Author:
Laura McKinney
Date Of Creation:
4 August 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
Fever, flu, sinusitis, stress and stress can all trigger headaches, causing pain in the head area. Migraine is another pain. Doctors describe migraines as recurrent headaches with symptoms such as dizziness, visual disturbances, tingling in the face or limbs, nausea, sensitivity to light, sounds and smells. . Migraine attacks can make a person debilitated and unable to go to school / work. In fact, in the US, nearly a quarter of all households will experience a migraine. Learning how to cope can help you know what to do with a migraine.
Steps
Method 1 of 4: Reduce the pain and severity of the pain
Prevent migraines from getting worse. You need to take immediate action to prevent your migraine from getting worse. As soon as the pain strikes, there are many things you can do to reduce the severity and cope with the headache.
- Find a quiet place and engage in challenging activities as much as possible.
- Turn off the lights in the room.
- Lie down or recline in a chair if possible.
- Relax in a dark, quiet room and try to sleep if you can.
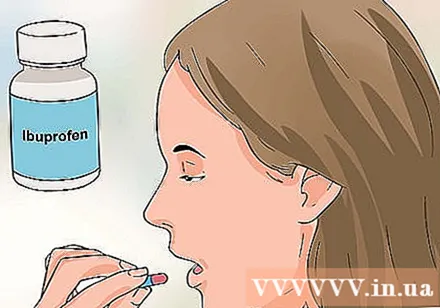
Take an over-the-counter pain reliever. Acetaminophen or over-the-counter ibuprofen can help relieve migraines in some cases. Be aware, however, that these drugs can cause liver and kidney damage if taken for a long time.- The oral doses of ibuprofen and acetaminophen are specified on the bottle. Do not exceed the recommended dose on the medicine bottle. Talk to your doctor to make sure there are no interactions with other medications you are taking or with any underlying medical condition.
- Overdose with an over-the-counter pain reliever can be life-threatening, causing significant liver or kidney damage. If you do overdose, you should seek emergency medical attention immediately.

Use a hot or cold compress. Some migraines may react with hot or cold compresses. You can try a hot or cold compress on the head where the pain is felt and see if the pain subsides. First, place a clean towel under running hot or cold running water to wet it. Then, squeeze out some of the water, then place a towel on your head.- Use a hot or cold compress for up to 15 minutes.
Method 2 of 4: Use medicine and herbs

Talk to your doctor about prescription medications that help prevent migraines. Your doctor may prescribe preventive medications to reduce the frequency and severity of migraines. There are many different types of preventive medicine available to take every day and include:- Beta blockers, often used to treat heart disease. Although it is not known why the drug works, doctors believe it helps prevent blood vessels from constricting and dilating in the brain. Beta blockers include Atenolol (Tenormin), Metoprolol (Lopressor), Propranolol (Inderal).
- Calcium channel blockers are another heart disease medication that is used to reduce the frequency and duration of headaches. Calcium channel blockers include Verapamil (Calan) or Diltiazem (Cardizem).
- Tricyclic antidepressants (Tricyclic) help prevent other headaches and migraines. Medicines include Amitriptyline (Elavil), Nortriptyline (Pamelor), Doxepin (Sinequan), Imipramine (Tofranil).
- Although not sure why, doctors have found that some anticonvulsants also help prevent migraines. Some anticonvulsants that help prevent migraines effectively include Divalproex sodium (Depakote), Gabapentin (Neurontin), Topiramate (Topamax).
- Botox injections are also approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat migraines. It helps in some cases and is injected several times into the forehead, temples, back of the neck and shoulders every 3 months.
Talk to your doctor about acute medications or abortion pills. Acute medications or abortion pills are designed to prevent headaches. The drug is taken orally when the first symptoms appear. Different drugs are used to treat migraine-related pain or symptoms.
- Triptans are the first class of drugs prescribed to relieve pain, nausea, sensitivity to light, sound, and scent. Triptans include Almotriptan (Axert), Eletriptan (Relpax), Frovatriptan (Frova), Naratriptan (Amerge), Rizatriptan (Maxalt), Sumatriptan (Imitrex), Zolmitriptan (Zomig).
- Ergot drugs work by constricting blood vessels, but causing more side effects than the Triptans. This is the second group of drugs used to relieve pain and related symptoms (symptoms can be worse than migraine). Ergot drugs include Dihydroergotamine (Migranal) and Ergotamine (Ergomar).
- Isometheptene, Dichloralphenazone and Acetaminophen called Midrin, combine pain relievers, sedatives, and drugs that help constrict blood vessels, thereby helping to relieve headache pain.
- Narcotic drugs, such as codeine, are intended for people who cannot take Triptans or Ergots due to side effects, allergic reactions, or reactions to other medications. Keep in mind that the narcotic group of medications can cause drug dependence and relapse headaches.
Try using the heat button (needle button). You might consider using calming buttons daily to prevent migraines or reduce the severity of the pain. On the other hand, the button has not been shown to reduce the severity or frequency of headaches. However, there is some evidence that the calming button works, so you can try it.
- Freeze-dried capsules are recommended, as calming chamomile tea is often bitter and can irritate the mucous membranes in the mouth.
- You should talk to your doctor and pharmacist before you want to use heat buttons daily. Cucumber can interact with other medications you are taking.
- Pregnant women, women trying to give birth, women who are breast-feeding, and who are taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin or ibuprofen should not take heat buttons.
- If you do not want to drink the calming button anymore, you should stop drinking slowly. Stopping the heat button too quickly can cause a migraine to return, with more symptoms such as increased nausea and vomiting.
Consider using spines to reduce migraine severity and frequency. The effectiveness of thorns is based only on anecdotal evidence and has not been scientifically proven, but this herb can be taken regularly for up to 4 months. You should ask your doctor about the use of hemp extract and the dose appropriate for your weight, age and medical condition (if any).
- Keep in mind that people who are allergic to ragweed may be allergic to hair spines.
- Women who are pregnant, nursing or trying to become pregnant should not use hair spines.
Method 3 of 4: Lifestyle changes
Get a good rest. Hormone changes are one of the triggers of migraine triggers. Your body produces and secretes hormones like melatonin and cortisol based on the number of hours you sleep and when you go to bed. This hormone change, coupled with lack of sleep, causes migraines.
Limit alcohol and caffeine intake. Alcohol and caffeine affect the nervous system. Although the exact cause of a migraine has not been established, most doctors believe that a change in the nervous system can trigger migraines.
- Small amounts of caffeine can increase the effectiveness of Acetaminophen if taken when the headache has just started. Usually, drinking a cup of coffee with Acetaminophen is enough. Conversely, drinking too much (more than 2 cups) can cause headaches to return.
Stress management. Stress can stimulate the secretion of hormones that affect the nervous system, thereby provoking migraine attacks. Each stress reduction method will work differently from person to person, so you need to find the method that works best for you.
- Prioritize what work should be done first and gradually address each challenge. Don't get overwhelmed by tasks that have to be completed.
- Practice deep breathing. Deep breathing can help lower your heart rate and reduce stress.Positive, positive self-talk can also help reduce stress.
- Exercise regularly. Exercise can help reduce stress, improve your mood and help you feel more confident. You can walk for 15 minutes after each meal, go swimming, go for a slow jog at night after returning from work, or cycle with friends.
- Get enough sleep. Lack of sleep not only affects hormone levels but also causes stress. According to research conducted at the University of Pennsylvania (USA), researchers found that lack of sleep (even a few hours) also increases feelings of sadness, stress, anger and exhaustion. Therefore, it is best to get 7-8 hours of sleep each night.
Quit smoking. The Michigan Institute of Neurology and Headache (USA) recommends quitting smoking to reduce the frequency and severity of migraines. Cigarettes trigger migraines in three different ways. Smoking:
- Increases the concentration of carbon monoxide in the blood and brain
- Reduces the concentration of oxygen in the blood and brain
- Toxic to the brain and changes the metabolism of the liver, reducing the effectiveness of drugs that prevent migraines.
Take a daily supplement to prevent migraines. You should talk to your doctor before taking any daily supplement.
- Magnesium helps with migraine relief in women during menstruation or in those with abnormally low magnesium levels. Side effects include diarrhea and lower blood pressure.
- 5-HTP is an amino acid that converts to serotonin in the body. Certain migraine prescription medications can affect serotonin levels in your body. Do not use 5-HTP supplements if you are taking antidepressants or natural herbal supplements such as St. John's. John's Wort, pregnant, nursing or trying to become pregnant.
- Vitamin B2 or riboflavin may help reduce the frequency and severity of migraines. However, you should not take vitamin B2 supplements if you are taking Tricyclic antidepressants or anticholinergics.
Method 4 of 4: Get medical help
Know when to seek medical attention. A migraine is actually not caused by a tumor or other structural changes in the brain. However, only a doctor can determine if the headache is caused by a migraine or from another cause. Seek emergency medical attention if you:
- Get confused or confuse what people are saying
- Feeling like fainting
- Fever higher than 39 ° C
- Feeling numb, weak, or paralyzed
- A stiff neck
- Difficulty seeing, speaking or walking
- Loss of consciousness
Talk to your doctor about recurrent migraines. In some cases, the migraine can be recurring and severe. You should see your doctor if you have a migraine:
- Show up more often than before
- It's more serious than usual
- Do not get better with prescription medications or medications prescribed by your doctor
- Make it difficult for you to work, sleep, or participate in social activities.
Keep a migraine diary to identify triggers. Record each meal, your period (for women), chemical exposure (room sprays, home cleaning products, ...), caffeine consumption, sleep habits, and Change Weather. Use a journal to help your doctor determine the cause of your migraine. Once you've identified the cause, avoid it as much as you can. Some of the triggers that trigger migraines include:
- Stress
- Hormonal changes (during a woman's menstrual cycle)
- Skipping meals
- Consume too much caffeine
- Certain foods like cheese, pizza, chocolates, ice cream, fried foods, sausages, yogurts, processed foods, Aspartame, and MSG
- Drinks containing alcohol, especially red wine
- Sudden changes in sleep habits
- Smoke
- Change Weather
- Caffeine detox stage
- Exercise too much
- Noise and glare
- Fragrance or perfume
Advice
- Migraines are very common and often debilitating. To reduce migraine frequency, keep a diary to keep track of changes or substances that may trigger the migraine.
- Take preventive measures like limiting your exposure to triggers, getting enough sleep, reducing your stress level, to reduce migraine frequency.
- If home remedies don't work, see your doctor for a prescription for migraine prevention and treatment medications.