Author:
Clyde Lopez
Date Of Creation:
19 June 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 4: Improve Sleep Hygiene
- Method 2 of 4: Use Herbal Remedies and Supplements
- Method 3 of 4: Use Herbal Remedies for Children with Sleep Paralysis
- Method 4 of 4: Recognize Symptoms and Risk Factors
- Tips
- Additional articles
All people experience brief moments of sleep paralysis during sleep. Normal sleep paralysis is precisely what prevents a sleeping person from performing the actions they dream about. However, sometimes sleep paralysis takes on a threatening form when a person falls into a stupor and cannot speak or move, both during sleep and upon awakening. Sleep paralysis is often accompanied by hallucinations (visual, auditory, or tactile). For most people, sleep paralysis does not interfere with sleep, unless it happens too often or is so severe that it prevents you from falling asleep again. Sleep paralysis can last from a couple of seconds to several minutes. Fortunately, there are several ways to help prevent this condition.
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Improve Sleep Hygiene
 1 Create a relaxing environment in your bedroom. Do not do anything other than sleep and sex on your bed. Don't watch TV or read in bed. The bed should be firm enough to support your body securely while remaining comfortable. Consider applying a few drops of lavender essential oil to or near your pillow for a cozy, relaxing atmosphere.
1 Create a relaxing environment in your bedroom. Do not do anything other than sleep and sex on your bed. Don't watch TV or read in bed. The bed should be firm enough to support your body securely while remaining comfortable. Consider applying a few drops of lavender essential oil to or near your pillow for a cozy, relaxing atmosphere. - Although sleep disorders are treated differently, proper sleep hygiene can help improve sleep (even if there are no sleep disorders).
- Darken your bedroom with blackout curtains, block out external light sources, and use a sleeping mask if necessary.
- Keep your bedroom at a comfortable temperature. It is recommended to keep the air temperature around 18 ° C during sleep.
- Use a fan, ear plugs, or a white noise generator to muffle outside sounds that can disturb your sleep.
- Minimize the use of electronic devices (smartphones, tablets, laptops, and TVs) in the evening. These devices emit blue light that interferes with sleep.
 2 Avoid stimulants and stress before bed. Begin to calm down and relax before bed. Do not eat two hours before bed and do not drink coffee (especially after dinner), caffeinated and alcoholic beverages. Otherwise, it will be difficult for you to fall asleep and your sleep will be restless.You should also avoid strenuous physical activity before bed. If you are taking any medications, check with your doctor to see if they are interfering with sleep.
2 Avoid stimulants and stress before bed. Begin to calm down and relax before bed. Do not eat two hours before bed and do not drink coffee (especially after dinner), caffeinated and alcoholic beverages. Otherwise, it will be difficult for you to fall asleep and your sleep will be restless.You should also avoid strenuous physical activity before bed. If you are taking any medications, check with your doctor to see if they are interfering with sleep. - Remember to tell your doctor about the herbal medicines and supplements you are taking as they may interact with the medications you are prescribed.
- Instead of vigorous exercise in the evening, just take a walk, warm up a bit, or do stretching exercises. Save an intense workout for the morning or afternoon.
- Try not to go to bed under stress. Try writing your thoughts in a journal and put off thinking and solving current problems until the morning.
 3 Relax and release tension before bed. Develop a simple bedtime routine and try to follow it at all times. Include something relaxing, like taking a hot shower a couple of hours before bed. Despite the lack of precise research, many people believe that hot showers can increase melatonin production, making it easier to fall asleep later. You can also listen to soothing music or white noise, especially if you live in a noisy area.
3 Relax and release tension before bed. Develop a simple bedtime routine and try to follow it at all times. Include something relaxing, like taking a hot shower a couple of hours before bed. Despite the lack of precise research, many people believe that hot showers can increase melatonin production, making it easier to fall asleep later. You can also listen to soothing music or white noise, especially if you live in a noisy area. - Preparing for bed can include whatever you like. You can read, brush your teeth, make a bed, change into pajamas, meditate, dim the lights, or practice some relaxation technique. This mode will signal your body to sleep.
- 4 Go to bed at the same time every night. Help your body develop a consistent habit of falling asleep at a specific time. While this can be challenging with flexible work hours, it will make it easier for you to fall asleep and your sleep will improve.
- You can be a little flexible, but try not to deviate more than 30 minutes from your evening sleep and wake up times. For example, on weekends you can sleep half an hour longer.
- Also try to wake up at the same time every morning.
 5 Try to practice progressive muscle relaxation. To prepare well for sleep, gradually relax all the muscles in your body. Start with your toes: tense the muscles of your toes for five seconds, then relax them for about 30 seconds. After that, go to the calves, then to the thighs. Tighten the corresponding muscles for five seconds and then relax them for 30 seconds. In this way, go to the neck and, finally, to the face.
5 Try to practice progressive muscle relaxation. To prepare well for sleep, gradually relax all the muscles in your body. Start with your toes: tense the muscles of your toes for five seconds, then relax them for about 30 seconds. After that, go to the calves, then to the thighs. Tighten the corresponding muscles for five seconds and then relax them for 30 seconds. In this way, go to the neck and, finally, to the face. - Research has shown that this technique can reduce the incidence of sleep paralysis.
- You can also relax with taijiquan gymnastics, qigong, or yoga.
 6 Practice positive visualization. As you lie in bed, try to focus on positive things and memories. For example, try imagining your favorite places (real or imagined) or fond memories. In doing so, try to imagine as many different details as possible. Try to remember smells, sounds, and tactile sensations. As you do this, breathe deeply to relax more fully. Positive visualization can help drive away bad thoughts and help you prepare for a night's sleep.
6 Practice positive visualization. As you lie in bed, try to focus on positive things and memories. For example, try imagining your favorite places (real or imagined) or fond memories. In doing so, try to imagine as many different details as possible. Try to remember smells, sounds, and tactile sensations. As you do this, breathe deeply to relax more fully. Positive visualization can help drive away bad thoughts and help you prepare for a night's sleep. - For example, if you imagine yourself on the seashore, imagine the sound of the surf and a handful of sand in your hand. After some practice, no additional sounds or other details will be required, but at first the details will help you travel to an imaginary place.
Method 2 of 4: Use Herbal Remedies and Supplements
 1 Make herbal tea. To do this, boil water. Add 1 teaspoon of dried herb, 1 tablespoon of fresh herb, or a tea bag to a glass (250 milliliters) of boiling water and wait 5-10 minutes for the broth to infuse.
1 Make herbal tea. To do this, boil water. Add 1 teaspoon of dried herb, 1 tablespoon of fresh herb, or a tea bag to a glass (250 milliliters) of boiling water and wait 5-10 minutes for the broth to infuse. - Strain the tea if you were using individual leaves instead of a bag, and add honey or lemon for flavor if desired.
 2 Get quality nutritional supplements. Ask your pharmacist for a recommendation of a trusted brand; the market for food additives is poorly regulated, so sometimes substandard products come across. The pharmacist needs to know which manufacturers are trustworthy. Pay attention to the details and contact information of the company and how long it has been in the market. You can also search the internet for reviews of the company.
2 Get quality nutritional supplements. Ask your pharmacist for a recommendation of a trusted brand; the market for food additives is poorly regulated, so sometimes substandard products come across. The pharmacist needs to know which manufacturers are trustworthy. Pay attention to the details and contact information of the company and how long it has been in the market. You can also search the internet for reviews of the company. - Always follow the directions for use when taking nutritional supplements. Tell your doctor about any dietary supplements you are taking.
- Purchase only fresh nutritional supplements (check expiration date).
 3 Try valerian as a tea or dietary supplement. Valerian root is a mild sedative that helps you fall asleep faster and easier. Valerian has been used as a sleeping pill for thousands of years, although it should not be given to children younger than 3 years old.
3 Try valerian as a tea or dietary supplement. Valerian root is a mild sedative that helps you fall asleep faster and easier. Valerian has been used as a sleeping pill for thousands of years, although it should not be given to children younger than 3 years old. - You can add honey, cinnamon, cloves, or lemon to valerian tea for flavor.
- Valerian root can interact with medications such as certain antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications.
 4 Take passionflower as a tea or dietary supplement. Passionflower is used as a sedative and to lower blood pressure. If you are taking blood pressure medications, check with your doctor first. While passion flower itself has a light, pleasant taste, honey or lemon can be added to the tea if desired.
4 Take passionflower as a tea or dietary supplement. Passionflower is used as a sedative and to lower blood pressure. If you are taking blood pressure medications, check with your doctor first. While passion flower itself has a light, pleasant taste, honey or lemon can be added to the tea if desired. - Do not take passionflower during pregnancy as it can cause uterine contractions.
- Since passionflower has not been studied in children, consult a qualified healthcare professional to determine a safe dosage for your child.
 5 Take chamomile as a tea or dietary supplement. Chamomile has traditionally been used as a sleep aid, although clinical studies are needed to confirm its effectiveness. Chamomile has a calming effect and reduces anxiety. Buy German (more common) or Roman chamomile.
5 Take chamomile as a tea or dietary supplement. Chamomile has traditionally been used as a sleep aid, although clinical studies are needed to confirm its effectiveness. Chamomile has a calming effect and reduces anxiety. Buy German (more common) or Roman chamomile. - Chamomile is harmless to children, but in this case dilute the tea with warm water (pour ½ cup of tea and add ½ cup of water).
- Chamomile can interact with many medications, so check with a professional (doctor or pharmacist) before using it.
 6 Take lemon balm as a tea or dietary supplement. Melissa also soothes and improves sleep quality, but should not be taken if the thyroid gland is overactive or during pregnancy. Lemon balm is recognized as safe in the US and can be taken by children over the age of three, but in this case dilute the tea with warm water (½ cup of water for ½ cup of tea).
6 Take lemon balm as a tea or dietary supplement. Melissa also soothes and improves sleep quality, but should not be taken if the thyroid gland is overactive or during pregnancy. Lemon balm is recognized as safe in the US and can be taken by children over the age of three, but in this case dilute the tea with warm water (½ cup of water for ½ cup of tea). - Melissa can interact with some medications taken for hypothyroidism, HIV infection, or sleep problems (such as anxiety or insomnia). Check with your doctor before taking this remedy.
 7 Take a melatonin supplement. Take 1-3 milligrams of melatonin one hour before bed. This "sleep hormone" regulates sleep phases. Do not take melatonin every night without a doctor's recommendation. Also try raising your melatonin levels with a glass of tart cherry juice.
7 Take a melatonin supplement. Take 1-3 milligrams of melatonin one hour before bed. This "sleep hormone" regulates sleep phases. Do not take melatonin every night without a doctor's recommendation. Also try raising your melatonin levels with a glass of tart cherry juice. - Melatonin can interact with drugs and should not be taken by women who are pregnant or breastfeeding. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking this product.
 8 Take the dietary supplement 5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP). This substance is used by the body to make the neurotransmitter serotonin. Serotonin is known to regulate mood and behavior in ways that improve sleep. Take 50-100 milligrams of 5-HTP every night before bed for 6-12 weeks, unless your doctor recommends otherwise.
8 Take the dietary supplement 5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP). This substance is used by the body to make the neurotransmitter serotonin. Serotonin is known to regulate mood and behavior in ways that improve sleep. Take 50-100 milligrams of 5-HTP every night before bed for 6-12 weeks, unless your doctor recommends otherwise. - 5-HTP is not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women.
Method 3 of 4: Use Herbal Remedies for Children with Sleep Paralysis
 1 Prepare an herbal sleeping bag. Take a small bag and fill it with herbal remedies that will help your baby sleep. Simply fill a small cloth bag or pillowcase with the herbs listed below, then tie it up and place it near your baby's pillow. Put the following herbs in it:
1 Prepare an herbal sleeping bag. Take a small bag and fill it with herbal remedies that will help your baby sleep. Simply fill a small cloth bag or pillowcase with the herbs listed below, then tie it up and place it near your baby's pillow. Put the following herbs in it: - 1/2 cup hop cones
- 1/2 cup chamomile flowers
- 1/2 cup lavender flowers
- 1/2 cup lemon balm
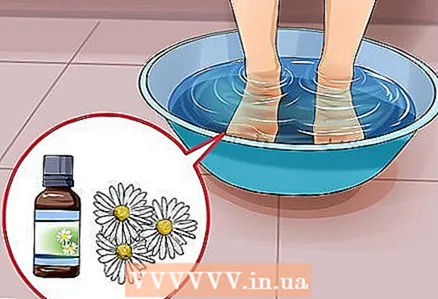 2 Give your child a warm herbal or foot bath. This will help your child relax before bed. Fill a tub or foot basin with warm (but not too hot) water. Add 1 to 2 drops of chamomile or lavender essential oil to the water. The oil will help the child calm down and fall asleep.
2 Give your child a warm herbal or foot bath. This will help your child relax before bed. Fill a tub or foot basin with warm (but not too hot) water. Add 1 to 2 drops of chamomile or lavender essential oil to the water. The oil will help the child calm down and fall asleep. - Do not use essential oils on babies younger than three months old.
 3 Make an herbal balm. For a massage balm: Mix one or two drops of chamomile or lavender essential oil with 30 milliliters of shea butter or castor oil. Mix the ingredients well and apply some of the flavor mixture to your child's whiskey.
3 Make an herbal balm. For a massage balm: Mix one or two drops of chamomile or lavender essential oil with 30 milliliters of shea butter or castor oil. Mix the ingredients well and apply some of the flavor mixture to your child's whiskey. - The massage will help the child to calm down and relax the aching muscles.
Method 4 of 4: Recognize Symptoms and Risk Factors
 1 Identify the primary symptoms. With sleep paralysis, the part of the brain that recognizes threats becomes more active and oversensitive to stimuli. This increased sensitivity leads to temporary paralysis. To be diagnosed with sleep paralysis, a person must experience at least three of the following symptoms:
1 Identify the primary symptoms. With sleep paralysis, the part of the brain that recognizes threats becomes more active and oversensitive to stimuli. This increased sensitivity leads to temporary paralysis. To be diagnosed with sleep paralysis, a person must experience at least three of the following symptoms: - Inability to move: Feels as if some external force is causing paralysis.
- Feelings of fear, dread, or anxiety caused by paralysis.
- Paralysis on awakening and on full consciousness.
- Clear perception of the environment: you can mark the current time, see the moonlight outside the window, flowers on the windowsill, and so on.
 2 Watch for possible symptoms. In addition to the primary symptoms, sleep paralysis can also be accompanied by the following symptoms:
2 Watch for possible symptoms. In addition to the primary symptoms, sleep paralysis can also be accompanied by the following symptoms: - Feeling of overwhelming fear and horror.
- Feeling the presence of someone else.
- Chest pressure.
- Labored breathing.
- Lying on your back, even if you do not like to sleep in this position.
- Visual, olfactory, or auditory hallucinations. They can be associated with a sense of the presence of someone else.
- Feeling of impending doom or death.
 3 Assess your risk factors for experiencing sleep paralysis. Researchers estimate that sleep paralysis is experienced by 5 to 40% of all people, regardless of gender and age, although sleep paralysis most often begins to manifest itself in adolescence. The following risk factors increase the likelihood of sleep paralysis:
3 Assess your risk factors for experiencing sleep paralysis. Researchers estimate that sleep paralysis is experienced by 5 to 40% of all people, regardless of gender and age, although sleep paralysis most often begins to manifest itself in adolescence. The following risk factors increase the likelihood of sleep paralysis: - Family history of sleep paralysis.
- Change your sleep routine.
- Presence of other sleep disorders, such as insomnia, narcolepsy, parasomnias (such as somnambulism or sleep speaking), awakening with confusion, enuresis, nightmares, hypersomnia (excessive sleep duration).
- Depression, anxiety, panic disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and bipolar disorder. These mental disorders also cause more vivid hallucinations.
- Leg cramps during sleep and restless legs syndrome (RLS).
- Taking medications, including those used to treat anxiety disorder and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
- Alcohol and drug abuse.
 4 Know when to see your doctor. If various treatments have not reduced your sleep paralysis frequency within 2-4 weeks, or if you are severely sleep deprived, consult your doctor. You can even make an appointment with a sleep specialist. Sleep paralysis can be a symptom of another sleep disorder or a serious mental problem, and only a doctor can find out.
4 Know when to see your doctor. If various treatments have not reduced your sleep paralysis frequency within 2-4 weeks, or if you are severely sleep deprived, consult your doctor. You can even make an appointment with a sleep specialist. Sleep paralysis can be a symptom of another sleep disorder or a serious mental problem, and only a doctor can find out. - For example, sleep paralysis may indicate narcolepsy, a condition characterized by daytime sleepiness and sudden “fits” of falling asleep.
Tips
- Note that some sleep paralysis is a normal part of sleep. It prevents our physical reactions to what we see in dreams that would interfere with normal sleep. If you have truly sleep paralysis, then you must be aware of it.
- If you are struggling to sleep, do not lie in bed for a long time trying to fall asleep. Get up and try to calm down and relax, as you usually do before bed.
- If you drink herbal tea before bed, you may wake up to visit the restroom.
Additional articles
 How to fall asleep quickly
How to fall asleep quickly  How not to be tired
How not to be tired  How to get rid of sleepiness
How to get rid of sleepiness  How to stop drooling in your sleep
How to stop drooling in your sleep  How to choose a pillow
How to choose a pillow  How to sleep naked
How to sleep naked  How to induce sleep paralysis
How to induce sleep paralysis  How to increase the duration of REM sleep
How to increase the duration of REM sleep  How to make a person fall asleep
How to make a person fall asleep  How to fall asleep on a hot night
How to fall asleep on a hot night  How to sleep if someone snores nearby
How to sleep if someone snores nearby  Wake up somebody
Wake up somebody  How to make a person stop snoring
How to make a person stop snoring  How to induce nightmares
How to induce nightmares