Author:
Peter Berry
Date Of Creation:
18 February 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
Candida yeast infection is an infection caused by the fungus Candida albicans. The disease can affect the mouth, vagina, skin, stomach, and urinary tract. Most women will get a vaginal yeast infection once in their lifetime, and most HIV / AIDS patients will get Candida infection. Oral thrush (thrush) is a common disease in babies, the elderly, and people with weakened immune systems.
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Take traditional drugs
Identify symptoms. Your risk of a yeast infection increases if you take antibiotics, are pregnant, overweight, have diabetes, or have a weak immune system. Symptoms of a yeast infection include:
- Itching, irritation, pain, and burning sensation in the vagina
- The discharge is white, lumpy and has an odor
- Rashes on the skin, patches and blisters in the groin area
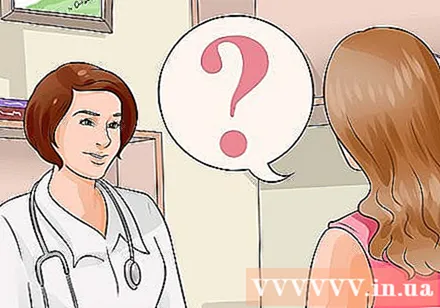
Ask your doctor. See your doctor if you suspect that you have a yeast infection, have your first symptoms of a yeast infection, or have other symptoms. Your doctor may take a sample for testing, such as a vaginal smear test, CT scan or stool test in case of widespread infection. If you have frequent yeast infections, your doctor may test to detect weakened immunity or other illnesses. You can get a complicated yeast infection if:- Have serious signs and symptoms, such as severe redness, swelling, and itching leading to tearing, cracking, or ulcers.
- Recurrent yeast infection - more than 4 times a year.
- Infection caused by a fungus other than Candida albicans.
- Pregnant.
- Have diabetes.
- Taking certain medications, for example HIV.

Use an antifungal cream. Your doctor may prescribe an antifungal medicine to help cure a fungal infection or recommend over-the-counter medications. Yeast infections are actually caused by fungi, making over-the-counter antifungal creams one of the most popular treatments.- See your doctor if symptoms do not improve after 3-4 days of taking the medicine.
- DO NOT take over-the-counter medications for women who are pregnant or have recurrent yeast infections. In this case, you should see your doctor for treatment.
- Be sure to use a specialized antifungal cream to treat a yeast infection. Other antifungal creams may contain a formula that should not be used around the vagina.
- The over-the-counter cream is used for 1-7 days. Follow the instructions on the package for how often to use the cream.
Buy a vaginal suppository. Like antifungal creams, over-the-counter vaginal suppositories are used to treat fungal infections by coming into direct contact with the fungus that causes the disease. The composition of each medicine may vary slightly, but it usually contains an antifungal such as Clotrimazole, Butoconazole, Miconazole, or Tioconazole.- Over-the-counter vaginal suppositories can also be used for 1-7 days. Carefully read the instructions that come with the medication to know how often to use and how to properly order the medicine.
- Vaginal suppositories are usually conical, rod-shaped, or wedge-shaped and are inserted directly into the vagina.
Take over-the-counter medications. Over-the-counter tablets are also used but are not as popular as topical medications and are not effective against serious yeast infections. You should consult your doctor before taking a new medication, as some medicines can cause side effects when taken with other medicines, herbs or supplements.
- Carefully read the label on the package to determine the correct dose and frequency of taking. The course of treatment with over-the-counter pills usually takes 1-7 days.
- These pills contain an antifungal ingredient that is safe to take orally.
- Avoid overdosing on antibiotics as this will destroy the probiotics that help control Candida.
Apply anti-itch cream. Anti-itch medication should only be applied around the vagina and should not be applied inside. Vaginal creams can be combined with mild corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and itching and are often sold with tools that help you accurately measure the amount of cream needed.
- Consult your doctor before using over-the-counter creams.
- Creams are usually thicker than Lotion but can still run, so consider using a tampon or underwear pad. Do not use tampons (tampons) as the tampons will absorb the cream and reduce its effectiveness.
- Anti-itch creams don't help treat a yeast infection, but they can alleviate the itching, irritation, and general discomfort associated with a yeast infection. It is recommended to use anti-itch cream with antifungal, vaginal suppositories or oral tablets.
- Use only anti-itch cream specifically designed for the vaginal area. Other anti-itch creams can upset the balance of vaginal pH and worsen yeast infections.
Method 2 of 4: Changing your diet
Avoid certain foods and drinks. Dieting will help reduce the presence of bacteria that cause yeast infections. Experts recommend avoiding alcohol, sweets and beverages containing artificial sweeteners, refined carbohydrates, and foods high in yeast.
- Certain dairy products, including cheese and butter, can contribute to yeast infections. However, more research is still needed.
- If your blood sugar is low or you are unsure of what foods to avoid, you should consult with your doctor or a registered dietitian to develop the right diet.
Take vitamin C supplements. Vitamin C, or ascorbic acid, is a natural antioxidant important for supporting immune function. Vitamin C can be taken in supplement form with the recommended dosage of 500-1000 mg, divided into 2-3 times daily. In addition, you can include foods rich in vitamin C in your daily diet. Consult your doctor before taking vitamin C supplements if you are taking immunosuppressants or have a weak immune system. On the other hand, natural sources of vitamin C have no side effects and you can consider:
- Red or green bell peppers
- Citrus fruits such as oranges, grapefruit, lemons or non-concentrated citrus fruit juices
- Spinach (spinach), broccoli, and Brussels sprouts
- Strawberries and raspberry
- Tomato
- Mango, papaya and cantaloupe
Fortified with vitamin E. Vitamin E is an antioxidant that boosts the immune system and is effective in case of a yeast infection caused by a weak immune system. The recommended adult dose is 15 mg per day. Foods rich in vitamin E include:
- Vegetable oil
- Almond
- Lost
- Hazelnut
- Sunflower seed
- Spinach
- Broccoli
Eat foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Essential fatty acids can help reduce inflammation and burning sensation in people with a yeast infection. Experts recommend a combination of omega-6 (found in primrose extract) and omega-3 (found in fish oil or flaxseed oil). Add 2 teaspoons of oil per day or 1000-15000 mg, divided into 2 doses per day. Foods rich in omega-3 include:
- Egg
- Pinto beans, soybeans and black-eyed beans
- Tofu
- Wild salmon and sardines
- Walnuts, almonds, chia seeds and flax seeds
- Rapeseed oil, fish oil and flaxseed oil
Take a probiotic supplement. Probiotics are probiotics commonly found in the inner lining of the intestines and stomach, and function as an antifungal factor that helps control Candida bacteria, while also boosting the immune system. Some studies suggest that yogurt contains live probiotic yeast that may help prevent yeast infections. Some ways to boost probiotics include:
- Try taking probiotic supplements at a rate of 1-10 billion Bifidobacterium, up to 2 times per day.
- Check with your doctor before taking probiotics if you are taking immunosuppressive drugs or taking antibiotics.
- Eat 250 ml of plain, sugar-free yogurt every day to help reduce yeast infections.
- You can buy a probiotic vaginal suppository to help restore the balance of bacteria in the vagina.
Method 3 of 4: Use home remedies
Eat a lot of garlic. Garlic is famous for its antibacterial and antifungal properties because it contains the natural ingredient allicin. You should eat 1 raw garlic clove per day or add 2-3 crushed garlic cloves to your dish. For dietary supplements, you can supplement the equivalent of 1 clove of garlic per day or 1 tablet with 4000-5000 mg of allicin.
- Garlic can interact with a number of medications, including HIV medications. Garlic also increases the risk of bleeding in people with weak immune systems, people taking blood thinners, people who have had trauma or surgery. You should consult your doctor before using garlic or garlic supplements.
Take Echinacea chamomile extract. Echinacea is an antiviral, antioxidant herb that boosts immune function, reduces inflammation, and restores hormone balance. Echinacea is also very useful when used in combination with Econazole - an antifungal agent used in the treatment of yeast infections, in reducing the incidence of recurrent yeast infections. Research shows that supplementing with 2-9 ml of Echinacea chamomile extract or 1 cup of Echinacea tea per day can help control yeast infections caused by Candida bacteria.
- To brew the tea, simply soak 1-2 g of dried Echinacea root or extract in warm water for about 5 minutes. Strain and drink.
- Echinacea can interact with many medications, so it's important to consult your doctor before taking it.
- Some people will experience side effects such as abdominal pain, nausea, dizziness, and dry eyes. Do not take Echinacea on an empty stomach.
- Do not take Echinacea in case of multiple sclerosis, tuberculosis, connective tissue disorder, leukemia, diabetes, HIV / AIDS, autoimmune disease or liver disorder.
Try a tea tree oil bath. Tea tree oil is famous for its antiviral and antifungal properties. Research suggests that tea tree oil may be effective in treating vaginal yeast infections. However, do not apply essential oils directly to the vagina. Instead, try taking a tea tree oil bath.
- Put 10-15 drops of essential oil in the bath and soak for about 15 minutes. Repeat this process 2-3 times per week. This will help control a yeast infection and prevent it from coming back.
Method 4 of 4: Prevent yeast infections
Clean personal hygiene. You can prevent recurrent yeast infections and future yeast infections by keeping the vaginal area dry, clean. Some hygiene tips to help you avoid yeast infections: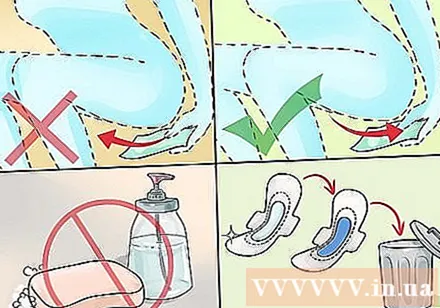
- Do not use soap in the vaginal area. Only wash the vagina with warm water.
- Always clean from the front to the next after using the toilet.
- Avoid using products such as perfumes, feminine sprays, and vaginal powders.
- Change tampons, menstrual cups and cotton swabs every 2 to 4 hours.
Wear comfortable clothes. Avoid wearing tight clothing, such as tights, leggings or tights. These clothing can irritate and worsen symptoms of a yeast infection. Also, avoid wearing wet or exercise clothes for long periods of time. Wash wet, sweaty clothes after each use.
- Wear cotton underwear or stockings instead of silk or nylon, as silk and nylon can increase vaginal sweating and cause irritation.
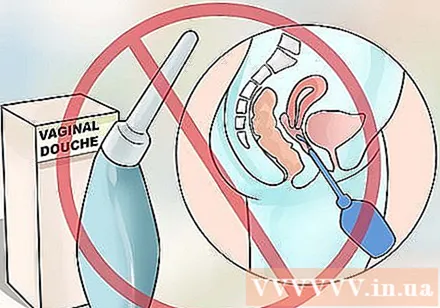
Avoid douching. Many people think that douching can help clean the vagina. However, douching will only worsen the yeast infection. Douching can alter the natural pH balance in the vagina, irritating and damaging the skin and mucous membranes (whether you use herbal or medicinal products). Douching also increases the risk of vaginal infections, pelvic inflammatory disease and complications during pregnancy. advertisement