Author:
Christy White
Date Of Creation:
9 May 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- To step
- Part 1 of 2: Measuring the correct diameter
- Part 2 of 2: Conversion to nominal pipe diameter
- Tips
Measuring the diameter of a pipe can be a bit confusing at first, but anyone can learn how to do it. To find the right size, you first need to figure out whether you need to measure the outside or inside diameter and then measure with a ruler or tape measure. The measurement must then be converted to the 'nominal' pipe diameter, or the description of the pipe in the store. Measuring the diameter is a useful skill you may need on plumbing and construction projects.
To step
Part 1 of 2: Measuring the correct diameter
 Determine whether your pipe has a "male" or "female" thread or no thread at all. Threads are small grooves on the end of some pipes that allow the pipes to fit together. Male threads are on the end of some pipes and female threads on the inside.
Determine whether your pipe has a "male" or "female" thread or no thread at all. Threads are small grooves on the end of some pipes that allow the pipes to fit together. Male threads are on the end of some pipes and female threads on the inside. 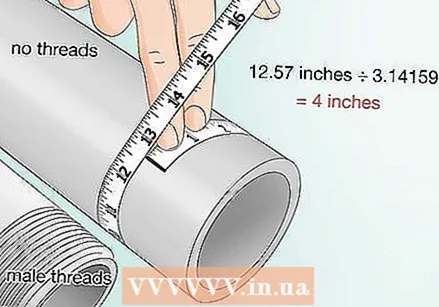 Find the outside diameter if the pipe has male threads or no threads at all. The outside diameter runs from outside edge to outside edge across the pipe. To know the diameter, measure around the circumference of the pipe with a flexible tape measure. Divide the circumference by pi, or approximately 3.14159.
Find the outside diameter if the pipe has male threads or no threads at all. The outside diameter runs from outside edge to outside edge across the pipe. To know the diameter, measure around the circumference of the pipe with a flexible tape measure. Divide the circumference by pi, or approximately 3.14159. - For example, if the circumference is 320 mm, you divide by pi and you get an outer diameter of about 100 mm.
- Use a piece of string to measure if you don't have a tape measure. Mark with a point on the string where you twisted it around the circumference of the tube. Then remove the string, measure it with a ruler and divide this length by pi.
 Measure the inside diameter when the pipe has a female thread. That is the distance across the center of the pipe, not including the thickness of the pipe walls. Use a ruler or a vernier caliper and measure at the end of the pipe where there is a cross section.
Measure the inside diameter when the pipe has a female thread. That is the distance across the center of the pipe, not including the thickness of the pipe walls. Use a ruler or a vernier caliper and measure at the end of the pipe where there is a cross section. - Remember not to measure from the outside, but rather from inside edge to inside edge.
Part 2 of 2: Conversion to nominal pipe diameter
 Convert your diameter to the nominal size if it is smaller than 360 mm. If the diameter is 360 mm or more, you do not have to convert because the diameter is already equal to the nominal diameter.
Convert your diameter to the nominal size if it is smaller than 360 mm. If the diameter is 360 mm or more, you do not have to convert because the diameter is already equal to the nominal diameter. 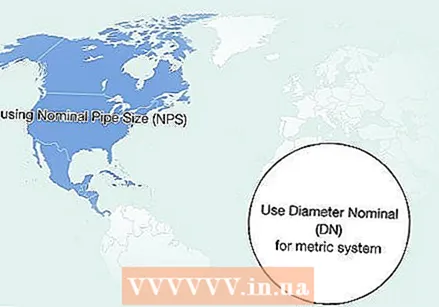 Find out if you need to convert to NPS or DN. Convert to Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) when in North America, or to Nominal Diameter (DN) when using the metric system.
Find out if you need to convert to NPS or DN. Convert to Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) when in North America, or to Nominal Diameter (DN) when using the metric system. - If you are unsure, you can go to the website of a tube store in your country. If they describe the pipes in inches, you must use the NPS system.
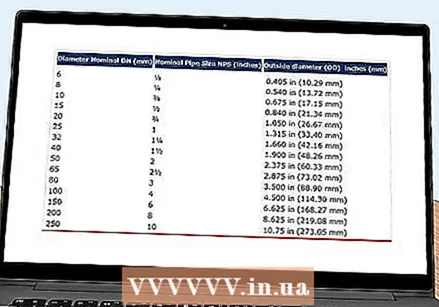 Convert your inside or outside diameter measurements to the correct nominal size. The nominal size will be the description of the tube in the store. You can do this by using a table.
Convert your inside or outside diameter measurements to the correct nominal size. The nominal size will be the description of the tube in the store. You can do this by using a table. - This table is useful for NPS measurements: https://www.zoro.com/pipe-fitting-size-guide
- This table contains both NPS and DN measurements: https://www.massflow-online.com/faqs/where-do-nps-or-dn-stand-for/
- For example, if you measured a diameter of 27 mm, this will translate into a nominal size of ¾ in NPS, or 20 in DN.
Tips
- Tables can also help you find out the "pipe size" of your pipe, which is related to the thickness of the wall.
- If you have pipes instead of pipes, you do not have to convert to the nominal diameter. Pipes are measured based on the outside diameter.
- If you have a PEX (cross-linked polyethylene pipe), the nominal diameter is equal to the inner diameter.