Author:
John Pratt
Date Of Creation:
14 April 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- To step
- Method 1 of 4: With the Base and the Height
- Method 2 of 4: Using the Length of Each Side (Heron's formula)
- Method 3 of 4: Using One Side of a Rectangular Triangle
- Method 4 of 4: Using the Length of Two Sides and the Included Corner
- Tips
While the most common method of calculating the area of a triangle is to multiply the half of the base by the height, there are a number of other ways to calculate the area of a triangle, depending on the data that is known. This includes the length of all three sides, the length of one side of an equilateral triangle, and the length of two sides together with the included angle. Read here how you can calculate the area of a triangle with the help of this data.
To step
Method 1 of 4: With the Base and the Height
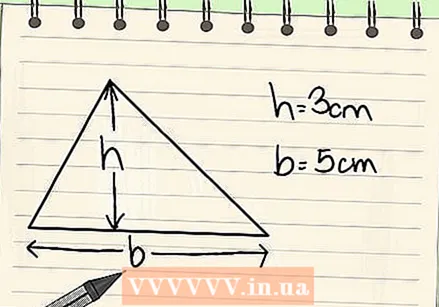 Determine the base and the height of your triangle. The base of the triangle is the length of one side, which is usually the bottom side of the triangle. Height is the length from the base to the top corner of the triangle, which is perpendicular to the base. In a right triangle, the base and the height are the two sides that meet at a 90 degree angle. However, in another triangle, as shown below, the contour line will go right through the shape.
Determine the base and the height of your triangle. The base of the triangle is the length of one side, which is usually the bottom side of the triangle. Height is the length from the base to the top corner of the triangle, which is perpendicular to the base. In a right triangle, the base and the height are the two sides that meet at a 90 degree angle. However, in another triangle, as shown below, the contour line will go right through the shape. - Once you have determined the base and the height of the triangle, you are ready to start using the formula.
 Write down the formula for finding the area of a triangle. The formula for this type of problem is Area = 1/2 (base x height), or 1/2 (bra). Once you have noted everything down, you can start by filling in the length of the height and the base.
Write down the formula for finding the area of a triangle. The formula for this type of problem is Area = 1/2 (base x height), or 1/2 (bra). Once you have noted everything down, you can start by filling in the length of the height and the base. 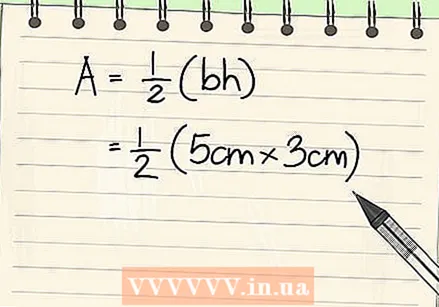 Enter the values for the base and the height. Determine the base and height of the triangle and use these values in the equation. In this example, the height of the triangle is 3 cm and the base of the triangle is 5 cm. This is what the formula would look like after entering these values:
Enter the values for the base and the height. Determine the base and height of the triangle and use these values in the equation. In this example, the height of the triangle is 3 cm and the base of the triangle is 5 cm. This is what the formula would look like after entering these values: - Area = 1/2 x (3 cm x 5 cm)
 Solve the equation. You can multiply the height times the base first because those values are in parentheses. Then multiply the result by 1/2. Remember to give the answer in square meters because you are working in two-dimensional space. Here's how to fix this for the final answer:
Solve the equation. You can multiply the height times the base first because those values are in parentheses. Then multiply the result by 1/2. Remember to give the answer in square meters because you are working in two-dimensional space. Here's how to fix this for the final answer: - Area = 1/2 x (3 cm x 5 cm)
- Area = 1/2 x 15 cm
- Surface = 7.5 cm
Method 2 of 4: Using the Length of Each Side (Heron's formula)
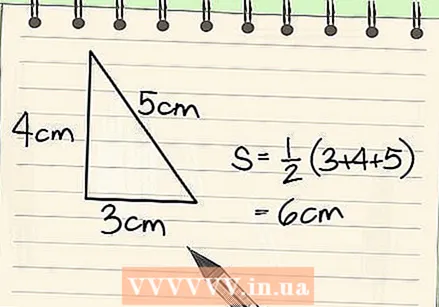 Calculate the half circumference (semiperimeter) of the triangle. To find the half circumference of the triangle, all you have to do is add all the sides together and divide the result by two. The formula for finding the half circumference of a triangle is as follows: semiperimeter = (length of side a + length of side b + length of side c) / 2, or s = (a + b + c) / 2. Since all three lengths are given of the right triangle, 3 cm, 4 cm, and 5 cm, you can enter them directly in the formula and solve the problem for the half circumference:
Calculate the half circumference (semiperimeter) of the triangle. To find the half circumference of the triangle, all you have to do is add all the sides together and divide the result by two. The formula for finding the half circumference of a triangle is as follows: semiperimeter = (length of side a + length of side b + length of side c) / 2, or s = (a + b + c) / 2. Since all three lengths are given of the right triangle, 3 cm, 4 cm, and 5 cm, you can enter them directly in the formula and solve the problem for the half circumference: - s = (3 + 4 + 5) / 2
- s = 12/2
- s = 6
 Enter the correct values in the formula to find the area of a triangle. This formula for finding the area of a triangle is also called Heron's formula and goes as follows: Area = √ {s (s - a) (s - b) (s - c)}. We repeat the previous step where s the half circumference is and a, b, and c the three sides of the triangle. Use the following sequence of operations: start by solving everything inside the parentheses, then everything below the square root sign, and finally the square root itself. Here you can see what this formula will look like when you have entered all known values:
Enter the correct values in the formula to find the area of a triangle. This formula for finding the area of a triangle is also called Heron's formula and goes as follows: Area = √ {s (s - a) (s - b) (s - c)}. We repeat the previous step where s the half circumference is and a, b, and c the three sides of the triangle. Use the following sequence of operations: start by solving everything inside the parentheses, then everything below the square root sign, and finally the square root itself. Here you can see what this formula will look like when you have entered all known values: - Area = √ {6 (6 - 3) (6 - 4) (6 - 5)}
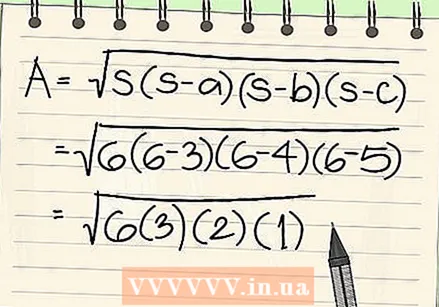 Subtract the values within the parentheses. So: 6 - 3, 6 - 4, and 6 - 5. Here you see the result on paper:
Subtract the values within the parentheses. So: 6 - 3, 6 - 4, and 6 - 5. Here you see the result on paper: - 6 - 3 = 3
- 6 - 4 = 2
- 6 - 5 = 1
- Area = √ {6 (3) (2) (1)}
 Multiply the results of these operations. Multiply 3 x 2 x 1 to get 6 as the answer. You must multiply these numbers before multiplying them by 6 because they are in parentheses.
Multiply the results of these operations. Multiply 3 x 2 x 1 to get 6 as the answer. You must multiply these numbers before multiplying them by 6 because they are in parentheses.  Multiply the previous result by the half circumference. Then multiply the result, 6, by the half circumference, which is also 6. 6 x 6 = 36.
Multiply the previous result by the half circumference. Then multiply the result, 6, by the half circumference, which is also 6. 6 x 6 = 36. 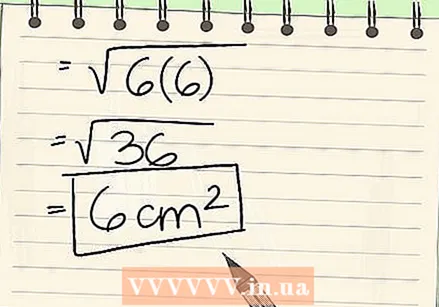 Calculate the square root. 36 is a perfect square and √36 = 6. Don't forget the unit you started with - centimeters. Express the final answer in square centimeters. The area of the triangle with sides 3, 4, and 5 is 6 cm.
Calculate the square root. 36 is a perfect square and √36 = 6. Don't forget the unit you started with - centimeters. Express the final answer in square centimeters. The area of the triangle with sides 3, 4, and 5 is 6 cm.
Method 3 of 4: Using One Side of a Rectangular Triangle
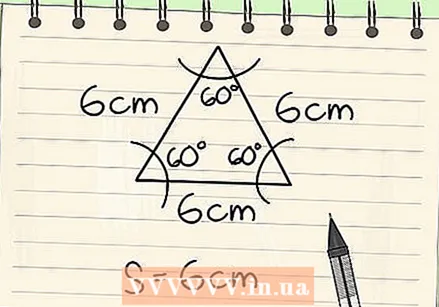 Find the side of the equilateral triangle. An equilateral triangle has sides of equal length and equal angles. You know that you are dealing with an equilateral triangle, either because this is a given, or because you know that all angles and all sides have the same value. The value of one side of this triangle is 6 cm. Make a note of this.
Find the side of the equilateral triangle. An equilateral triangle has sides of equal length and equal angles. You know that you are dealing with an equilateral triangle, either because this is a given, or because you know that all angles and all sides have the same value. The value of one side of this triangle is 6 cm. Make a note of this. - If you know you're dealing with an equilateral triangle, but only the circumference is known, just divide this value by 3. For example, the length of one side of an equilateral triangle with a circumference of 9 is very simply 9/3, or 3.
 Write down the formula for finding the area of an equilateral triangle. The formula for this type of problem is area = (s ^ 2) (√3) / 4. Note that s Means "silk".
Write down the formula for finding the area of an equilateral triangle. The formula for this type of problem is area = (s ^ 2) (√3) / 4. Note that s Means "silk".  Apply the value of one side to the equation. First, calculate the square of the side with the value 6 to get 36. Then find the value of √3, if the answer is to be given in decimal places. Now enter √3 in your calculator to get 1.732. Divide this number by 4. Note that you can also divide 36 by 4 and then multiply by √3 - the order of the operations has no effect on the answer.
Apply the value of one side to the equation. First, calculate the square of the side with the value 6 to get 36. Then find the value of √3, if the answer is to be given in decimal places. Now enter √3 in your calculator to get 1.732. Divide this number by 4. Note that you can also divide 36 by 4 and then multiply by √3 - the order of the operations has no effect on the answer.  Solve. Now it mainly comes to normal calculations. 36 x √3 / 4 = 36 x .433 = 15.59 cm The area of an equilateral triangle with a side 6 cm long is 15.59 cm.
Solve. Now it mainly comes to normal calculations. 36 x √3 / 4 = 36 x .433 = 15.59 cm The area of an equilateral triangle with a side 6 cm long is 15.59 cm.
Method 4 of 4: Using the Length of Two Sides and the Included Corner
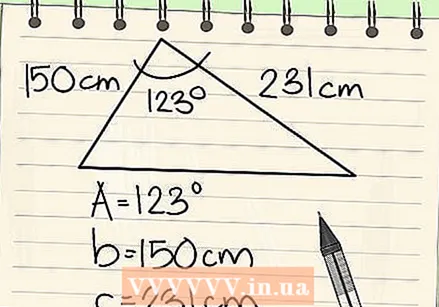 Find the value of the lengths of two sides and the included angle. The included angle is the angle between the two known sides of the triangle. You need to know these values to find the area of a triangle using this method. Let's assume a triangle with the following dimensions:
Find the value of the lengths of two sides and the included angle. The included angle is the angle between the two known sides of the triangle. You need to know these values to find the area of a triangle using this method. Let's assume a triangle with the following dimensions: - angle A = 123º
- side b = 150 cm
- side c = 231 cm
 Write down the formula for finding the area of the triangle. The formula for finding the area of a triangle with two known sides and a known included angle is as follows: Area = 1/2 (b) (c) x sin A. In this equation, "b" and "c" represent the side lengths and "A" the angle. You always have to take the sine of the angle in this equation.
Write down the formula for finding the area of the triangle. The formula for finding the area of a triangle with two known sides and a known included angle is as follows: Area = 1/2 (b) (c) x sin A. In this equation, "b" and "c" represent the side lengths and "A" the angle. You always have to take the sine of the angle in this equation.  Enter the values in the equation. Here's what the equation looks like after you enter these values:
Enter the values in the equation. Here's what the equation looks like after you enter these values: - Area = 1/2 (b) (c) x sin A
- Area = 1/2 (150) (231) x sin A.
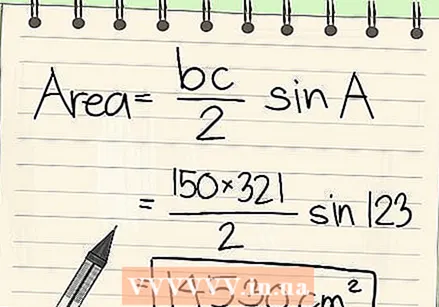 Solve. To solve this equation, first multiply the sides and divide the result by two. Then multiply this result by the sine of the angle. You can find the value of the sine with your calculator. Don't forget to give your answer in cubic units. Here's how to do that:
Solve. To solve this equation, first multiply the sides and divide the result by two. Then multiply this result by the sine of the angle. You can find the value of the sine with your calculator. Don't forget to give your answer in cubic units. Here's how to do that: - Area = 1/2 (150) (231) x sin A.
- Area = 1/2 (34,650) x sin A
- Area = 17,325 x sin A
- Area = 17,325 x .8386705
- Surface = 14,530 cm
Tips
- If you do not fully understand why the basic altitude formula works in this way, here is a brief explanation. If you make a second, identical triangle and put it together, it will form either a rectangle (two right triangles) or a parallelogram (two non right triangles). To find the area of a rectangle or parallelogram, all you have to do is multiply the base by the height. Since a triangle equals half a rectangle or parallelogram, it follows that the area of a triangle equals half a base times its height.



