Author:
Tamara Smith
Date Of Creation:
28 January 2021
Update Date:
29 June 2024

Content
- To step
- Part 1 of 3: Treating severe back pain yourself
- Part 2 of 3: Alternative treatments
- Part 3 of 3: Getting medical treatment
- Tips
- Warnings
Back pain can be debilitating and it can take over your entire life. It is more difficult for you to move, sleep and even think. There can be many causes of back pain, but keep in mind that the severity of the pain is not always related to how severe the condition is. In other words, a minor problem (such as an irritated nerve) can be very painful, while a life-threatening condition (such as a tumor) sometimes causes little pain. Try some of the home remedies below, but keep an eye out for the signs or symptoms that would require an appointment with your doctor.
To step
Part 1 of 3: Treating severe back pain yourself
 Wait a minute. Your spine is a complex collection of joints, nerves, muscles, blood vessels and connective tissue. There are many parts that can hurt if you move your back incorrectly or if your back is hit. Severe back pain can come on suddenly, but it can sometimes pass quickly (without any treatment) because the body has a tremendous ability to heal itself. That's why it's good to be patient for a few hours, avoid strenuous activities, and stay positive if you suddenly have back pain.
Wait a minute. Your spine is a complex collection of joints, nerves, muscles, blood vessels and connective tissue. There are many parts that can hurt if you move your back incorrectly or if your back is hit. Severe back pain can come on suddenly, but it can sometimes pass quickly (without any treatment) because the body has a tremendous ability to heal itself. That's why it's good to be patient for a few hours, avoid strenuous activities, and stay positive if you suddenly have back pain. - Signs and symptoms that require immediate medical attention include: muscle weakness and / or loss of sensation in your arms or legs, inability to control urination or defecation, high fever or sudden unexplained weight loss.
- It is not good to just lie in bed with most types of back pain, because a little exercise (such as a short walk) is actually good to stimulate your blood flow so that you heal faster. If you are in a lot of pain, you can wait two to three days before resuming your daily activities.
- If your back pain is related to exercise, you may be exercising too aggressively or doing it wrong - in which case, consult a personal trainer.
- If you think the back pain is related to your job, talk to your boss about alternative activities, or adjust your desk - a better desk chair or a footrest can help.
 Put something cold on your back. With acute trauma to the musculoskeletal system, including your back, it is good to apply a cold compress within 24 to 48 hours. Cold therapy can reduce inflammation and numb the pain in the most painful part of your back. Apply a cold compress to your back every 10 to 15 minutes, reducing as the pain and swelling subside.
Put something cold on your back. With acute trauma to the musculoskeletal system, including your back, it is good to apply a cold compress within 24 to 48 hours. Cold therapy can reduce inflammation and numb the pain in the most painful part of your back. Apply a cold compress to your back every 10 to 15 minutes, reducing as the pain and swelling subside. - You can reduce inflammation by holding a cold compress with an elastic bandage against the back.
- Always wrap an ice pack or ice cubes in a thin towel so that your skin is not damaged by the cold.
- If you don't have ice or ice packs, you can use a bag of frozen peas.
- Ice is not suitable for chronic back pain - moist heat actually provides more relief.
 Take a warm bath. Lying down in a warm bath with Epsom salts will reduce pain and swelling, especially if the pain is caused by overexertion or muscle cramps. The magnesium in the salt helps the muscles to relax. If there is inflammation of the joints, tendons or nerves in the back, a warm bath or compress is not a good idea.
Take a warm bath. Lying down in a warm bath with Epsom salts will reduce pain and swelling, especially if the pain is caused by overexertion or muscle cramps. The magnesium in the salt helps the muscles to relax. If there is inflammation of the joints, tendons or nerves in the back, a warm bath or compress is not a good idea. - Do not make the bath too hot (or you will burn yourself) and do not lie in it for more than 30 minutes, as the salt will dry out your body.
- You can also place a warm compress (for example a heating pad from the microwave, which often contains essential oil such as lavender) on your aching back to relax.
 Consider taking a pain reliever. An anti-inflammatory painkiller (NSAID) from the drug store such as ibuprofen, naproxen, or aspirin can be a short-term solution if you have a lot of back pain. Remember that these drugs can be bad for your stomach, kidneys and liver, so don't take them for more than 2 weeks in a row.
Consider taking a pain reliever. An anti-inflammatory painkiller (NSAID) from the drug store such as ibuprofen, naproxen, or aspirin can be a short-term solution if you have a lot of back pain. Remember that these drugs can be bad for your stomach, kidneys and liver, so don't take them for more than 2 weeks in a row. - You can also take another pain reliever such as acetaminophen if you have back pain, but don't take it with an anti-inflammatory pain reliever.
- Another option is an analgesic cream or gel that you can put directly on your back, especially if the pain is related to your muscles. Some products contain capsaicin and menthol, natural ingredients that distract the brain from pain by making the skin tingle.
 Use a massage roller. Rolling over a piece of firm foam is a good way to massage the spine and relieve some of the pain, especially if it's in the center of the back. Massage rollers are often used in physiotherapy, yoga and pilates.
Use a massage roller. Rolling over a piece of firm foam is a good way to massage the spine and relieve some of the pain, especially if it's in the center of the back. Massage rollers are often used in physiotherapy, yoga and pilates. - Buy a massage roller from a sporting goods store. They are not expensive and last a very long time.
- Place the massage roller on the floor, perpendicular to how you lie down. Lie on your back so that the massage roller is under your shoulders and roll back and forth. Repeat as often as you like. However, it can hurt your muscles a bit at first.
 Use a tennis ball. Lie on your back and tuck a tennis ball between your shoulder blades. Roll back and forth until you find a sore spot. Lie down for 30 seconds or until you feel the pain subside. Then move on to another painful area.
Use a tennis ball. Lie on your back and tuck a tennis ball between your shoulder blades. Roll back and forth until you find a sore spot. Lie down for 30 seconds or until you feel the pain subside. Then move on to another painful area. - Repeat this every day until the pain is gone. You can use this as a precaution because these trigger points, also known as muscle knots, are often caused by poor posture or overuse.
 Do exercises. While the pain may make it more difficult to move or exercise, stretching and strength exercises can reduce back pain. Before starting these exercises, it is good to consult your doctor or physiotherapist to find out if they are suitable for your specific condition.
Do exercises. While the pain may make it more difficult to move or exercise, stretching and strength exercises can reduce back pain. Before starting these exercises, it is good to consult your doctor or physiotherapist to find out if they are suitable for your specific condition. - Exercises such as squats, plank exercises, or simple stretches can relieve back pain. In this article you will find more ideas for these types of exercises: Treating upper back pain.
 Assess your sleeping environment. A mattress that is too soft or a pillow that is too thick can cause back pain. Do not sleep on your stomach, as this can rotate your neck and head, which can aggravate back pain and compress the lower vertebrae too much. The best sleeping position if you have back pain is on your side or on your back with a pillow under your knees, as this will relieve the pressure on your lower back.
Assess your sleeping environment. A mattress that is too soft or a pillow that is too thick can cause back pain. Do not sleep on your stomach, as this can rotate your neck and head, which can aggravate back pain and compress the lower vertebrae too much. The best sleeping position if you have back pain is on your side or on your back with a pillow under your knees, as this will relieve the pressure on your lower back. - While some people are comfortable on a waterbed, most benefit from a firm, orthopedic mattress.
- An innerspring mattress lasts about eight to ten years, depending on your weight or that of your partner.
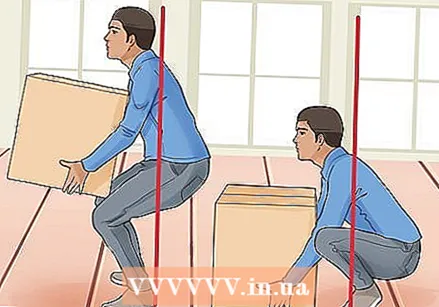 Make sure you lift correctly. Severe back pain is often caused or aggravated by poor lifting posture. If you need to lift something, make sure it isn't too heavy to carry alone (and get help if it is). Keep the load close to your body, and lower your legs instead of bending at the waist.
Make sure you lift correctly. Severe back pain is often caused or aggravated by poor lifting posture. If you need to lift something, make sure it isn't too heavy to carry alone (and get help if it is). Keep the load close to your body, and lower your legs instead of bending at the waist. - There is still some disagreement about the best way to lift a heavy load, but if you want to lift without straining your back, squat, bend the hips and knees while keeping the back straight, and then rise from this position. Then you lift from your legs and not from your back.
Part 2 of 3: Alternative treatments
 Make an appointment with a chiropractor or osteopath. Chiropractors and osteopaths are experts in the spine, and they focus on establishing proper movement and functioning of the small joints that connect the vertebrae. Manual therapy, also called squatting, can be used to straighten joints that are slightly crooked.
Make an appointment with a chiropractor or osteopath. Chiropractors and osteopaths are experts in the spine, and they focus on establishing proper movement and functioning of the small joints that connect the vertebrae. Manual therapy, also called squatting, can be used to straighten joints that are slightly crooked. - Although the back pain is sometimes completely over after a treatment, it usually takes 3-5 times before you really get results. Your health insurance only reimburses a chiropractor or osteopath if you have an additional package.
- Chiropractors and osteopaths also apply a variety of therapies targeting muscle strain, which may be better for your problem.
- Traction or stretching the spine using an inversion table can also help. Some therapists have an inversion table in their treatment room that allows you to hang upside down in an easy and controlled manner, stretching your spine under gravity. You might even consider buying an inversion table for your home.
 Get a professional massage. If the muscle tissue tears, you get an overloaded muscle, which hurts or can become inflamed, and you can experience muscle cramps. A deep tissue or connective tissue massage can help with mild to moderate pain because it reduces cramps, fights inflammation, and promotes relaxation. Start with a 30-minute massage that targets your entire spine and your hips. Let the masseur massage you as hard as you can handle without making you feel pain.
Get a professional massage. If the muscle tissue tears, you get an overloaded muscle, which hurts or can become inflamed, and you can experience muscle cramps. A deep tissue or connective tissue massage can help with mild to moderate pain because it reduces cramps, fights inflammation, and promotes relaxation. Start with a 30-minute massage that targets your entire spine and your hips. Let the masseur massage you as hard as you can handle without making you feel pain. - Always drink plenty of water after a massage to flush out all inflammatory substances and lactic acid from your body. If you don't, you may get a headache or feel a little nauseous.
 Try acupuncture. In acupuncture, very thin needles are inserted into the skin at specific energy points to reduce pain and inflammation. Acupuncture can be very effective for back pain, especially if the symptoms have just started. Acupuncture is based on the principles of traditional Chinese medicine, and it works by stimulating the production of all kinds of substances such as endorphins and serotonin.
Try acupuncture. In acupuncture, very thin needles are inserted into the skin at specific energy points to reduce pain and inflammation. Acupuncture can be very effective for back pain, especially if the symptoms have just started. Acupuncture is based on the principles of traditional Chinese medicine, and it works by stimulating the production of all kinds of substances such as endorphins and serotonin. - There is varying scientific evidence that acupuncture can help relieve chronic back pain, but there are countless stories from people who find it very effective.
- Acupuncture points that can help reduce back pain are not all close to where you feel the pain - sometimes they are located in completely different parts of the body.
- Acupuncture is nowadays performed by all kinds of therapists, including general practitioners, chiropractors, naturopaths, physiotherapists and masseurs. Just make sure you pick someone who is certified.
- Dry needling is another form of therapy that uses acupuncture needles, but without the Chinese medical techniques. It can be very helpful for pain.
 Try relaxation techniques. Exercises for stress relief, such as meditation, tai chi, and breathing techniques, can be very helpful for musculoskeletal pain and help many people avoid injury. Yoga is good for relaxation and consists of different postures and breathing techniques.
Try relaxation techniques. Exercises for stress relief, such as meditation, tai chi, and breathing techniques, can be very helpful for musculoskeletal pain and help many people avoid injury. Yoga is good for relaxation and consists of different postures and breathing techniques. - Yoga poses can stretch and strengthen your muscles and improve your posture, although you will need to adjust some postures if your back hurts too much.
- Try mindful meditation. Mindful meditation is a form of pain relief that can be done anytime, anywhere. Research shows that three 20-minute meditation sessions over three days not only reduce pain, but also that its effect extends well beyond the 20 minutes spent in meditation.
Part 3 of 3: Getting medical treatment
 See your doctor. If home remedies or alternative therapies don't work, make an appointment with your doctor to rule out potentially serious spinal conditions, such as a hernia, a pinched nerve, an infection, osteoporosis, a fracture, osteoarthritis, or a tumor.
See your doctor. If home remedies or alternative therapies don't work, make an appointment with your doctor to rule out potentially serious spinal conditions, such as a hernia, a pinched nerve, an infection, osteoporosis, a fracture, osteoarthritis, or a tumor. - Your doctor can make the correct diagnosis with an X-ray, an MRI or CT scan and nerve conduction examination.
- The doctor may also perform blood tests to rule out osteoarthritis or spinal infection such as meningitis.
- Your doctor may refer you to a medical specialist such as an orthopedist, neurologist, or rheumatologist to find out what's wrong with your back.
 Get referred to a physiotherapist. If the back pain keeps coming back and is caused by weak muscles, poor posture, or a degenerative condition such as osteoarthritis, consider some form of rehabilitation. A physiotherapist can recommend all kinds of specific exercises for your back. Physiotherapy usually requires 2-3 treatments per week for 4 to 8 weeks to effectively manage chronic back pain.
Get referred to a physiotherapist. If the back pain keeps coming back and is caused by weak muscles, poor posture, or a degenerative condition such as osteoarthritis, consider some form of rehabilitation. A physiotherapist can recommend all kinds of specific exercises for your back. Physiotherapy usually requires 2-3 treatments per week for 4 to 8 weeks to effectively manage chronic back pain. - If needed, a physical therapist can also treat your back with electrotherapy, such as therapeutic ultrasound or transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS).
- Good exercises to strengthen your back include swimming, rowing, and back stretching, but make sure you are free of pain before starting.
 Consider an injection. An injection of steroids close to or into the muscles, tendons, or weights of the spine can quickly reduce pain and inflammation and return normal movement. Corticosteroids are hormones that have powerful anti-inflammatory properties. Most of the agents used for this are prednisone, dexamethasone and triamcinolone.
Consider an injection. An injection of steroids close to or into the muscles, tendons, or weights of the spine can quickly reduce pain and inflammation and return normal movement. Corticosteroids are hormones that have powerful anti-inflammatory properties. Most of the agents used for this are prednisone, dexamethasone and triamcinolone. - Possible side effects of corticosteroid injection include infections, bleeding, weakening of the tendons, local muscle atrophy and nerve damage.
- If corticosteroids aren't helping your back pain, surgery could be a last resort.
Tips
- To have good posture when standing, you must distribute your weight evenly on both feet and do not lock your knees. Tighten your abs and glutes so that your back is straight. Wear shoes with sufficient support if you have to stand a lot; relieves tired back muscles by alternately putting one foot on a small stool.
- Stop smoking, as this impedes blood flow and prevents your muscles and other tissues from getting enough oxygen and nutrients.
- If you've been sitting at a desk all day and think that's where the back pain is coming from, consider a new office chair.
- Stay fit, because back pain is especially common in people who are in poor physical condition.
- For a good sitting posture you need a sturdy chair, preferably with armrests. Keep your upper back straight and your shoulders relaxed. A small pad in your lower back can help maintain the natural curve of your spine. Place your feet flat on the floor or use a footrest if necessary.
Warnings
- See a doctor immediately if you have any of the following symptoms: sudden, worsening back pain, inability to control urination or poop, muscle weakness in your arms or legs, high fever, or sudden unexplained weight loss.