Author:
Alice Brown
Date Of Creation:
28 May 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024
Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 3: Rectangular boxes
- Method 2 of 3: Cylindrical boxes
- Method 3 of 3: Problem Solving
- Tips
- What do you need
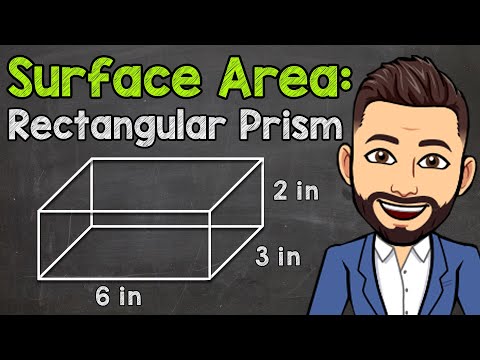
The surface area of a box is fairly easy to find if you know the length of its edges - in this case, plug the known values into the appropriate formula. There is also a formula for calculating the surface area of cylindrical boxes.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Rectangular boxes
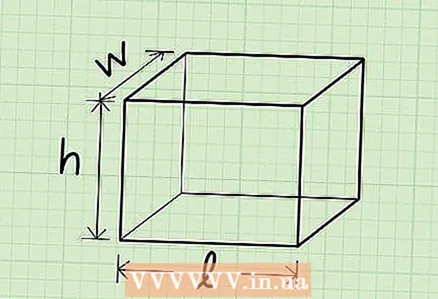
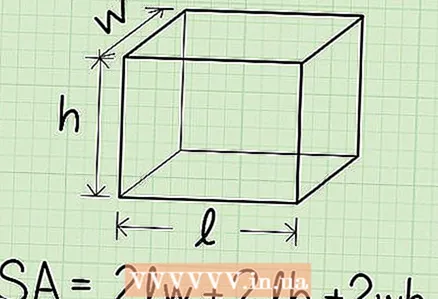 1 To find the surface area of a box, add up the areas of all of its edges. The surface area of a box is equal to the sum of the areas of its edges. To find the area of a face that is a rectangle, multiply its different-sized sides. But there is a formula for calculating surface area that will make the process easier:
1 To find the surface area of a box, add up the areas of all of its edges. The surface area of a box is equal to the sum of the areas of its edges. To find the area of a face that is a rectangle, multiply its different-sized sides. But there is a formula for calculating surface area that will make the process easier:- l - the length of the box (longest edge).
- h - the height of the box.
- w - the width of the box.
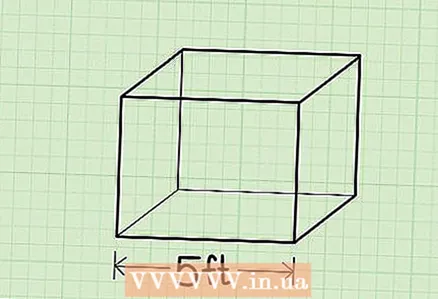 2 Measure the length of the box. This is the longest rib. Any box has 4 long ribs. To make it easier to measure the box, place it on the face that is formed by the long and short edges.
2 Measure the length of the box. This is the longest rib. Any box has 4 long ribs. To make it easier to measure the box, place it on the face that is formed by the long and short edges. - Example: the length of the box is 50 cm.
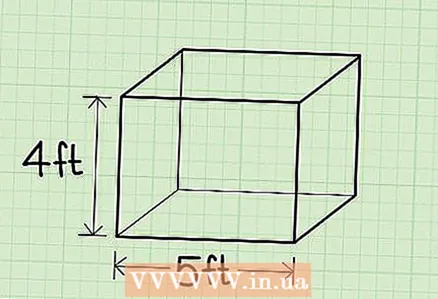 3 Measure the height of the box, that is, the distance from the floor to the top of the box. Don't confuse height with length!
3 Measure the height of the box, that is, the distance from the floor to the top of the box. Don't confuse height with length! - Example: the height of the box is 40 cm.
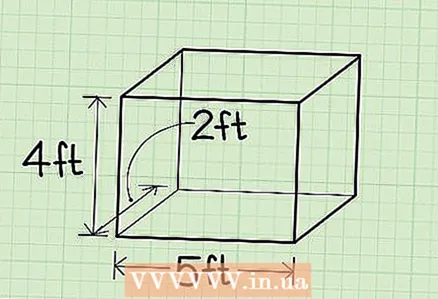 4 Measure the width of the box. This is the edge that is perpendicular (forming a right angle) to the longest edge of the box. Don't confuse width with height!
4 Measure the width of the box. This is the edge that is perpendicular (forming a right angle) to the longest edge of the box. Don't confuse width with height! - Example: the width of the box is 20 cm.
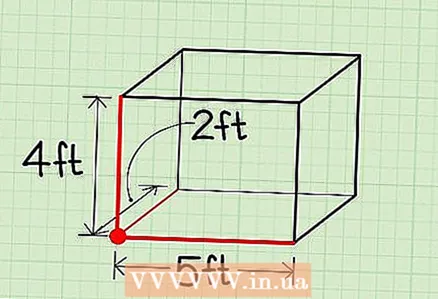 5 Make sure you don't measure the same edge twice. The edges to be measured must intersect at one point. In order not to be mistaken, take any vertex of the box and measure the three edges that converge at that vertex.
5 Make sure you don't measure the same edge twice. The edges to be measured must intersect at one point. In order not to be mistaken, take any vertex of the box and measure the three edges that converge at that vertex. - Be aware that the edges may be equal. But make sure you measure three different edges of the box, even if two or all three edges are equal.
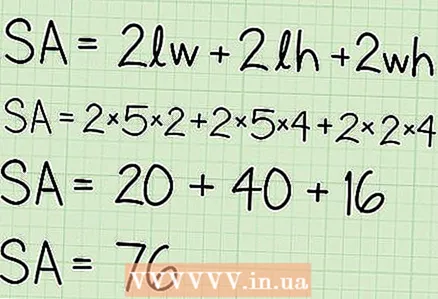 6 Substitute the found values into the formula to calculate the surface area. Multiply the corresponding values and find the sum of the results of the multiplication.
6 Substitute the found values into the formula to calculate the surface area. Multiply the corresponding values and find the sum of the results of the multiplication. 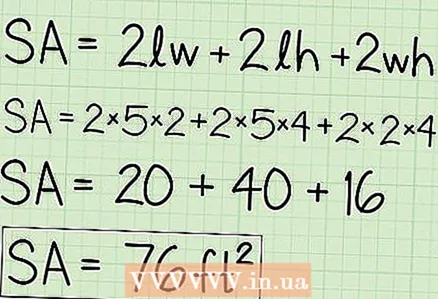 7 Surface area is expressed in square units, which are integral to the answer. Use the unit of measurement in which all calculations were performed. In our example, the edges of the box were measured in centimeters, so the surface area of the box will be expressed in square centimeters.
7 Surface area is expressed in square units, which are integral to the answer. Use the unit of measurement in which all calculations were performed. In our example, the edges of the box were measured in centimeters, so the surface area of the box will be expressed in square centimeters. - Find the surface area of a box that is 50 cm long, 40 cm high, and 20 cm wide.
- Answer: 7600 cm
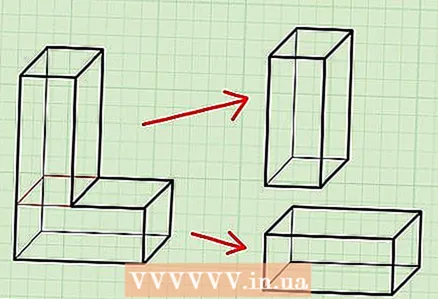 8 If the box has a complex shape, mentally break it down into its component parts to find the surface area. For example, the box is L-shaped. In this case, mentally break this box into two - a horizontal box and a vertical box. Calculate the surface area of each of the two boxes, then add the values together to get the surface area of the original box. For example, you have a U-shaped box.
8 If the box has a complex shape, mentally break it down into its component parts to find the surface area. For example, the box is L-shaped. In this case, mentally break this box into two - a horizontal box and a vertical box. Calculate the surface area of each of the two boxes, then add the values together to get the surface area of the original box. For example, you have a U-shaped box. - Let's say the horizontal surface area of a box is 12 square units.
- Let's say that the surface area of each vertical box is 15 square units.
- Original box surface area: 12 + 15 + 15 = 42 square units.
Method 2 of 3: Cylindrical boxes
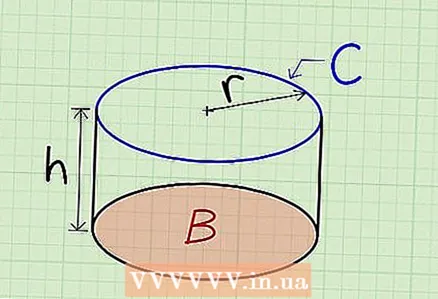
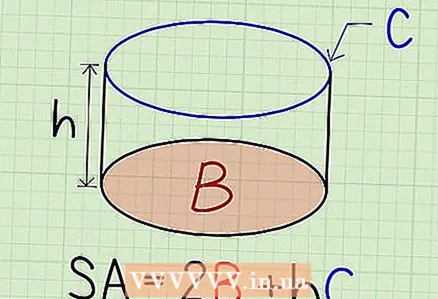 1 To find the surface area of a cylindrical box, add the base areas and the height times the circumference. This method is applicable exclusively to regular cylinders (their bases are perpendicular to the height). Formula for calculating the area of a cylinder:
1 To find the surface area of a cylindrical box, add the base areas and the height times the circumference. This method is applicable exclusively to regular cylinders (their bases are perpendicular to the height). Formula for calculating the area of a cylinder:For example, find the surface area of a cylindrical box if the base area is 3, the height is 5, the circumference is 6. Answer: 36 square units.
- B Is the area of the cylinder base.
- h Is the height of the cylinder.
- C Is the circumference of any base of the cylinder.
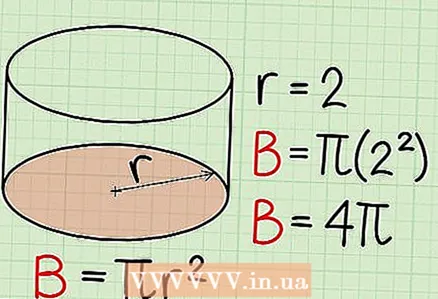 2 Calculate the area at the base of the cylinder. The base is a circular plane that bounds a cylindrical surface from below or from above. The base area is calculated using the following formula: B = π * r where r - radius of the round base, π Is a mathematical constant, which is approximately equal to 3.14. If you don't have a calculator, just write π in your answer.
2 Calculate the area at the base of the cylinder. The base is a circular plane that bounds a cylindrical surface from below or from above. The base area is calculated using the following formula: B = π * r where r - radius of the round base, π Is a mathematical constant, which is approximately equal to 3.14. If you don't have a calculator, just write π in your answer. - Example: Find the area of the base if its radius is 2.
- π*(2)
- B = 4π
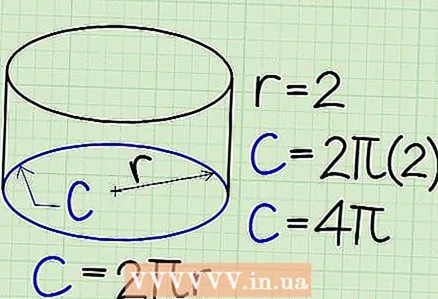 3 Find the circumference of the base. It is calculated by the formula: C = 2 * r * π In our example:
3 Find the circumference of the base. It is calculated by the formula: C = 2 * r * π In our example: - 2*π*(2)
- C = 4π
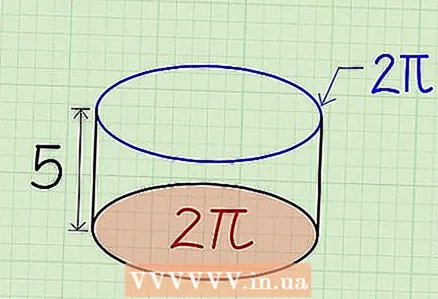 4 Find the height of the cylinder by measuring the distance between the bases. Height is the line that connects the centers of the bases.
4 Find the height of the cylinder by measuring the distance between the bases. Height is the line that connects the centers of the bases. - Example: The height of a cylinder with a base radius of 2 cm is 5 cm.
 5 Substitute the found values into the formula to find the surface area of a cylindrical box. In the formula, you need to substitute the base area, circumference and height.
5 Substitute the found values into the formula to find the surface area of a cylindrical box. In the formula, you need to substitute the base area, circumference and height. - S = 2B + hC
- S = 2 (4π) + (5) (4π)
- S = 8π + 20π
- S = 28π
 6 Surface area is expressed in square units, which are integral to the answer. For example, surface area is measured in square centimeters. Use the units of measurement given in the problem. If units are not listed, write “square units” in your answer.
6 Surface area is expressed in square units, which are integral to the answer. For example, surface area is measured in square centimeters. Use the units of measurement given in the problem. If units are not listed, write “square units” in your answer. - In our example, the units are centimeters. So the final answer is: 28π cm.
Method 3 of 3: Problem Solving
 1 Try to find the surface area of rectangular boxes. To see the answers, highlight the blank space behind the arrow:
1 Try to find the surface area of rectangular boxes. To see the answers, highlight the blank space behind the arrow: - L = 10, W = 3, H = 2, → 112 square units
- L = 6.2, W = 2, H = 5.4 → 113.36 square units
- The dimensions of one face of the rectangular box are 5x3x2, and the other face is 6x2x2. → 118π square units
 2 Try to find the surface area of cylindrical boxes. To see the answer, highlight the blank space behind the arrow:
2 Try to find the surface area of cylindrical boxes. To see the answer, highlight the blank space behind the arrow: - Base area = 3, height = 10, circumference = 1.5 → 21 square units
- Base area = 25, Height = 3, Circumference = 10π → 80π square units
- Radius = 3, Height = 3 → 36π square units
Tips
- In the case of a real box, measure equal edges and then find the average.
What do you need
- A box and a tool to measure it.
- Known edge lengths of a real or imaginary box.



