Author:
Gregory Harris
Date Of Creation:
10 August 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 4: Facial Cysts
- Method 2 of 4: Baker's Cyst
- Method 3 of 4: Ovarian Cyst
- Method 4 of 4: Pilonidal Cyst
- Warnings
A cyst is a fluid-filled cavity that forms under the skin. Usually, cysts are not dangerous, but very often they cause pain and irritation. Depending on what type of cyst you have, there are several treatment options available to you, and your doctor will remove it if necessary.
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Facial Cysts
 1 Decide if you need medical attention. Doctors call cysts on the face sebaceous cysts. These cysts can be annoying and often ruin your appearance, but most often do not require medical attention. If the cyst is not painful, it will probably be best left in place to avoid complications that may arise with removal. However, you need to see your doctor in the following situations:
1 Decide if you need medical attention. Doctors call cysts on the face sebaceous cysts. These cysts can be annoying and often ruin your appearance, but most often do not require medical attention. If the cyst is not painful, it will probably be best left in place to avoid complications that may arise with removal. However, you need to see your doctor in the following situations: - Facial cysts are usually small, round lumps under the skin. They can be black, red, or yellowish in color, and a foul-smelling liquid may come out of them. Cysts are usually more painful compared to other skin problems like acne.
- If the cyst ruptures, there is a risk of wound infection - in such cases, timely treatment and removal of the cyst is necessary.
- If the cyst suddenly becomes painful and swelling develops around it, there is a high probability of infection. See your doctor to have the cyst removed and to prescribe an appropriate course of antibiotics for you.
- In very rare cases, a cyst can lead to skin cancer. During your regular check-up, ask your doctor to examine the cyst and determine if there is a risk of cancer.
 2 Ask your doctor for a special injection. If the cyst is infected or painful, the doctor may inject a special drug directly into the cyst. This will not completely remove the cyst, but it will reduce the swelling and redness, making the cyst less visible.
2 Ask your doctor for a special injection. If the cyst is infected or painful, the doctor may inject a special drug directly into the cyst. This will not completely remove the cyst, but it will reduce the swelling and redness, making the cyst less visible. 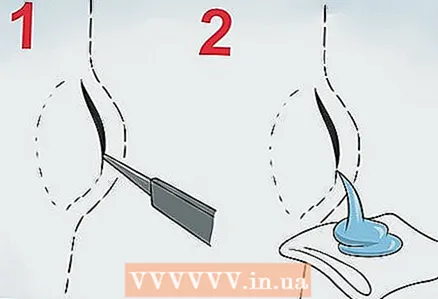 3 Pumping liquid. If the cyst has grown significantly in size or is uncomfortable, then you can remove it. The doctor can cut the cyst and pump out all the fluid.
3 Pumping liquid. If the cyst has grown significantly in size or is uncomfortable, then you can remove it. The doctor can cut the cyst and pump out all the fluid. - During the procedure, the doctor will open the cyst and pump the fluid out of it with a syringe. This procedure is quick enough and usually painless.
- The main disadvantage of this method is only that, after opening and drainage, the cyst can form again.
 4 Surgery. Surgery is the only way to remove the cyst completely. If you want to remove the cyst, talk with your doctor about the possibility of surgery.
4 Surgery. Surgery is the only way to remove the cyst completely. If you want to remove the cyst, talk with your doctor about the possibility of surgery. - Surgery to remove a cyst is considered relatively straightforward. The recovery period after surgery is short, but you may need to visit your doctor after surgery again to have the stitches removed.
- Surgery to remove the cyst is safe and usually does not recur. Cysts, as a rule, are not hazardous to health, so more often than not, insurance does not cover the cost of their treatment.
Method 2 of 4: Baker's Cyst
 1 R.I.C.E. Baker's cyst is a fluid-filled cavity at the base of the knee that is very common as a result of knee injuries or chronic conditions such as arthritis. R.I.C.E. (from the English rest - rest, ice - ice, compression - compression, elevation - lifting) can be effective in this case.
1 R.I.C.E. Baker's cyst is a fluid-filled cavity at the base of the knee that is very common as a result of knee injuries or chronic conditions such as arthritis. R.I.C.E. (from the English rest - rest, ice - ice, compression - compression, elevation - lifting) can be effective in this case. - R.I.C.E. suggests resting the leg, applying ice to the knee, using a compression bandage, and keeping the leg elevated whenever possible.
- For a Baker cyst, rest your leg, preferably in an elevated position. Never apply ice directly to your skin. Be sure to wrap it in a piece of cloth or towel.
- Purchase a special compression bandage from a pharmacy and apply it as directed on the package. If you have a medical condition with an increased risk of blood clots, do not use a compression bandage without talking to your doctor.
- R.I.C.E. helps to reduce pain in the joint where the cyst appeared, that is, thanks to the above actions, the cyst can decrease in size and stop hurting.
- You can use over-the-counter pain relievers. Rest your leg and lift it higher if possible - if these actions do not relieve pain, then take a pain reliever: ibuprofen, paracetamol (acetaminophen), or aspirin.
 2 Ask your doctor about pumping fluid out of the cyst. To remove a cyst, you must see a doctor - it will pump out the fluid. If the R.I.C.E. did not help cure Baker's cyst, then see your doctor.
2 Ask your doctor about pumping fluid out of the cyst. To remove a cyst, you must see a doctor - it will pump out the fluid. If the R.I.C.E. did not help cure Baker's cyst, then see your doctor. - The fluid from the cyst can be aspirated with a needle. The procedure is not too painful, but many are very anxious before it. If you are afraid of needles, ask a loved one to come with you for the procedure so you will have support.
- When the doctor pumps out the fluid, Baker's cyst should be gone. However, in some cases, Baker's cyst gives a relapse. Talk to your doctor about the cause of the cyst to avoid reoccurring cysts.
 3 Get physical therapy. After the cyst has drained, your doctor may recommend physical therapy.Exercise under the guidance of a trained professional will help bring joints back to normal and also reduce the risk of cyst reoccurrence. Ask your doctor to refer you to a professional physical therapist after the cyst has been pumped out.
3 Get physical therapy. After the cyst has drained, your doctor may recommend physical therapy.Exercise under the guidance of a trained professional will help bring joints back to normal and also reduce the risk of cyst reoccurrence. Ask your doctor to refer you to a professional physical therapist after the cyst has been pumped out.
Method 3 of 4: Ovarian Cyst
 1 Waiting tactics. Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled cavities on the surface of the ovaries. Unfortunately, ovarian cysts are difficult to remove, and, as a rule, after diagnosis, they are only regularly observed and waited for.
1 Waiting tactics. Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled cavities on the surface of the ovaries. Unfortunately, ovarian cysts are difficult to remove, and, as a rule, after diagnosis, they are only regularly observed and waited for. - Some ovarian cysts go away on their own. The doctor may ask you to wait and come back for a follow-up check in a few months.
- The doctor should regularly monitor the condition of the cyst, checking if it is increasing in size, since at some point medical intervention may be required.
 2 Hormonal contraceptives. With an ovarian cyst, as a rule, the first step is prescribed a course of contraceptive drugs, since they can reduce the cysts. Ask your doctor if you should be taking any hormonal birth control.
2 Hormonal contraceptives. With an ovarian cyst, as a rule, the first step is prescribed a course of contraceptive drugs, since they can reduce the cysts. Ask your doctor if you should be taking any hormonal birth control. - Hormonal birth control pills can shrink cysts and often prevent new ones from forming. These drugs also reduce the risk of ovarian cancer, especially when taken for a long time.
- There are different types of hormonal drugs and plans for taking them. Some plans call for monthly periods, while others may have fewer periods. Some preparations contain iron and some do not. It is imperative that you talk to your doctor about which drug is best for you based on your lifestyle, goals, and overall health.
- Some women may have side effects from taking birth control pills, including breast tenderness, mood swings, or bleeding between periods of starting hormonal drugs. All of these effects should subside or diminish in a few months.
 3 Surgery. Ovarian cysts can be very painful and even dangerous if they continue to grow. If the cyst does not go away after some time on its own, then the doctor may send for an operation to remove it.
3 Surgery. Ovarian cysts can be very painful and even dangerous if they continue to grow. If the cyst does not go away after some time on its own, then the doctor may send for an operation to remove it. - If the cyst remains for two to three menstrual cycles, your doctor will likely recommend surgical removal, especially if the cyst grows larger. Cysts can cause pain and disrupt the regularity of your menstrual cycle.
- In some cases, the entire infected ovary may be removed during surgery. However, more often than not, doctors are able to remove only the cyst itself, without touching the ovary. Very rarely, cysts are cancerous - in such cases, the surgeon will most likely remove all of the reproductive organs.
 4 Get inspected regularly. The best way to treat ovarian cysts is through prevention. Get regular check-ups with your gynecologist and pay attention to any changes in your menstrual cycle. The sooner the cyst is found, the easier it will be to heal. Even with a routine examination of the pelvic area, the doctor can identify certain abnormalities that can lead to the formation of a cyst.
4 Get inspected regularly. The best way to treat ovarian cysts is through prevention. Get regular check-ups with your gynecologist and pay attention to any changes in your menstrual cycle. The sooner the cyst is found, the easier it will be to heal. Even with a routine examination of the pelvic area, the doctor can identify certain abnormalities that can lead to the formation of a cyst.
Method 4 of 4: Pilonidal Cyst
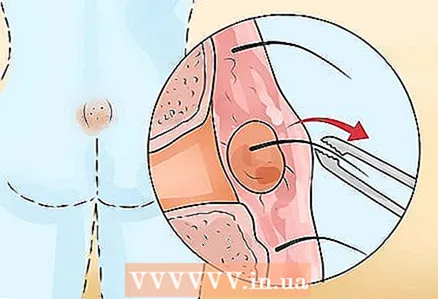 1 Removal of hair follicles causing cysts. A pilonidal cyst is a cyst that forms in the buttocks or the lower back. The cyst may be warm to the touch and may drain pus or other fluid. To prevent cyst growth, keep the area where the cyst is clean and dry. Pilonidal cysts are often caused by ingrown hairs that get stuck under the skin's surface. Removing any hair follicles near the cyst helps prevent ingrown hairs from forming.
1 Removal of hair follicles causing cysts. A pilonidal cyst is a cyst that forms in the buttocks or the lower back. The cyst may be warm to the touch and may drain pus or other fluid. To prevent cyst growth, keep the area where the cyst is clean and dry. Pilonidal cysts are often caused by ingrown hairs that get stuck under the skin's surface. Removing any hair follicles near the cyst helps prevent ingrown hairs from forming.  2 Show the cyst to your doctor. Since pilonidal cysts can cause serious infections, you should definitely see your doctor. Make an appointment with a therapist if you have a pilonidal cyst.
2 Show the cyst to your doctor. Since pilonidal cysts can cause serious infections, you should definitely see your doctor. Make an appointment with a therapist if you have a pilonidal cyst. - The doctor should do a short examination and check the cyst. He may also ask if you noticed any fluid coming out of the cyst, if it is painful, and how long ago it formed.
- The doctor should also check for any other symptoms. If you have a rash or a fever due to a cyst, your doctor will recommend removing the cyst as soon as possible. If the cyst is not causing any problems, then no treatment is required.
 3 Pump the fluid out of the cyst. The least invasive way to remove a pilonidal cyst is by drainage, where the cyst is opened and fluid is pumped out. The doctor will make a small hole in the cyst and remove excess fluid, and then apply a bandage on top. You may be prescribed a course of antibiotics to prevent infections.
3 Pump the fluid out of the cyst. The least invasive way to remove a pilonidal cyst is by drainage, where the cyst is opened and fluid is pumped out. The doctor will make a small hole in the cyst and remove excess fluid, and then apply a bandage on top. You may be prescribed a course of antibiotics to prevent infections.  4 Surgical removal of the cyst. Sometimes, even after draining, the cysts may reappear. In such cases, surgical removal is recommended. Surgery to remove a cyst is short-lived, but recovery can take a long time, and you may have an open wound that needs to be cleaned regularly.
4 Surgical removal of the cyst. Sometimes, even after draining, the cysts may reappear. In such cases, surgical removal is recommended. Surgery to remove a cyst is short-lived, but recovery can take a long time, and you may have an open wound that needs to be cleaned regularly.
Warnings
- Do not try to remove fluid from the cyst yourself. This can lead to scarring or infection.
- Check with your doctor annually for new cysts. In rare cases, cysts are a sign of serious medical conditions such as cancer.