Author:
Lewis Jackson
Date Of Creation:
13 May 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
The human body is an incredibly complex and lubricated machine to fight disease. White blood cells, including natural cells and T-lymphocytes as well as other groups of cells, are guarding the body. To strengthen the immune system, you can take a variety of measures.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Boost immune system with diet
Eat citrus fruits. Vitamin C is an excellent antioxidant. It is believed to strengthen white blood cells, antibodies, and interferon to stop viruses from entering. However, to confirm this, more research is needed.
- You don't have to buy an expensive juicer. Just eat the inside of the fruit and you can sometimes add the peel to supplement vitamin C.
- Get 200 mg of vitamin C daily by eating a minimum of 6 servings of fruits and vegetables to meet daily needs. You can also get vitamin C found in broccoli, spinach, bell peppers, strawberries, raspberries, and more.
- Eat plenty of vitamin C rich foods throughout the day. Excess vitamin C is excreted in the urine.
Take in beta carotene. Beta carotene is an antioxidant precursor to vitamin A found in fruits and vegetables. This substance enhances the natural defense and kill cells, promotes immunity, and can suppress and eradicate cancer cells (through natural tumor necrosis factor increase).- Beta carotene and other carotenoids are found in dark orange and yellow fruits and vegetables such as cantaloupe, sweet potatoes, pumpkin, and carrots. Spinach also contains a lot of these two substances. You should eat at least five servings of fruits and vegetables a day to get at least 6 mg of beta carotene.
- Control your vitamin intake. Pure vitamin A in high doses can be toxic, but when you eat foods containing beta carotene, your body only converts the amount of vitamin A it needs.
Eat garlic. They contain allicin and sulfur, two important ingredients in maintaining good health. Garlic enhances white blood cells, antibodies, and killer cells. You should eat plenty of garlic raw or cooked to get the most out of the benefits they provide. Research has shown that people who eat garlic or take garlic extract supplements have a 30% lower risk of colon cancer.- You can eat garlic as much as you want without fear of poisoning. However, your breath will smell if you eat too much!
- Garlic is an antioxidant that helps to remove free radicals that promote the aging process.

Add zinc to your diet. Zinc is a mineral that boosts the immune system because it stimulates production and strengthens white blood cells and killer cells.- Zinc is found in foods such as zinc-rich grains, beans, beef, dairy products, turkey, oysters and crab meat.
- However, if the amount of zinc absorbed above 75 mg per day can weaken the immune system. 15-25 mg per day should be sufficient.
Add more len. This is a mineral found in many foods that promote cell destruction and boost the immune system. Lean, when combined with vitamin E, can be improved as an antioxidant.
- Lean is found in foods like fish and seafood, vegetables, whole grains, brown rice, garlic, and more. A daily intake of 55 micrograms is sufficient. If it is too much, it can increase the risk of diabetes, so you should not take acetone supplements.
Consume omega-3 fatty acids. Fatty fish such as salmon and tuna, algae and mollusks, some vegetables and seed oils are good sources of omega-3 fatty acids that enhance white blood cell activity, heart health, and cabbage. good brain and digestive tract.
- Omega-3 fatty acids are comprised of three types: EPA, DHA, and ALA. EPA and DHA are found in fish, mollusks, and seaweeds. ALA is found in some fruits and vegetables such as flaxseeds, soybeans, pumpkin seeds and some fruits like pecans. EPA and DHA are easily absorbed by the body, but ALA needs to be converted into EPA and DHA. This process is quite complicated.
- Adults should eat two servings of fish per week to get enough omega-3s. Your doctor may recommend higher dosages if you have high blood pressure or cholesterol. However, you should not eat more than 3g per day. If you take an omega-3 oil supplement, combine it with vitamin E.
Avoid processed foods. Fresh foods have many benefits, including boosting the immune system. You should not eat nutrient-poor foods such as processed, refined, or fried foods that are high in sugar, fat, and salt.
- Fresh, unprocessed (or pre-processed) foods that boost vitamin P boost the immune system by purifying cells from toxins. You should eat nine servings of fruits and vegetables each day so that your body receives adequate amounts of vitamin P.
Breastfeeding. Breast milk contains all the nutrients needed to strengthen your baby's immune system. The baby receives antibodies, immune factors, and white blood cells from milk feeding. This process is called "passive natural immunity".
- Breastfeeding also promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria in the baby's gut, essential for a good immune system.
- Immunity passed from mother to child lays the foundation for a long lasting immune system.
Method 2 of 3: Take supplements
Get the maximum amount of nutrients from your diet. The best way to get enough nutrients is through a well-balanced diet. However, if your diet doesn't provide enough nutrients, talk to your doctor about the right supplements.
Use multivitamins. The diet sometimes lacks one or more nutrients. The human body is streamlined by retaining the missing vitamin and the rest is excreted out.
- Vitamins A, B2, and B6 also play a role in supporting the immune system.
- Taking lots of vitamins is not always beneficial and the body will eliminate excess. So, instead of taking many vitamins in high doses, you should use multivitamins.
Supplement with vitamin E. This is an antioxidant that stimulates and strengthens immune cells.Furthermore, vitamin E also prevents aging due to reduced immunity.
- Diets often do not provide enough vitamin E (mainly found in avocados, beans, vegetable oils, and grains) as well as multivitamins are not recommended. Therefore, you should get 400 mg per day with supplements.
Use spirulina. This algae is green and blue in color and is considered the most nutrient dense food. They are often packed with proteins, vitamins, minerals, and nutrients such as B vitamins, beta carotene, vitamin E, iron, zinc, and cesium. Spirulina promotes cell regeneration, strengthens the immune system, protects against allergies, and improves anemia including iron deficiency.
- Spirulina is usually available in powdered or cotton form to add to smoothies. Although science has not established the standard dosage, you can take 2g per day for best.
- Buy spirulina from a reputable manufacturer because algae, if not from a clear source, can be contaminated with heavy metals and toxins.
Use wild chamomile. The effectiveness of this herb is still being scientifically proven. Chamomile belongs to the chamomile family and is available in supplement form and often works to boost the immune system and cure colds.
- Note when using wild chamomile. Children under 12 years of age can develop a rash. People with allergies or taking anticoagulants or ibuprofen / naproxen may experience serious side effects.
- Do not take this herb every day. Use 300 mg of powdered extract (or the equivalent of tincture or tea) three times a day during a cold.
Using probiotics. In the intestinal tract, hundreds of beneficial bacteria live. Probiotics such as lactobacillus acidophilus have been shown to boost immune cells and replenish the lack of beneficial bacteria.
- The use of probiotics is still being studied. According to one theory, probiotics help digest food in the gut, creating an unfavorable environment for "bad" bacteria.
- Scientists agree on the fact that yogurt and other probiotic-rich products have beneficial effects on the gut.
- Depending on the source of probiotics, when using a probiotic-rich supplement or dairy product, you only need to consume between 1 and 15 billion colony units (or CFUs) for good gut health.
Be careful with DHEA. Some believe this medication is extremely helpful. DHEA is a hormone secreted by the adrenal glands. People with impaired immune function often have low DHEA levels. However, currently there is still very little research on the effects of daily use of DHEA to promote immunity in healthy people.
- Do not take more than 50 mg of DHEA daily.
Does not absorb silver. Colloidal silver (the liquid that contains tiny silver beads like silver jewelry) is advertised as being quite useful when taken by mouth, injected, or applied to the skin. Silver's immune boosting ability has not been scientifically proven.
- Silver is not an essential mineral for the body.
- Silver, when it accumulates in the body because it is not used, can cause kidney damage and seizures.
Method 3 of 3: Lifestyle changes
Shots. The vaccine works to boost immunity by creating a false infection that stimulates the production of reactive antibodies. These antibodies then learn how to actually attack harmful microorganisms and protect the body from infectious diseases later on.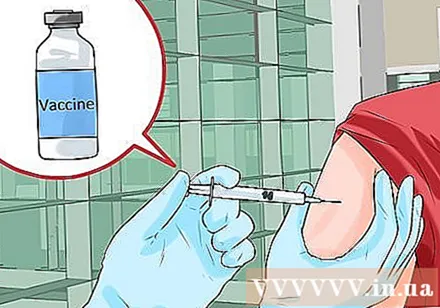
- Vaccination schedule that starts immediately after birth includes chickenpox, diphtheria, flu, hepatitis A and B vaccines, haemophilus influenzae (or Hib, the bacteria that cause meningitis), measles, meningitis, mumps , polio, enteritis and gastroenteritis virus, German measles, tetanus, and pertussis. Some vaccination schedules have additional HPV.
- Vaccines are made from weakened or destroyed microorganisms and are not likely to infect you; They only cause a symptomatic reaction such as redness with the shot or a mild fever.
- Vaccines are very safe, do not cause autism, and rarely lead to a severe allergic reaction, for example if you are allergic to eggs. The illnesses you get are usually worse than getting vaccinated.
Moderate exposure to pathogens. Natural exposure to disease helps to build antibodies and then fight the same disease later.
- Do not overdo hand sanitizer. The antibacterial products can actually form antibacterial-resistant bacteria, so when infected with antibodies, they cannot play their role. Wash your hands with regular (non-antibacterial) soap and water.
- Allow children to stain, pet dogs, or play toys that are on the floor. You just need to wash their hands with regular soap.
- This may seem strange, but research has shown that children who are exposed to the bacteria are less likely to develop cardiovascular disease later in life.
- Do not expose children to chickenpox and other illnesses. This is a very serious disease and can only be best prevented with a vaccine.
- Understand the body's immunity. Some people boost their immunity by being exposed to certain foods, vegetables, and even snake venom. This method of boosting immunity can be dangerous and even fatal.
Reduce stress. Prolonged stress raises the level of cortisol in the blood, which weakens the immune system.
- Learn to manage stress with some physical and mental routine, such as meditating, playing a sport, adopting a balanced diet, or journaling.
- One of the most effective ways to cope with stress is cognitive behavioral therapy. A therapist will teach you how to feel and deal with the problem, tolerable uncertainty, and exposure to stressors.
- Studies have shown that journaling your feelings helps you control your emotions by suppressing negative feelings and releasing emotions.
Laugh. Laughter reduces stress, releases endorphins that fuel the brain and body, and improves the immune system.
- Laughter is a great cure for stress. You can do some laughing therapy yourself by watching a comedy or taking a yoga class to laugh.
Sun exposure. Vitamin D is proven not only to help strengthen bones by assisting the body to absorb calcium, but also by strengthening the immune system.
- Sun for 10 to 15 minutes three times a day. Take care not to get sunburned by using sunscreen, drinking water, and wearing a hat. The benefits of vitamin D can be maintained even with short-term sun exposure.
- If you take a supplement, you can consume 15 micrograms per day for adults.
Get enough sleep. At night the body restes and recovers through sleep. The immune system then secretes a protein called xytokin. This protein is needed when you are stressed or sick. Therefore, if you do not get enough sleep, the body does not produce enough xytokin, making the immune system weak.
- Adults need seven to eight hours of sleep each night.
Do not clean the colon. Some people think that purifying the colon with water, coffee, or other substances can boost the immune system by flushing out toxins. However, this view has not been confirmed, and this method can be harmful to health.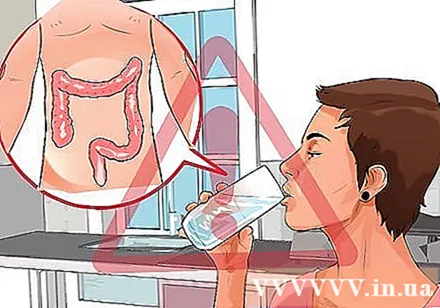
Get treatment. If you are diagnosed with immunodeficiency, your doctor will recommend an intravenous injection.
- Immunoglobulin therapy involves either a direct injection or an intravenous infusion of antibody proteins to fight disease. This is an outpatient treatment.
- If immunodeficiency is a threat to your life, you may need a cell transplant to prevent this. The stem cells of the donor and receiver must match; however, this method still does not guarantee certain success.
- Immunotherapy is not required for healthy people wishing to boost the immune system.
Advice
- Scientists are still continuing to study the human immune system. They learn how immunity is affected by drugs, herbs, and supplements. Whatever it is, the best method is to practice a healthy lifestyle.