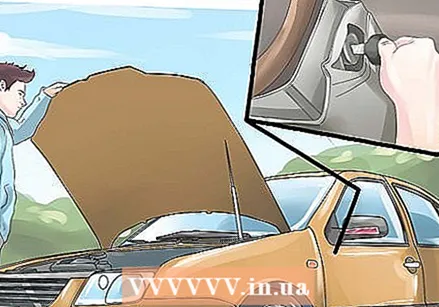 Turn off the engine and open the hood. Apply the parking brake and turn the engine off. Open the hood and look for the ignition coil. The exact location varies from car to car, but you will usually find the ignition coil at the rear of the engine compartment or under the hood of the distributor. On cars without a distributor, the spark plugs are directly connected to the ignition coil.
Turn off the engine and open the hood. Apply the parking brake and turn the engine off. Open the hood and look for the ignition coil. The exact location varies from car to car, but you will usually find the ignition coil at the rear of the engine compartment or under the hood of the distributor. On cars without a distributor, the spark plugs are directly connected to the ignition coil. - A good way to locate the ignition coil is to follow the wire from the distributor that does not lead to a spark plug.
- For your own safety, wear safety glasses and gloves and only use insulated tools to avoid shock.
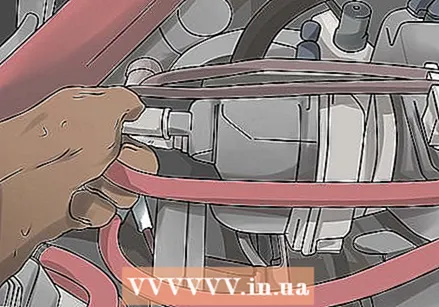 Remove a spark plug wire from the spark plug. Normally the cables run from the distributor to the different spark plugs.
Remove a spark plug wire from the spark plug. Normally the cables run from the distributor to the different spark plugs. 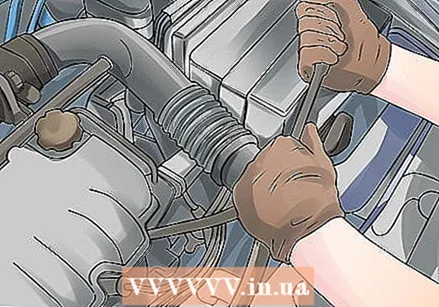 Remove the spark plug with a spark plug wrench. After you have removed the spark plug wire, you can remove the spark plug. This is best done with a special spark plug wrench.
Remove the spark plug with a spark plug wrench. After you have removed the spark plug wire, you can remove the spark plug. This is best done with a special spark plug wrench. - If your engine has been running for a long time, the various components will be very hot. If so, let the engine cool down for 5-10 minutes before starting.
- To save time and prevent your spark plug from getting damaged, consider using a spark plug tester instead. Instead of reattaching the spark plug to the wire, attach the spark plug tester to the wire. Ground the clamp. Have your friend start the engine and watch for sparks in the mouth of the tester.
- Using a spark plug tester also means that you don't expose your combustion chamber to dirt.
 Remove the spark plug using a spark plug cap. Once you've removed the spark plug wire, remove the spark plug itself. This is easiest with a specialized socket wrench called a spark plug cap.
Remove the spark plug using a spark plug cap. Once you've removed the spark plug wire, remove the spark plug itself. This is easiest with a specialized socket wrench called a spark plug cap. - From now on, be careful that nothing falls into the hole created by removing the spark plug. If something falls into the hole in the cylinder head, it can seriously damage the engine, and it is very difficult to get anything that has fallen in it. So make sure nothing falls in.
- Cover the cavity with a clean cloth or towel to prevent dirt from entering the combustion chamber.
 Reattach the spark plug to the spark plug wire. Now you have a spark plug that is connected to the distributor, but is no longer stuck in the cylinder head. Only handle the spark plug with an insulated tool to avoid shock.
Reattach the spark plug to the spark plug wire. Now you have a spark plug that is connected to the distributor, but is no longer stuck in the cylinder head. Only handle the spark plug with an insulated tool to avoid shock.  Allow the threaded portion of the spark plug to contact metal of the engine. You move the spark plug with the pliers (with the cable still attached) so that the threaded "head" makes contact with a metal part of the engine. This can be any part of the engine block - even the engine itself.
Allow the threaded portion of the spark plug to contact metal of the engine. You move the spark plug with the pliers (with the cable still attached) so that the threaded "head" makes contact with a metal part of the engine. This can be any part of the engine block - even the engine itself. - Never touch the spark plug with your hands, use insulated pliers (and wear gloves). Failure to do so may result in electric shock in the following steps.
- Failure to remove the fuel pump relay means that the cylinder under test will not fire because there is no spark plug. However, it is still flooded with fuel, which can cause serious damage.
- Consult your manual to locate the fuel pump relay.
 Ask someone to turn the ignition key. Have someone turn the ignition without starting the car. Now the car's electrical system is activated and current is applied to the spark plug that you hold with the pliers (assuming your ignition coil is working).
Ask someone to turn the ignition key. Have someone turn the ignition without starting the car. Now the car's electrical system is activated and current is applied to the spark plug that you hold with the pliers (assuming your ignition coil is working).  Check for blue sparks. If your ignition coil is working properly, you will see blue sparks when the ignition key is turned, near the electrodes on the spark plug. This spark is clearly visible in daylight. If you don't see a blue spark, your ignition coil is probably no longer good. This must then be replaced.
Check for blue sparks. If your ignition coil is working properly, you will see blue sparks when the ignition key is turned, near the electrodes on the spark plug. This spark is clearly visible in daylight. If you don't see a blue spark, your ignition coil is probably no longer good. This must then be replaced. - Orange sparks are a bad sign. This indicates a shortage of electricity supplied to the spark plug (this can be for a number of reasons, including cracks in the ignition coil housing, not enough power, poor connections, etc.).
- If you don't see any sparks at all, either the ignition coil is completely broken, the electrical connections are bad, or you did something wrong in your test.
 Reinstall the spark plug in the cylinder head and attach the spark plug wire. When you have finished your test, the ignition should be off again. Then you can perform the steps in reverse order. Disconnect the spark plug from the spark plug wire, tighten the spark plug in the hole with a spark plug wrench, and reattach the spark plug wire.
Reinstall the spark plug in the cylinder head and attach the spark plug wire. When you have finished your test, the ignition should be off again. Then you can perform the steps in reverse order. Disconnect the spark plug from the spark plug wire, tighten the spark plug in the hole with a spark plug wrench, and reattach the spark plug wire. - Congratulations! You have performed a spark test to test your ignition coil!
Method 2 of 2: Test the ignition coil by measuring its resistance
 Remove the ignition coil from the car. The test described above is not the only way to test the operation of the ignition coil. If you have access to a resistance meter or a multimeter, you can measure the resistance of the ignition coil. From this you can objectively deduce whether your ignition coil is working properly, and that is better than the somewhat subjective method from the first section. But to measure resistance, you must first remove the ignition coil from the car.
Remove the ignition coil from the car. The test described above is not the only way to test the operation of the ignition coil. If you have access to a resistance meter or a multimeter, you can measure the resistance of the ignition coil. From this you can objectively deduce whether your ignition coil is working properly, and that is better than the somewhat subjective method from the first section. But to measure resistance, you must first remove the ignition coil from the car. - Read the maintenance book for your type of car for precise instructions on how to remove the ignition coil. Usually the ignition coil must first be disconnected from the distributor cable, then the ignition coil must be unscrewed with an open-end or ring spanner. Your engine must be off before you start.
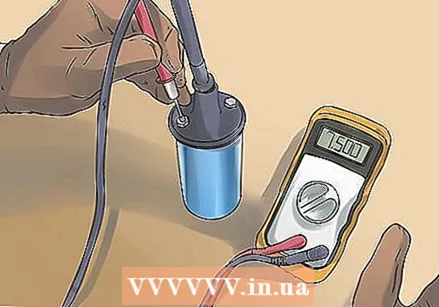 Find the correct resistance values for your ignition coil. Each ignition coil has unique electrical resistance specifications within the coil. If the measured resistance is not within these values, there is something wrong with the ignition coil. In most cases you can find the values in the maintenance manual of your car. But if you can't find it there, you can inquire with the dealer or search online.
Find the correct resistance values for your ignition coil. Each ignition coil has unique electrical resistance specifications within the coil. If the measured resistance is not within these values, there is something wrong with the ignition coil. In most cases you can find the values in the maintenance manual of your car. But if you can't find it there, you can inquire with the dealer or search online. - In general, the primary coil should have a resistance value between 0.7 and 1.7 ohms, the secondary coil should have a value between 7500 and 10500 ohms.
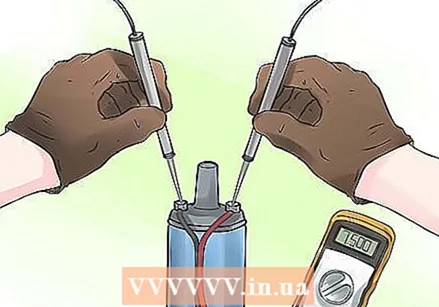 Place the pins of the multimeter on the poles of the primary coil. The distributor has three electrical contacts - one on each side and the third in the center. These contact points can be protruding or recessed - it doesn't matter. Turn on the multimeter, set the multimeter to measure resistance, and let the two pins make contact with the outer contacts. Write down the measurement - this is the resistance of the primary coil.
Place the pins of the multimeter on the poles of the primary coil. The distributor has three electrical contacts - one on each side and the third in the center. These contact points can be protruding or recessed - it doesn't matter. Turn on the multimeter, set the multimeter to measure resistance, and let the two pins make contact with the outer contacts. Write down the measurement - this is the resistance of the primary coil. - Some newer ignition coils have the contact points positioned differently. If you are unsure which contacts correspond to the primary coil, check the service manual for further information.
 Place the pins of the multimeter on the poles of the secondary coil. Hold one pin against one of the outer contact points and hold the other pin against the middle contact point (where the main divider cable is connected. Write down the measured value - this is the resistance of the secondary coil.
Place the pins of the multimeter on the poles of the secondary coil. Hold one pin against one of the outer contact points and hold the other pin against the middle contact point (where the main divider cable is connected. Write down the measured value - this is the resistance of the secondary coil.  Determine whether the measured values fall within the normal values for your type of ignition coil. Ignition coils are delicate components of a car's electrical system. If the primary or secondary coil readings are outside the normal values, even if only slightly, then there is already a damaged or malfunctioning ignition coil. In that case, the ignition coil must be replaced.
Determine whether the measured values fall within the normal values for your type of ignition coil. Ignition coils are delicate components of a car's electrical system. If the primary or secondary coil readings are outside the normal values, even if only slightly, then there is already a damaged or malfunctioning ignition coil. In that case, the ignition coil must be replaced.
Tips
- If you don't see sparks with the first method, you better try the second method.
Necessities
- Socket or ring wrenches (and a spark plug wrench)
- Screwdriver
- Insulated pliers
- Spark plug
- Spark plug cable
- Ignition key
- Resistance meter or multimeter (for the second method)