Content
- To step
- Method 1 of 3: Reset from the BIOS itself
- Method 2 of 3: Remove the CMOS battery
- Method 3 of 3: Reset the jumper
- Tips
- Warnings
This wikiHow shows you how to reset the BIOS (Basic Input / Output Settings) of your Windows computer to the factory settings. You can do this on most computers on the BIOS page. However, if you can no longer access your computer's BIOS, then you will need to reset the BIOS by opening your computer's case and removing the CMOS battery from the motherboard, or resetting the jumper switch on the motherboard if you have a desktop. In some cases, however, the warranty may be voided if you open the case of your computer. There is also a significant risk that opening your computer will permanently damage your computer. If you cannot access your computer's BIOS, it is best to take your computer to a computer store instead of trying to fix the problem yourself.
To step
Method 1 of 3: Reset from the BIOS itself
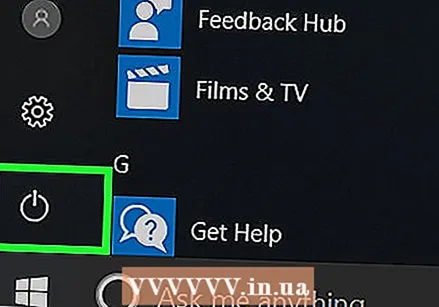 Restart your computer. Open the Start menu
Restart your computer. Open the Start menu  Wait until the first boot screen appears. When the start-up screen appears, you only have a very short time to press the setup button.
Wait until the first boot screen appears. When the start-up screen appears, you only have a very short time to press the setup button. - If you see a text like "Press [key] to enter setup" or similar appear briefly at the bottom of the screen, then you should restart the computer and try again.
Tip: it is best to start by pressing the setup key immediately when the computer restarts.
 Press several times Del or F2 to get into the BIOS. The screen may indicate that you need to press another key. If so, press the key in question.
Press several times Del or F2 to get into the BIOS. The screen may indicate that you need to press another key. If so, press the key in question. - If it is with Del or F2 doesn't work, try F8, F10, Esc or Tab ↹.
- Usually you use one of the function keys (F1-F12) to get into the BIOS. The function keys are located at the top of your keyboard, but you may need to use the FnSearch key and hold down while pressing the appropriate function key.
- You can check your computer's user manual or the computer brand website to find out which key to press to enter your computer's BIOS.
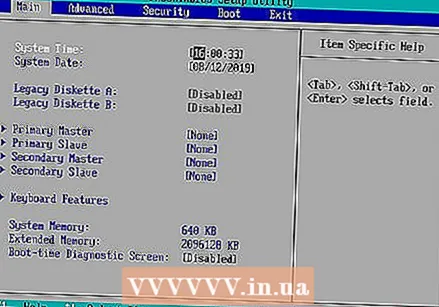 Wait for the BIOS to load. After you have pressed the right key at the right time, the BIOS will be loaded. This should only last a short time. When the BIOS is loaded, you will enter the BIOS settings menu.
Wait for the BIOS to load. After you have pressed the right key at the right time, the BIOS will be loaded. This should only last a short time. When the BIOS is loaded, you will enter the BIOS settings menu. - If you cannot get into your BIOS because you don't know the password or because the BIOS is corrupted, use one of the other methods in this article.
 Locate the option "Setup Defaults". Where you can find this option and its name varies by BIOS, but it is always in English and is usually labeled "Reset to Default", "Factory Default", "Setup Defaults" or something similar. You may be able to find the option in one of the tabs or near the navigation buttons.
Locate the option "Setup Defaults". Where you can find this option and its name varies by BIOS, but it is always in English and is usually labeled "Reset to Default", "Factory Default", "Setup Defaults" or something similar. You may be able to find the option in one of the tabs or near the navigation buttons. - If your BIOS does not have this option, use one of the other methods in this article.
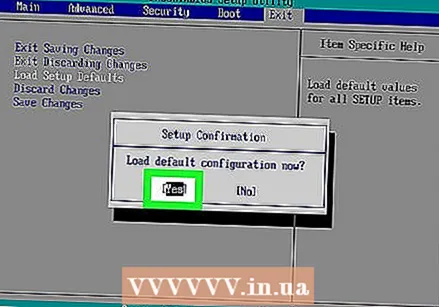 Select the option "Load Setup Defaults" and press ↵ Enter. Use the arrow keys to select the option. If you're on ↵ Enter your BIOS will usually be reset immediately.
Select the option "Load Setup Defaults" and press ↵ Enter. Use the arrow keys to select the option. If you're on ↵ Enter your BIOS will usually be reset immediately. - Again, the option may have a slightly different name.
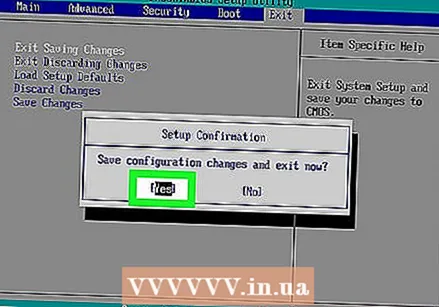 If necessary, save the changes and confirm your choice. You usually have to do this to exit the BIOS. Your computer will restart automatically. If you want to adjust the BIOS settings after the reset, you may have to restart your computer to get into the BIOS and change them.
If necessary, save the changes and confirm your choice. You usually have to do this to exit the BIOS. Your computer will restart automatically. If you want to adjust the BIOS settings after the reset, you may have to restart your computer to get into the BIOS and change them.
Method 2 of 3: Remove the CMOS battery
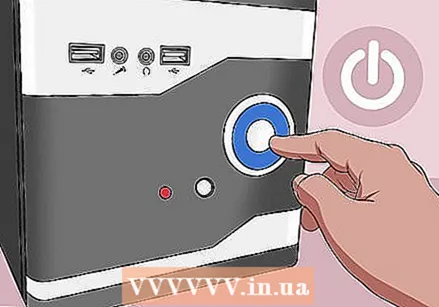 Shut down your computer. Use the Start menu to shut down your computer or press and hold the power button on your computer until the computer shuts down.
Shut down your computer. Use the Start menu to shut down your computer or press and hold the power button on your computer until the computer shuts down. - If you have a desktop, you can usually turn off the computer completely by flipping a switch on the back of the case or the power supply.
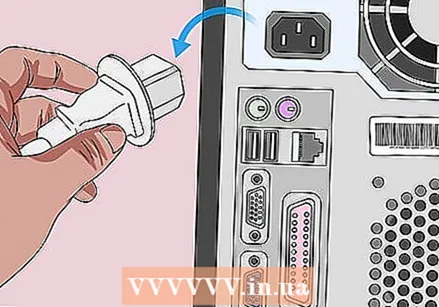 Unplug all power cables from the computer. Remove all power cables from your computer if you have a desktop and all charging cables if you have a laptop.
Unplug all power cables from the computer. Remove all power cables from your computer if you have a desktop and all charging cables if you have a laptop. 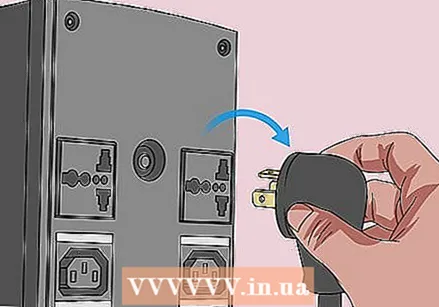 If necessary, remove the battery from your computer. If you're using a laptop (or a desktop with spare battery), remove the battery before continuing.
If necessary, remove the battery from your computer. If you're using a laptop (or a desktop with spare battery), remove the battery before continuing.  Discharge all static electricity before continuing. Before opening your computer, touch an unpainted metal surface to get rid of any static electricity. Touching the motherboard and other parts of your computer without properly grounding can permanently damage your computer.
Discharge all static electricity before continuing. Before opening your computer, touch an unpainted metal surface to get rid of any static electricity. Touching the motherboard and other parts of your computer without properly grounding can permanently damage your computer. 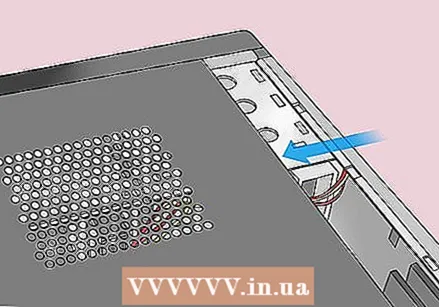 Open the casing of your computer. You should be able to access your computer's motherboard. Be very careful when working with the inside of your computer as sensitive components can be easily damaged by static electricity.
Open the casing of your computer. You should be able to access your computer's motherboard. Be very careful when working with the inside of your computer as sensitive components can be easily damaged by static electricity. - With many laptops you can access the CMOS battery via a cover at the bottom of your laptop that you can remove. If you don't see a cover, you probably need to take the laptop apart to access the battery.
 Remove the CMOS battery. The battery is usually located near the PCI slots, but it can be in a different location depending on the brand of motherboard you have. The battery may be hidden by expansion cards and cables. The CMOS battery is usually a regular 3 volt flat watch battery (CR2032).
Remove the CMOS battery. The battery is usually located near the PCI slots, but it can be in a different location depending on the brand of motherboard you have. The battery may be hidden by expansion cards and cables. The CMOS battery is usually a regular 3 volt flat watch battery (CR2032). Tip: you cannot always remove the CMOS battery. If you can't get the battery out, don't try to use force, reset the jumper on your motherboard instead.
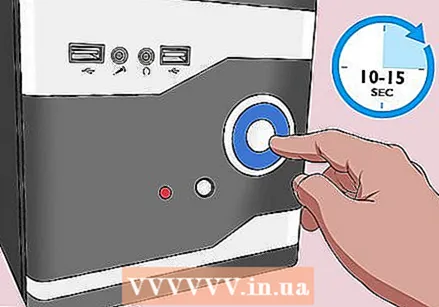 Press the power button on your computer. Press and hold the power button on your computer for 10-15 seconds to drain any remaining voltage from the capacitors. Discharging the voltage will reset the CMOS memory, which will reset your BIOS.
Press the power button on your computer. Press and hold the power button on your computer for 10-15 seconds to drain any remaining voltage from the capacitors. Discharging the voltage will reset the CMOS memory, which will reset your BIOS. 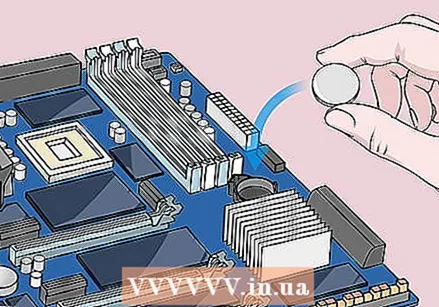 Replace the CMOS battery. Gently push the CMOS battery back into place. Make sure you put the battery back in the right way. The slightly smaller side should face down.
Replace the CMOS battery. Gently push the CMOS battery back into place. Make sure you put the battery back in the right way. The slightly smaller side should face down.  Reassemble your computer and seal the case. Do this carefully and don't forget to discharge yourself from time to time.
Reassemble your computer and seal the case. Do this carefully and don't forget to discharge yourself from time to time. 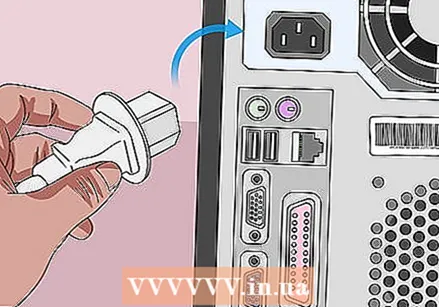 Reconnect your computer to its power source. If you have unplugged your computer and / or removed the battery, plug it back in and / or replace the battery. Don't forget to turn on the switch on the back of your computer case or power supply.
Reconnect your computer to its power source. If you have unplugged your computer and / or removed the battery, plug it back in and / or replace the battery. Don't forget to turn on the switch on the back of your computer case or power supply.  Turn your computer back on. Depending on your computer, you may need to reset some things in the BIOS, such as boot order and date and time.
Turn your computer back on. Depending on your computer, you may need to reset some things in the BIOS, such as boot order and date and time.
Method 3 of 3: Reset the jumper
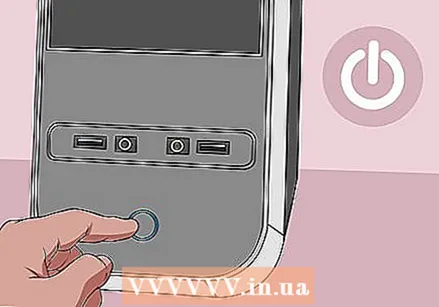 Shut down your computer. Use the Start menu to shut down your computer or press and hold the power button on your computer until the computer shuts down.
Shut down your computer. Use the Start menu to shut down your computer or press and hold the power button on your computer until the computer shuts down. - If you have a desktop, you can usually turn off the computer completely by flipping a switch on the back of the case or power supply.
 Unplug all power cables from the computer. Remove all power cables from your computer if you have a desktop and all charging cables if you have a laptop.
Unplug all power cables from the computer. Remove all power cables from your computer if you have a desktop and all charging cables if you have a laptop. 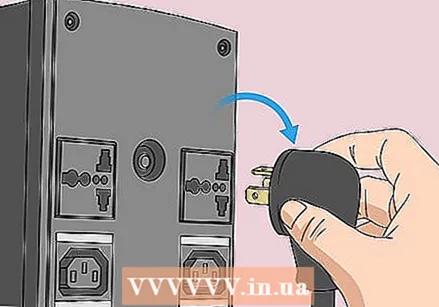 If necessary, remove the battery from your computer. If you're using a laptop (or a desktop with spare battery), remove the battery before continuing.
If necessary, remove the battery from your computer. If you're using a laptop (or a desktop with spare battery), remove the battery before continuing.  Discharge all static electricity before continuing. Before opening your computer, touch an unpainted metal surface to get rid of any static electricity. Touching the motherboard and other parts of your computer without properly grounding can permanently damage your computer.
Discharge all static electricity before continuing. Before opening your computer, touch an unpainted metal surface to get rid of any static electricity. Touching the motherboard and other parts of your computer without properly grounding can permanently damage your computer. 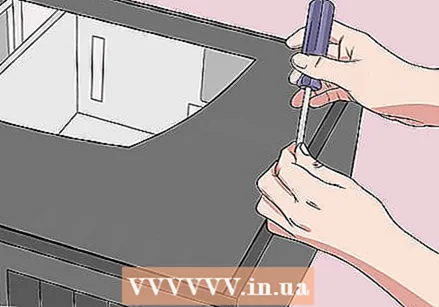 Open the casing of your computer. You must be able to access your computer's motherboard. Be very careful when working with the inside of your computer as sensitive components can be easily damaged by static electricity.
Open the casing of your computer. You must be able to access your computer's motherboard. Be very careful when working with the inside of your computer as sensitive components can be easily damaged by static electricity. 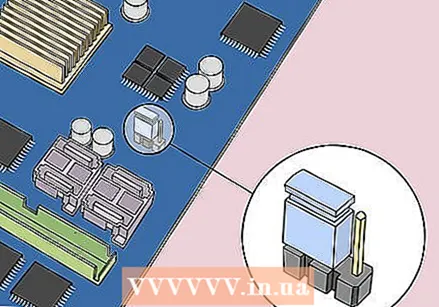 Find the CMOS jumper. Find the three-pin jumper on your motherboard that monitors the BIOS. You can usually find it near the CMOS battery. The jumper covers two of the three available pins.
Find the CMOS jumper. Find the three-pin jumper on your motherboard that monitors the BIOS. You can usually find it near the CMOS battery. The jumper covers two of the three available pins. Pay attention: the jumper can be labeled CLEAR, CLR, CLEAR CMOS, PSSWRD or a number of other names. Check the user manual of your motherboard to find the correct jumper.
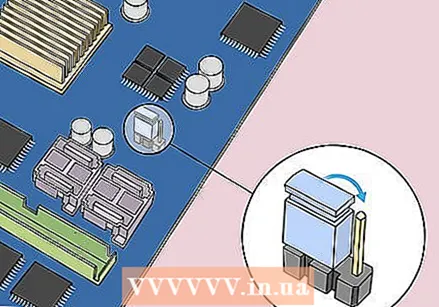 Move the jumper to the other two pins. For example, if the jumper covers the first and second pins, move it to the second and third pins. Make sure to pull the jumper straight up when you remove it so that the pins don't bend.
Move the jumper to the other two pins. For example, if the jumper covers the first and second pins, move it to the second and third pins. Make sure to pull the jumper straight up when you remove it so that the pins don't bend. 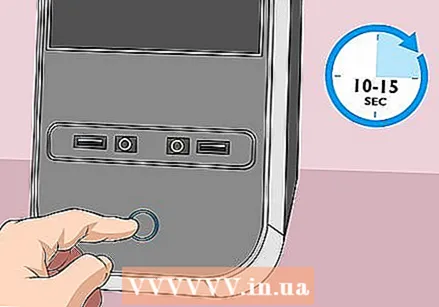 Press the power button on your computer. Press and hold the power button on your computer for 10-15 seconds to drain any remaining voltage from the capacitors. This will reset your BIOS.
Press the power button on your computer. Press and hold the power button on your computer for 10-15 seconds to drain any remaining voltage from the capacitors. This will reset your BIOS.  Move the jumper to its old position. Put the jumper back on the pins it covered first. This will allow you to enter the BIOS when you start your computer.
Move the jumper to its old position. Put the jumper back on the pins it covered first. This will allow you to enter the BIOS when you start your computer.  Reassemble your computer and seal the case. Do this carefully and don't forget to discharge yourself from time to time.
Reassemble your computer and seal the case. Do this carefully and don't forget to discharge yourself from time to time.  Reconnect your computer to its power source. If you have unplugged your computer and / or removed the battery, plug it back in and / or replace the battery. Don't forget to turn on the switch on the back of your computer case or power supply.
Reconnect your computer to its power source. If you have unplugged your computer and / or removed the battery, plug it back in and / or replace the battery. Don't forget to turn on the switch on the back of your computer case or power supply.  Turn your computer back on. Depending on your computer, you may need to reset some things in the BIOS, such as boot order and date and time.
Turn your computer back on. Depending on your computer, you may need to reset some things in the BIOS, such as boot order and date and time.
Tips
- Most computers should still function properly with the default settings.
Warnings
- Ground yourself before touching the parts inside your computer to avoid damaging your computer from static electricity.