Author:
Sara Rhodes
Date Of Creation:
12 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 2: Calculating the Surface Area of Any Regular Pyramid
- Method 2 of 2: Calculating the Surface Area of a Square Pyramid
- What do you need
- Similar articles
The surface area of any pyramid is equal to the sum of the area of the base and the areas of the side faces. Given a correct pyramid, its surface area is calculated using a formula, but you need to know how to find the area of the base of the pyramid. Since any polygon can lie at the base of the pyramid, you need to be able to find the areas of polygons, including pentagons and hexagons. The surface area of a regular square pyramid is very easy to find if the side of the square (which lies at the base) and the apothem of the pyramid are known.
Steps
Method 1 of 2: Calculating the Surface Area of Any Regular Pyramid
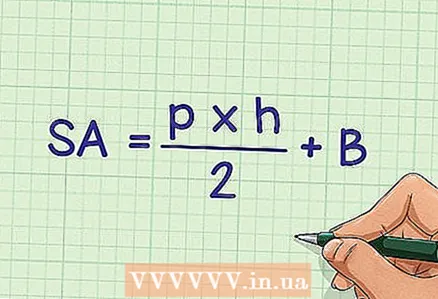 1 Write down a formula for calculating the surface area of a regular pyramid. Formula:
1 Write down a formula for calculating the surface area of a regular pyramid. Formula: , where
- the surface area of the pyramid,
- base perimeter,
- apothem,
- base area.
- The basic formula for calculating the surface area of any pyramid (correct or incorrect): Surface area = base area + side area.
- Don't confuse apothem with height. The apothem of the pyramid is the height of the side face that descends from the top of the side face to the side of the base. The height of the pyramid descends from the top of the pyramid to the base.
 2 Plug in the perimeter value into the formula. If no perimeter is given but the side of the base is known, the perimeter is calculated by multiplying the side value by the number of sides of the base.
2 Plug in the perimeter value into the formula. If no perimeter is given but the side of the base is known, the perimeter is calculated by multiplying the side value by the number of sides of the base. - For example, find the surface area of a regular hexagonal pyramid if the side of the base is 4 cm. Here the perimeter of the base is
because the hexagon has six sides. Thus, the perimeter of the base is 24 cm and the formula will be written as follows:
.
- For example, find the surface area of a regular hexagonal pyramid if the side of the base is 4 cm. Here the perimeter of the base is
 3 Plug in the value of the apothem into the formula. Don't confuse apothem with height. The problem must be given an apothem; otherwise, use another method.
3 Plug in the value of the apothem into the formula. Don't confuse apothem with height. The problem must be given an apothem; otherwise, use another method. - For example, the apothem of a hexagonal pyramid is 12 cm. The formula will be written as follows:
.
- For example, the apothem of a hexagonal pyramid is 12 cm. The formula will be written as follows:
 4 Calculate the area of the base. The formula for calculating the area of the base depends on the shape underlying the base. To find out how to find the areas of regular polygons, read this article.
4 Calculate the area of the base. The formula for calculating the area of the base depends on the shape underlying the base. To find out how to find the areas of regular polygons, read this article. - In our example, a hexagonal pyramid is given, that is, a hexagon lies at the base. To find out how to calculate the area of a hexagon, read this article. Formula:
, where
Is the side of the hexagon. Since the side of the hexagon is 4 cm, the calculation looks like this:
Thus, the base area is 41.57 square centimeters.
- In our example, a hexagonal pyramid is given, that is, a hexagon lies at the base. To find out how to calculate the area of a hexagon, read this article. Formula:
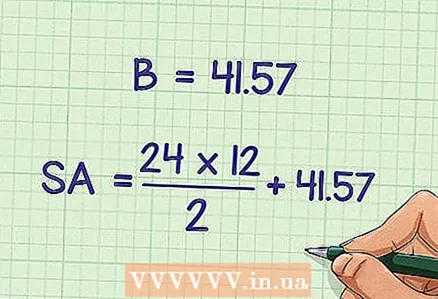 5 Plug the base area into the formula. Substitute the found value of the base area instead of
5 Plug the base area into the formula. Substitute the found value of the base area instead of .
- In our example, the area of the hexagonal base is 41.57 square centimeters, so the formula will be written like this:
- In our example, the area of the hexagonal base is 41.57 square centimeters, so the formula will be written like this:
 6 Multiply the perimeter of the base and the apothem. Divide the result by two. You will find the area of the side surface of the pyramid.
6 Multiply the perimeter of the base and the apothem. Divide the result by two. You will find the area of the side surface of the pyramid. - For example:
- For example:
 7 Add two values. The sum of the lateral surface area and the base area is the surface area of the pyramid (in square units).
7 Add two values. The sum of the lateral surface area and the base area is the surface area of the pyramid (in square units). - For example:
Thus, the surface area of a hexagonal pyramid, in which the base side is 4 cm and the apothem is 12 cm, is 185.57 square centimeters.
- For example:
Method 2 of 2: Calculating the Surface Area of a Square Pyramid
 1 Write down a formula for calculating the surface area of a square pyramid. Formula:
1 Write down a formula for calculating the surface area of a square pyramid. Formula: , where
- side of the base,
- apothem.
- Don't confuse apothem with height. The apothem of the pyramid is the height of the side face that descends from the top of the side face to the side of the base. The height of the pyramid descends from the top of the pyramid to the base.
- Note that this formula is another way of writing the basic formula: pyramid surface area = base area (
) + lateral surface area (
). This formula only applies to regular square pyramids.
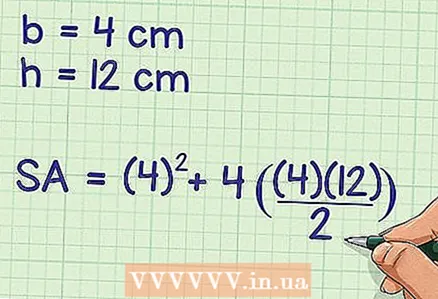 2 Plug the base side and apothem into the formula. The base side value is substituted for
2 Plug the base side and apothem into the formula. The base side value is substituted for , and apothems - instead of
.
- For example, the side of the base of a square pyramid is 4 cm, and the apothem is 12 cm.In this case, the formula will be written as follows:
.
- For example, the side of the base of a square pyramid is 4 cm, and the apothem is 12 cm.In this case, the formula will be written as follows:
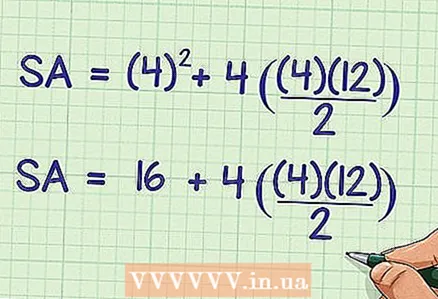 3 Square the side of the base. You will find the base area.
3 Square the side of the base. You will find the base area. - For example:
- For example:
 4 Multiply the side of the base and the apothem. Divide the result by 2 and then multiply by 4. You will find the side area of the pyramid.
4 Multiply the side of the base and the apothem. Divide the result by 2 and then multiply by 4. You will find the side area of the pyramid. - For example:
- For example:
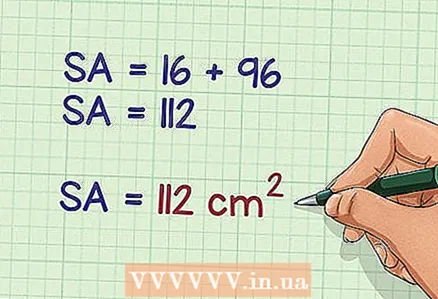 5 Add up the base area and the side area. You will find the surface area of the pyramid (in square units).
5 Add up the base area and the side area. You will find the surface area of the pyramid (in square units). - For example:
Thus, the surface area of a square pyramid, in which the base side is 4 cm and the apothem is 12 cm, is 112 square centimeters.
- For example:
What do you need
- Pencil
- Paper
- Calculator (optional)
- Ruler (optional)
Similar articles
- How to calculate the volume of a square pyramid
- How to find the surface area of a triangular prism
- How to find the volume of a pyramid
- How to find the surface area of a prism
- How to calculate the area of a square by the length of the diagonal
- How to find interest
- How to find the scope of a function
- How to calculate ratios
- How to calculate the diameter of a circle



