Author:
Bobbie Johnson
Date Of Creation:
8 April 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 3: Thinning Mucus
- Method 2 of 3: Prevent Congestion with Food and Drink
- Method 3 of 3: Medication
- Tips
- Warnings
Congestion in the chest creates discomfort and discomfort. Fortunately, there are many ways to loosen mucus in your lungs and get rid of congestion. Try gargling with salt water and steam, and stay hydrated. If these home remedies don't work, try an over-the-counter expectorant. If the congestion worsens, see your doctor so that he can determine the cause and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Thinning Mucus
 1 Breathe steam over a bowl of hot water, or take an extended hot shower. The warm, moist steam will help loosen mucus deep in the throat and lungs. Take a hot shower or fill a bowl with very hot water and breathe in the steam (try to inhale it as deeply as possible without causing a cough). Breathe in the steam for at least 15-20 minutes 1-2 times a day until the unpleasant symptoms are alleviated.
1 Breathe steam over a bowl of hot water, or take an extended hot shower. The warm, moist steam will help loosen mucus deep in the throat and lungs. Take a hot shower or fill a bowl with very hot water and breathe in the steam (try to inhale it as deeply as possible without causing a cough). Breathe in the steam for at least 15-20 minutes 1-2 times a day until the unpleasant symptoms are alleviated. - When breathing steam over a bowl of hot water, bend over it and place a towel over your head to trap the steam. Breathe in the steam deeply for at least 15 minutes.
- You can add a few drops of peppermint or eucalyptus essential oil to the hot water to loosen mucus.
 2 Put a humidifier in your bedroom and turn it on overnight. Doing so will increase the humidity in the air, which will relieve congestion and clear the airways. In addition, it will help to clear the nasal passages and thus make breathing much easier. Position the humidifier so that it evaporates moisture towards the head of your bed, 2-3 meters from your head.
2 Put a humidifier in your bedroom and turn it on overnight. Doing so will increase the humidity in the air, which will relieve congestion and clear the airways. In addition, it will help to clear the nasal passages and thus make breathing much easier. Position the humidifier so that it evaporates moisture towards the head of your bed, 2-3 meters from your head. - A humidifier will be most beneficial if the air in your home is dry.
- If you turn on the humidifier every night, you should refill it every 3-4 days, or as soon as the water tank is empty.
 3 Garglesaline for 1-2 minutes to relieve congestion. It is an effective way to break up mucus in the airways. Add 1–2 tablespoons (12.5–25 grams) of salt to 1/2 cup (120 ml) warm water. Stir the water to dissolve the salt and put it in your mouth. Gargle with salt water as deeply as possible for 1-2 minutes, then spit it out.
3 Garglesaline for 1-2 minutes to relieve congestion. It is an effective way to break up mucus in the airways. Add 1–2 tablespoons (12.5–25 grams) of salt to 1/2 cup (120 ml) warm water. Stir the water to dissolve the salt and put it in your mouth. Gargle with salt water as deeply as possible for 1-2 minutes, then spit it out. - Gargle in this way 3-4 times a day until the congestion starts to go away.
 4 For chest congestion, apply a heating pad to your upper chest. Lie with your head raised and a warm heating pad or rag over your sternum. Place a towel under the heating pad to prevent it from burning your skin. Lie down for 10-15 minutes so that the warmth acts on the chest. Repeat 2-3 times a day to loosen mucus in your lungs.
4 For chest congestion, apply a heating pad to your upper chest. Lie with your head raised and a warm heating pad or rag over your sternum. Place a towel under the heating pad to prevent it from burning your skin. Lie down for 10-15 minutes so that the warmth acts on the chest. Repeat 2-3 times a day to loosen mucus in your lungs. - Apply a heating pad or hot rag to your throat and chest - the external heat will warm your airways and help relieve congestion. It also looses the mucus and makes it easier to cough up the mucus.
- A heating pad can be purchased at your nearest pharmacy.
- You can also apply a hot cloth compress by dampening a towel with water and heating it in the microwave for 60–90 seconds.
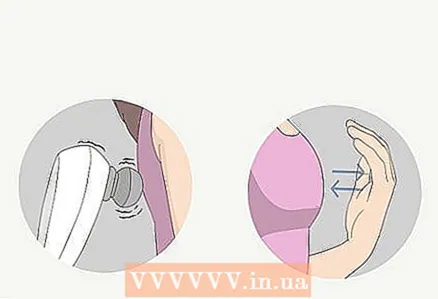 5 Rub your back and chest with a hand-held massager to relieve congestion. Apply the massager to the part of your chest where you feel the most congested (for example, the upper chest for bronchitis). You can also ask someone to massage your back if you can't reach it yourself. If you don't have a massager, you can simply fold your palms in a boat and pat your chest to cleanse it.
5 Rub your back and chest with a hand-held massager to relieve congestion. Apply the massager to the part of your chest where you feel the most congested (for example, the upper chest for bronchitis). You can also ask someone to massage your back if you can't reach it yourself. If you don't have a massager, you can simply fold your palms in a boat and pat your chest to cleanse it. - You can also ask a friend or loved one to pat you on the back with their folded palms.
- Depending on where you feel the congestion, it is sometimes helpful to bend forward or lean back to clear your lungs. For example, if your lower lungs are congested, take the Downward Dog or Baby Pose and have someone pat you on the lower chest.
 6 As you sleep, use 2–3 pillows under your head to lift it up. This will make it easier for mucus from the nose and upper throat to drain into the stomach. This will help you sleep better and will prevent you from waking up with severe congestion. Place some pillows under your head and neck so that it sits slightly above your torso.
6 As you sleep, use 2–3 pillows under your head to lift it up. This will make it easier for mucus from the nose and upper throat to drain into the stomach. This will help you sleep better and will prevent you from waking up with severe congestion. Place some pillows under your head and neck so that it sits slightly above your torso. - You can also place a 5 x 10 or 10 x 10 centimeters board under the head of the mattress to raise it slightly.
 7 Cough 5–8 times to clear mucus after thinning it out. Sit in a chair and take a deep breath to fill your lungs with air. Tighten your abdominal muscles and contract them 3 times in a row to cough up your throat. Make a "ha" sound every time you cough. Repeat 4-5 times until sputum begins to cough up.
7 Cough 5–8 times to clear mucus after thinning it out. Sit in a chair and take a deep breath to fill your lungs with air. Tighten your abdominal muscles and contract them 3 times in a row to cough up your throat. Make a "ha" sound every time you cough. Repeat 4-5 times until sputum begins to cough up. - Coughing helps the body to clear excess mucus from the lungs. While an uncontrolled or shallow cough is not beneficial, a controlled deep cough helps clear mucus and relieve congestion.
Method 2 of 3: Prevent Congestion with Food and Drink
 1 Drink herbal tea and other caffeine-free drinks. Typically, the hot liquid helps break down the mucus that causes chest congestion, and tea has a double benefit as the herbs and spices also help relieve chest pain and congestion. Brew tea from peppermint, ginger, chamomile, or rosemary and drink 4-5 glasses a day. Add an expectorant or some honey for sweetness.
1 Drink herbal tea and other caffeine-free drinks. Typically, the hot liquid helps break down the mucus that causes chest congestion, and tea has a double benefit as the herbs and spices also help relieve chest pain and congestion. Brew tea from peppermint, ginger, chamomile, or rosemary and drink 4-5 glasses a day. Add an expectorant or some honey for sweetness. - Avoid caffeinated beverages such as black or green tea and coffee. Caffeine can stimulate mucus production and thus worsen chest congestion.
 2 Eat spicy foods and foods such as ginger and garlic to relieve congestion. Certain foods help clear mucus from the chest. They stimulate the body to excrete mucus by irritating the nasal passages, which causes it to release thin and watery mucus, which absorbs other, thicker mucus, and is easily excreted along with it. Try eating more spicy foods, citrus fruits, garlic, onions, and ginger to relieve chest congestion faster. Eat these foods at lunch and dinner for 3-4 days.
2 Eat spicy foods and foods such as ginger and garlic to relieve congestion. Certain foods help clear mucus from the chest. They stimulate the body to excrete mucus by irritating the nasal passages, which causes it to release thin and watery mucus, which absorbs other, thicker mucus, and is easily excreted along with it. Try eating more spicy foods, citrus fruits, garlic, onions, and ginger to relieve chest congestion faster. Eat these foods at lunch and dinner for 3-4 days. - Some mild foods have been shown to help relieve chest congestion. These include licorice root, guava, ginseng, and pomegranate.
- Many of these spicy foods are also anti-inflammatory, which can also help relieve congestion, but it can take months to see the effect.
 3 Drink water throughout the day to keep your body hydrated. It is all the more important to drink water (especially hot water) if you are trying to get rid of chest congestion. If you don't drink enough fluids, the mucus in your chest and throat will become thicker and stickier, making it harder for you to get rid of it. Drink water throughout the day and with meals to loosen mucus.
3 Drink water throughout the day to keep your body hydrated. It is all the more important to drink water (especially hot water) if you are trying to get rid of chest congestion. If you don't drink enough fluids, the mucus in your chest and throat will become thicker and stickier, making it harder for you to get rid of it. Drink water throughout the day and with meals to loosen mucus. - There is no definitive recommendation as to how many glasses of water to drink per day, as the exact amount depends on many factors. Instead of counting the number of glasses, just drink water throughout the day so you don't feel thirsty.
 4 Drink sports drinks and juices to help maintain electrolyte balance. During illness, the body actively fights infection, and this can deplete electrolyte stores if not replenished. An effective way is to drink sports drinks.Drink as much sports drinks as you drink water, and try to keep at least one third of your daily fluid intake from drinks rich in electrolytes.
4 Drink sports drinks and juices to help maintain electrolyte balance. During illness, the body actively fights infection, and this can deplete electrolyte stores if not replenished. An effective way is to drink sports drinks.Drink as much sports drinks as you drink water, and try to keep at least one third of your daily fluid intake from drinks rich in electrolytes. - This is a good way to replenish your body fluids even if you don't like drinking plain water. Many people like the taste of sports drinks, with which they maintain their water balance.
- Choose a sports drink that is low in sugar and decaffeinated.
 5 Eliminate fatty foods from your diet as they increase mucus production. The secretion of mucus is increased by dairy products (for example, milk, butter, yogurt, ice cream), salt, sugar, fried foods. Refrain from such foods until you have cleared the chest congestion. Eliminate these foods from your diet for 3-4 days to make breathing easier.
5 Eliminate fatty foods from your diet as they increase mucus production. The secretion of mucus is increased by dairy products (for example, milk, butter, yogurt, ice cream), salt, sugar, fried foods. Refrain from such foods until you have cleared the chest congestion. Eliminate these foods from your diet for 3-4 days to make breathing easier. - Also, avoid pasta, bananas, cabbage, and potatoes - these foods can also increase mucus production.
Method 3 of 3: Medication
 1 Take an over-the-counter expectorant to help your body clear mucus. Expectorants thin the mucus and make it easier to remove from the body when you cough. There are many over-the-counter expectorant drugs available in pharmacies, such as Flavamed or Stopussin, which contain active ingredients such as ambroxol and guaifenesin. They can be bought at almost any pharmacy and effectively help remove excess phlegm. Take your medications according to the directions for use.
1 Take an over-the-counter expectorant to help your body clear mucus. Expectorants thin the mucus and make it easier to remove from the body when you cough. There are many over-the-counter expectorant drugs available in pharmacies, such as Flavamed or Stopussin, which contain active ingredients such as ambroxol and guaifenesin. They can be bought at almost any pharmacy and effectively help remove excess phlegm. Take your medications according to the directions for use. - The daily dose of guaifenesin can be up to 1200 milligrams. Always take your medicine with a glass of water.
- Expectorants are not safe for children under 6, so check with your pediatrician for an appropriate alternative.
 2 Use an inhaler if you find it difficult to breathe because of the congestion. Ask your doctor about inhalers and sprays that can help you breathe easier. These drugs (such as salbutamol) are usually prescription drugs that thin mucus and help relieve congestion. Try clearing your throat slightly after using an inhaler that loses mucus in your lungs. Always follow the directions for use supplied with the inhaler.
2 Use an inhaler if you find it difficult to breathe because of the congestion. Ask your doctor about inhalers and sprays that can help you breathe easier. These drugs (such as salbutamol) are usually prescription drugs that thin mucus and help relieve congestion. Try clearing your throat slightly after using an inhaler that loses mucus in your lungs. Always follow the directions for use supplied with the inhaler. - Inhalers are usually needed for severe chest congestion, but if you are sick and have accumulated phlegm annoying, ask your doctor if this method is right for you.
 3 See your doctor if chest congestion persists within one week. If none of the above methods have helped relieve your condition, visit your doctor and describe the severity and duration of your symptoms. Ask your doctor about ways to treat long-term, deep chest congestion, such as an antibiotic shot, nasal sprays, pills, or vitamin therapy.
3 See your doctor if chest congestion persists within one week. If none of the above methods have helped relieve your condition, visit your doctor and describe the severity and duration of your symptoms. Ask your doctor about ways to treat long-term, deep chest congestion, such as an antibiotic shot, nasal sprays, pills, or vitamin therapy. - See your doctor if you develop more serious symptoms such as high fever, shortness of breath, rash, or wheezing.
 4 Do not use cough suppressants for congestion. These drugs suppress coughing, but they can cause the mucus in your chest to thicken. Thick mucus makes it harder to clear your throat. Do not take cough suppressants or combined expectorant and cough suppressants, as these can make chest congestion worse.
4 Do not use cough suppressants for congestion. These drugs suppress coughing, but they can cause the mucus in your chest to thicken. Thick mucus makes it harder to clear your throat. Do not take cough suppressants or combined expectorant and cough suppressants, as these can make chest congestion worse. - Remember that coughing is a normal and healthy body response to chest congestion, so don't try to limit or stop it.
 5 Do not take any antihistamines if you have a wet cough. Also, do not take decongestants such as pseudoephedrine if you are coughing up phlegm. Both of these drugs can dry out the mucus in your lungs, making it harder to cough up. Some cough medicines contain antihistamines, so check the ingredients before purchasing any over-the-counter medicines.
5 Do not take any antihistamines if you have a wet cough. Also, do not take decongestants such as pseudoephedrine if you are coughing up phlegm. Both of these drugs can dry out the mucus in your lungs, making it harder to cough up. Some cough medicines contain antihistamines, so check the ingredients before purchasing any over-the-counter medicines. - A cough is called a productive cough if it produces phlegm.
- If your phlegm is yellow or light green with a cold or flu, this is normal. However, if it turns out to be any other color, see your doctor.
Tips
- Do not smoke or inhale tobacco smoke if you have chest congestion. Substances in tobacco smoke irritate the nasal passages and cause unnecessary coughing. If you smoke and cannot quit this bad habit, take a break until you get rid of the congestion in your chest.
- In the absence of timely treatment, chest congestion can develop into pneumonia. Visit your doctor to check if you have an infectious disease!
- If you find it difficult to cough up phlegm, have someone knock on the upper left and right sides of your back. This will help loosen the mucus so it clears up more easily.
Warnings
- Do not drive a car after taking strong oral medications. Take these medications before bed to help you sleep better.
- If your child has chest congestion, do not give any medication without first talking to a doctor.