Author:
Lewis Jackson
Date Of Creation:
8 May 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
Gluten intolerance (linked to Celiac disease) is an immune response to a protein in wheat and other grains. The disease can present many symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, fatigue, rashes and joint pain after eating gluten-containing foods. Many patients find that removing Gluten from their diet improves their symptoms. There is no cure for gluten intolerance, but by avoiding gluten-containing foods and receiving proper diagnosis and treatment, you can reduce discomfort and other illnesses caused by intolerance. Gluten.
Steps
Part 1 of 2: Getting medical treatment
Go to the doctor. If you experience discomfort after eating gluten-containing foods, you should see your doctor. Your doctor will test to see if you have Celiac disease or another condition that makes your condition worse. Then, your doctor will recommend treatment to help manage your symptoms. Remember, Gluten intolerance cannot be cured, it can only be controlled.
- Your doctor may perform tests such as blood tests, endoscopy, and capsule endoscopy to determine if you have Celiac disease or gluten intolerance.
- Your doctor may also test to identify other health problems related to Celiac disease or gluten intolerance such as: anxiety, depression, migraine, thyroid disease, bowel cancer, osteoporosis, diabetes, herpes dermatitis, neuropathy, and arthritis.

Confirm diagnosis and treatment. After going through the tests, you will get a diagnosis from your doctor. From there, your doctor will recommend the best treatment for you.- Your doctor will tell you if you have Celiac disease or Gluten intolerance. If so, avoiding Gluten is the best treatment.
- Your doctor may prescribe other medications or vitamin supplements to help relieve other symptoms of Celiac disease and Gluten intolerance.
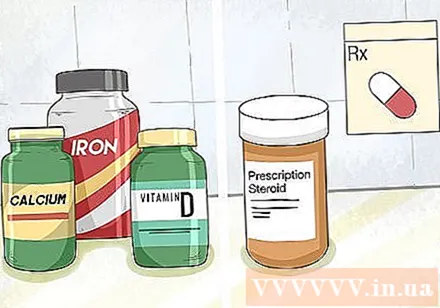
Take supplements and medications. Many people with Gluten intolerance experience nutritional deficiencies, enteritis or even blisters on the skin. Taking nutritional supplements and medications can help control the external symptoms of Gluten intolerance and Celiac disease.- A gluten-free diet is the key to controlling Gluten intolerance.
- You will likely need calcium, folate, iron, vitamin B12, vitamin D, vitamin K, and zinc.
- Your doctor may prescribe steroid medicine to control bowel inflammation.
- If you have itchy dermatitis and blisters on the rash, your doctor may prescribe Dapsone to reduce the rash.

See a registered dietitian. If you are having trouble following a Gluten-free diet, you should consider seeing a registered dietitian. An expert will help you identify gluten-containing foods, make better food choices and help you plan Gluten-free meals.- A gluten intolerance dietitian can provide you with complete information about Gluteln-free foods, potential gluten-free sources, and help you find alternatives when eating out.
- You can ask your doctor for referrals to a reputable dietitian, look for information online or join support groups of people with gluten intolerance.
Part 2 of 2: Eliminate Gluten from the Diet
Remove gluten-containing foods from the kitchen. Gluten-based foods promote gluten intolerance, so you need to remove these foods from your diet. This way, you can reduce your symptoms and avoid accidentally eating foods that may make your stomach more upset. Gluten-prone foods include:
- Barley, including malt and vinegar
- Rye
- Rye, a cross between barley and rye
- Wheat and wheat flour such as semolina, flour, durum, Graham, Kamut and flours.
Identify gluten-containing foods. Since wheat and flour are abundant in the diet, you will need to identify foods that contain wheat and / or gluten. It is also possible that you will need to avoid consuming some of your favorite foods to aid in the treatment of gluten intolerance. Some of the most common foods containing Gluten include:
- Beer
- Bread
- Cake
- Cereals
- Sponge cake (from flour)
- Crouton crispy bread
- Fried foods
- Gravy, sauces, salad dressings and toppings
- Fake meat and seafood meat
- The pasta
- Convenience food
- Soy
- Food and snacks with additives
- Soup
- If you are unsure, do not keep these. You can go online to look up a list of gluten-containing foods to eliminate from your diet.
Buy gluten-free foods. With gluten intolerance and a lot of foods to be eliminated from your diet, you can replenish and enjoy gluten-free alternatives or foods. Not buying gluten-containing foods or products will help you avoid accidentally cooking the food that causes your symptoms to flare.
- If a person you live with can still eat gluten-containing foods, you should keep your food separate to avoid confusion.
- You can comfortably eat the following natural gluten-free foods: beans, nuts, fresh eggs, fresh meats, fish, poultry, vegetables, and most dairy products.
- Most grocery stores sell a variety of gluten-free foods, but they may be foods that you need to get rid of. Therefore, you should ask your staff if there is a dedicated “Gluten-Free” food stand in the store that suits your needs.
Most grocery stores sell a variety of gluten-free foods, but they may be foods that you need to get rid of. Therefore, you should ask your staff if there is a dedicated “Gluten-Free” food stand in the store that suits your needs.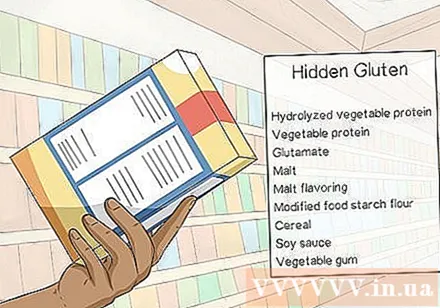
- Some of the natural gluten-free foods you can add to your diet include: amaranth seeds, arrowroot, buckwheat, corn and cornstarch, flaxseed, gluten-free flour, millet, quinoa. , rice, soybeans, flour and teff seeds.
- Words that often appear on gluten-containing food labels include: hydrolyzed vegetable protein, vegetable protein, monosodium glutamate, malt flavoring, refined starch, flour, cereal, soy sauce and substance. solidify.
- Avoid consuming processed foods or foods that are not specifically labeled “Gluten-free”, including seasonings.
- Check what you eat out when you eat out, eat at someone else's house (someone who doesn't share the same eating habits) or try a new food.
Make the menu as often as possible. Self-preparation of food is the safest way to ensure gluten is not consumed. Planning meals helps you avoid gluten-containing foods and prevent abdominal discomfort as well as ensure you get enough nutrients.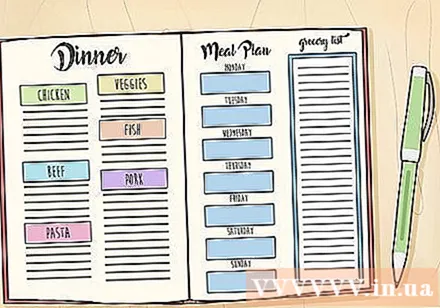
- Make a menu for each meal of the week. Pay special attention to meals you don't eat at home, such as lunch or dinner. In that case, you should pack your carry-on food. Or if you have to eat out, you need to read the menu carefully to order Gluten-free.
- For example, earlier in the week you can eat cheese with veggie omelets, a side dish of gluten-free toast with butter and fruit. In the afternoon, you can eat salmon salad, olive oil sauce and vinegar. In the evening, you can eat beef with broccoli and baked potatoes.
Order carefully when eating at the restaurant. It can be difficult to order Gluten-free at restaurants. Many restaurants use foods that contain potential gluten sources and increase the risk of food exposure to gluten-contaminated foods. Therefore, you should carefully ask about the menu and avoid ordering from gluten-containing foods to avoid accidentally consuming even a small amount of Gluten.
- Many restaurants have gluten-free foods on their menus. If not, you should ask the staff or chef about foods that may contain potential gluten on the menu.
- You can look up information online or ask acquaintances about restaurants that often offer gluten-free foods.
- Some foods to avoid when eating out of restaurants: Crouton bread; Wonton; fried onions and crisp noodles with salad; soups with wheat or barley; the dish is marinated with soy sauce or Teriyaki sauce; breaded food before frying; oil used for frying many breaded dishes; mashed potato; bread.
- Some restaurant dishes suitable for people with Gluten intolerance include steamed vegetables, roast meats, fruit desserts or ice cream.
- Always be prepared in case the restaurant is free of "Gluten Free" dishes.
Avoid Gluten cross contamination. Gluten exposure from gluten-contaminated foods is very common. Avoiding these situations will help you reduce symptoms and better treat the disease.
- When eating at a restaurant, you should inquire whether gluten-free and gluten-free foods are prepared on the same surface. If gluten is particularly sensitive, it is best to avoid these restaurants.
- Gluten cross-contamination can also occur when eaten at home. Therefore, you should use cutting boards separately and prepare food in different areas to avoid cross-contamination.
- Also, avoid sharing appliances like toasters, toasters, or pans.
Advice
- Gluten intolerance has symptoms similar to that of gluten sensitivity. However, when gluten is sensitive, the immune system will not produce antibodies and cause no intestinal damage.
Warning
- See a doctor right away if symptoms persist or worsen even if Gluten is eliminated from your diet.