Author:
Marcus Baldwin
Date Of Creation:
21 June 2021
Update Date:
20 June 2024

Content
- Steps
- Part 1 of 3: Collecting Data
- Part 2 of 3: Calculating Population Density
- Part 3 of 3: Working with a Population Density Value
- Tips
- What do you need
Population density is the average number of inhabitants per square kilometer of territory. This value is needed to find the amount of resources required for a certain territory, or to compare territories. To calculate this value, you need to find the total area of the territory and the population in this territory, and then substitute the collected data in the formula to determine the population density: population density = population / area.
Steps
Part 1 of 3: Collecting Data
 1 Find out the area of the territory. Think about what area you want to find out the population density, and define the boundaries of this area. You may need to find the population density of a particular country, region, or city. You need to find the area of this territory, measured in square kilometers (in rare cases - in square meters).
1 Find out the area of the territory. Think about what area you want to find out the population density, and define the boundaries of this area. You may need to find the population density of a particular country, region, or city. You need to find the area of this territory, measured in square kilometers (in rare cases - in square meters). - Most likely, the area of the territory you need is already known. Look up census data, encyclopedias, or the internet for the exact meaning.
- Find out if the area you are interested in has established boundaries. If not, then you need to define them yourself. For example, suburban area may not appear on census data, so be sure to include that area.
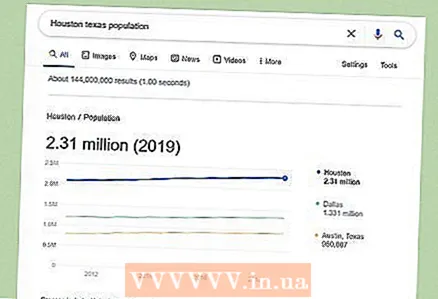 2 Find out the population size. You need to find the latest population data for the area of interest. Start by searching the internet; for example, enter "population of Moscow" in a search engine. If you are looking for the population of a specific country, then open note this site.
2 Find out the population size. You need to find the latest population data for the area of interest. Start by searching the internet; for example, enter "population of Moscow" in a search engine. If you are looking for the population of a specific country, then open note this site. - If the population size in the area you are interested in is unknown, calculate it yourself. For example, you can do this in a small settlement or village. Try to get as accurate a reading as possible.
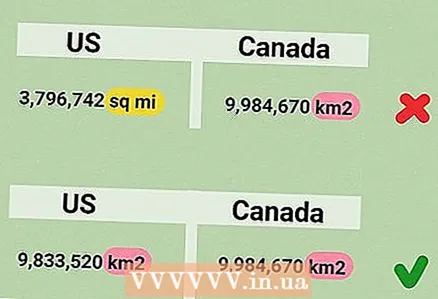 3 Convert units. If you are comparing two territories, then their areas should be given in the same units. For example, if the area of one territory is indicated in square kilometers, and the area of another territory is in square meters, then you need to convert the area of one of the territories to square meters or square kilometers.
3 Convert units. If you are comparing two territories, then their areas should be given in the same units. For example, if the area of one territory is indicated in square kilometers, and the area of another territory is in square meters, then you need to convert the area of one of the territories to square meters or square kilometers. - On this site you will find an online converter of various units of measurement.
Part 2 of 3: Calculating Population Density
 1 Remember the formula. To calculate the population density, it is necessary to divide the population by the area of the territory. Thus, population density = population / land area.
1 Remember the formula. To calculate the population density, it is necessary to divide the population by the area of the territory. Thus, population density = population / land area. - Typically, area is measured in square kilometers. Use square footage if you are looking at a very small area. In the overwhelming majority of scientific or professional articles, only square kilometers are used as units of measurement.
- The unit of measurement for population density is the number of people per unit area. For example, 2000 people per square kilometer.
 2 Plug the collected data into the formula. The required data are population and area. Let's look at an example. City N has a population of 145,000, and the area of this city is 9 square kilometers. Write it like this: 145000/9.
2 Plug the collected data into the formula. The required data are population and area. Let's look at an example. City N has a population of 145,000, and the area of this city is 9 square kilometers. Write it like this: 145000/9. 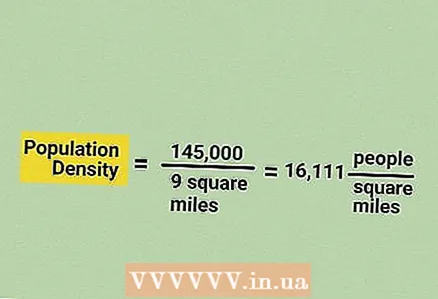 3 Divide the population by the area of the territory. Use a calculator or divide two numbers in a column. In our example: 145,000 / 9 = 16,111 people per square kilometer.
3 Divide the population by the area of the territory. Use a calculator or divide two numbers in a column. In our example: 145,000 / 9 = 16,111 people per square kilometer.
Part 3 of 3: Working with a Population Density Value
 1 Compare the population density. Select areas of interest and compare their population densities to draw some conclusions about those areas. For example, if city M has 60,000 inhabitants, and the area of this city is 8 square kilometers, then the population density will be 7,500 people per square kilometer. That is, the population density of the city N is higher than the population density of the city M. Now let us consider how these indicators can be used.
1 Compare the population density. Select areas of interest and compare their population densities to draw some conclusions about those areas. For example, if city M has 60,000 inhabitants, and the area of this city is 8 square kilometers, then the population density will be 7,500 people per square kilometer. That is, the population density of the city N is higher than the population density of the city M. Now let us consider how these indicators can be used. - If you calculate the population density over a relatively large area, for example, the population density of a city, then the value found will not allow you to understand the differences between urban areas. Therefore, it is better to find the population density of each urban area.
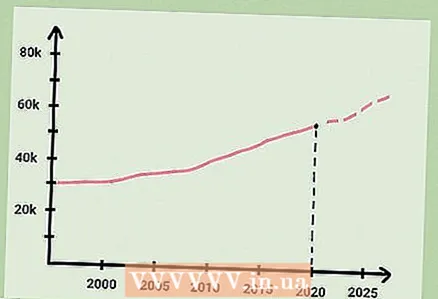 2 Try to include population growth in your analysis. For a specific area, calculate the population growth rate and compare the current population density with the predicted one. To do this, compare the data from the latest and penultimate population censuses. Try to figure out how population growth is changing and how this will affect population density.
2 Try to include population growth in your analysis. For a specific area, calculate the population growth rate and compare the current population density with the predicted one. To do this, compare the data from the latest and penultimate population censuses. Try to figure out how population growth is changing and how this will affect population density.  3 Be aware of the limitations of population density. This value is quite simple to calculate, but it does not provide detailed information about the area under consideration. This value is influenced by the type and size of the area under consideration. Population densities are better calculated for small and densely populated areas than for large areas, which may include both inhabited and uninhabited land.
3 Be aware of the limitations of population density. This value is quite simple to calculate, but it does not provide detailed information about the area under consideration. This value is influenced by the type and size of the area under consideration. Population densities are better calculated for small and densely populated areas than for large areas, which may include both inhabited and uninhabited land. - For example, you calculate the population density of a federal district, which contains not only large cities, but also vast unpopulated areas. In this case, you will get the wrong idea about the density of the urban population (that is, where the majority of the population lives).
- Remember that population density is average. It does not reflect the population density in each section of the territory under consideration. If you do not understand the reasons for this fact, try to calculate the population density in a small area within the area under consideration.
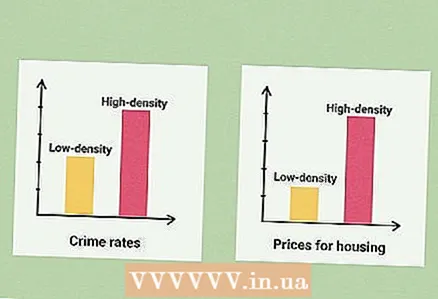 4 Predict various data. Various data can be predicted based on the population density value. For example, an area with a high population density tends to have a high crime rate, as well as high prices for housing and goods. On the other hand, in areas with a low population density, as a rule, farmers live or such an area includes huge unpopulated areas. The conclusions you draw about the area in question depend on your goals. Think about how you can use the population density value.
4 Predict various data. Various data can be predicted based on the population density value. For example, an area with a high population density tends to have a high crime rate, as well as high prices for housing and goods. On the other hand, in areas with a low population density, as a rule, farmers live or such an area includes huge unpopulated areas. The conclusions you draw about the area in question depend on your goals. Think about how you can use the population density value.
Tips
- Compare your population density value with values from other sources. If the value you calculate is different, you may have made a calculation error or the population density has changed over time.
- Use the formula in this article to determine the population density of animals, such as cattle.
What do you need
- Statistics (can be found on the Internet or in the encyclopedia)
- Map
- Calculator
- Pencil
- Paper