Author:
Joan Hall
Date Of Creation:
1 July 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Part 1 of 3: Recognizing the Symptoms of an Ectopic Pregnancy
- Part 2 of 3: Consider Your Risk Factors
- Part 3 of 3: Diagnosing and Treating an Ectopic Pregnancy
- Tips
- Warnings
In the early days of a healthy pregnancy, the fertilized egg moves through the fallopian tube and becomes anchored in the uterus. During an ectopic pregnancy, the egg is transferred to a different location, usually in the fallopian tube. An ectopic pregnancy is life threatening and requires emergency medical attention, especially when it is terminated, so it is important to be able to recognize the symptoms.
Steps
Part 1 of 3: Recognizing the Symptoms of an Ectopic Pregnancy
 1 Monitor early pregnancy symptoms. Some women with impaired ectopic pregnancy do not know about their pregnancy until they rush to the doctor or go to an ambulance for urgent life-saving. This means that it is extremely important to know and identify the earliest signs of pregnancy, including:
1 Monitor early pregnancy symptoms. Some women with impaired ectopic pregnancy do not know about their pregnancy until they rush to the doctor or go to an ambulance for urgent life-saving. This means that it is extremely important to know and identify the earliest signs of pregnancy, including: - The disappearance of menstruation
- Soreness of the mammary glands
- Nausea and vomiting ("morning sickness")
 2 Take abdominal and pelvic pain seriously. If you have pain in the lower abdomen, in the pelvic region, or pain in the lower abdomen, on one side of the pelvis, you may have an ectopic pregnancy. If the pain persists, intensifies, or any other symptoms appear along with it, see a doctor immediately.
2 Take abdominal and pelvic pain seriously. If you have pain in the lower abdomen, in the pelvic region, or pain in the lower abdomen, on one side of the pelvis, you may have an ectopic pregnancy. If the pain persists, intensifies, or any other symptoms appear along with it, see a doctor immediately.  3 Pay attention to back pain. Back pain can occur for a variety of reasons, but if you suffer from back pain, especially back pain, combined with other symptoms, see your doctor.
3 Pay attention to back pain. Back pain can occur for a variety of reasons, but if you suffer from back pain, especially back pain, combined with other symptoms, see your doctor.  4 Watch for vaginal bleeding. Abnormal vaginal bleeding is a sign of an ectopic pregnancy, but unfortunately, this sign is also one of the most difficult to detect: if you do not know about your pregnancy, you may think that it is bleeding from your menstrual period, and if you know that you were pregnant, may decide that this is an early miscarriage.
4 Watch for vaginal bleeding. Abnormal vaginal bleeding is a sign of an ectopic pregnancy, but unfortunately, this sign is also one of the most difficult to detect: if you do not know about your pregnancy, you may think that it is bleeding from your menstrual period, and if you know that you were pregnant, may decide that this is an early miscarriage.  5 Look for signs of termination of an ectopic pregnancy. When an ectopic pregnancy is terminated, your symptoms may become even more difficult. At such a moment, the condition is potentially fatal, so watch closely for:
5 Look for signs of termination of an ectopic pregnancy. When an ectopic pregnancy is terminated, your symptoms may become even more difficult. At such a moment, the condition is potentially fatal, so watch closely for: - Dizziness and fainting
- Feeling of pain or pressure in the rectum
- Lower blood pressure
- Additional shoulder pain
- Sudden, severe abdominal and pelvic pain
Part 2 of 3: Consider Your Risk Factors
 1 Factor in your pregnancy history. Some women will never know what caused their ectopic pregnancy, but there are certain factors that seem to increase your risk. The first is a history of ectopic pregnancies: if you have had a case before, there is a great risk that another will happen.
1 Factor in your pregnancy history. Some women will never know what caused their ectopic pregnancy, but there are certain factors that seem to increase your risk. The first is a history of ectopic pregnancies: if you have had a case before, there is a great risk that another will happen.  2 Consider your reproductive health. Sexually transmitted infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, and congenital problems with the fallopian tubes all increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
2 Consider your reproductive health. Sexually transmitted infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, and congenital problems with the fallopian tubes all increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy. - Genital surgery, including fallopian tube surgery and any other pelvic surgery, increases your risk.
 3 Be aware that fertility treatments can increase your risk. If you have already used fertility drugs or have experienced in vitro fertilization, there is a high risk of ectopic pregnancy.
3 Be aware that fertility treatments can increase your risk. If you have already used fertility drugs or have experienced in vitro fertilization, there is a high risk of ectopic pregnancy.  4 Remember that IUDs increase your risk. Women who use an intrauterine device (IUD) to prevent pregnancy have an increased risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy if the contraceptive method does not work and they become pregnant.
4 Remember that IUDs increase your risk. Women who use an intrauterine device (IUD) to prevent pregnancy have an increased risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy if the contraceptive method does not work and they become pregnant.  5 Age factor. Women over 35 are more likely to have an ectopic pregnancy.
5 Age factor. Women over 35 are more likely to have an ectopic pregnancy.
Part 3 of 3: Diagnosing and Treating an Ectopic Pregnancy
 1 Seek medical attention immediately. If you suspect an ectopic pregnancy, whether or not you have received a positive pregnancy test, contact your doctor or emergency room as soon as possible.
1 Seek medical attention immediately. If you suspect an ectopic pregnancy, whether or not you have received a positive pregnancy test, contact your doctor or emergency room as soon as possible.  2 Confirm pregnancy. If you haven't done a pregnancy test yet, your doctor will do it. The pregnancy test will be positive, regardless of whether the egg is located in the uterus or elsewhere.
2 Confirm pregnancy. If you haven't done a pregnancy test yet, your doctor will do it. The pregnancy test will be positive, regardless of whether the egg is located in the uterus or elsewhere.  3 Get a pelvic exam. If you are indeed pregnant, your doctor will most likely start with a routine pelvic exam. He will check for pain in specific areas or soreness in any tangible areas. At the same time, he will check to see if there is any visible cause for your symptoms.
3 Get a pelvic exam. If you are indeed pregnant, your doctor will most likely start with a routine pelvic exam. He will check for pain in specific areas or soreness in any tangible areas. At the same time, he will check to see if there is any visible cause for your symptoms. 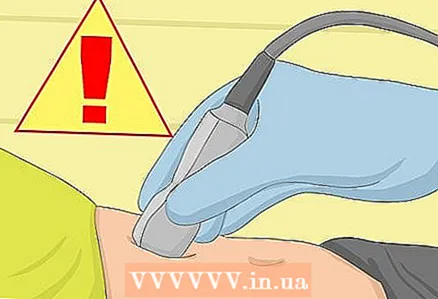 4 Ask for an ultrasound scan. If your doctor suspects an ectopic pregnancy, you should get a transvaginal ultrasound done right away. Your doctor will insert a small device into your vagina to get an ultrasound scan and look for signs of an ectopic pregnancy.
4 Ask for an ultrasound scan. If your doctor suspects an ectopic pregnancy, you should get a transvaginal ultrasound done right away. Your doctor will insert a small device into your vagina to get an ultrasound scan and look for signs of an ectopic pregnancy. - Sometimes an ectopic pregnancy may be too early to be seen on an ultrasound scan. In this case, and if the symptoms are mild or doubtful, your doctor may register you and schedule a second ultrasound at a later date. Although after a month, regardless of whether the pregnancy is normal or ectopic, it should be visible on an ultrasound scan.
 5 Get an ambulance while terminating an ectopic pregnancy. If you have heavy bleeding, symptoms of shock, or other signs of termination of an ectopic pregnancy, your doctor will skip the preliminary tests and proceed with the diagnosis and treatment with surgery.
5 Get an ambulance while terminating an ectopic pregnancy. If you have heavy bleeding, symptoms of shock, or other signs of termination of an ectopic pregnancy, your doctor will skip the preliminary tests and proceed with the diagnosis and treatment with surgery.  6 Understand that pregnancy is not viable. The only treatment for an ectopic pregnancy is to remove the developing cells. This is done through surgery.
6 Understand that pregnancy is not viable. The only treatment for an ectopic pregnancy is to remove the developing cells. This is done through surgery. - In some cases, your fallopian tubes may be removed. If this happens, be aware that many women successfully re-pregnant with even only one fallopian tube.
Tips
- If you have an ectopic pregnancy, know that you may still be able to have babies in the future. The success of your future pregnancy depends on a number of factors, including your general health and the reasons for the ectopic pregnancy. Talk to your doctor about your specific situation.
- You should consult your doctor before trying to get pregnant again. Depending on your specific circumstances, your doctor may insist that you wait three to six months before trying to get pregnant again.
- While most types of ectopic pregnancies cannot be prevented, you can reduce your risk by avoiding anything that could damage your fallopian tubes. This includes safe sex and treatment for sexually transmitted infections and other sexual and reproductive illnesses.
- Don't feel guilty or punish yourself. Most ectopic pregnancies cannot be prevented. It is very likely that you did nothing wrong. An ectopic pregnancy is not your fault.
- If you are experiencing intense emotions after an ectopic pregnancy, know that this is completely normal. Consider consulting or joining a support group for those who have had a miscarriage.
Warnings
- An ectopic pregnancy is fatal. If you think it's possible, don't wait. Seek medical attention immediately.