Author:
Robert Simon
Date Of Creation:
23 June 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024
Content
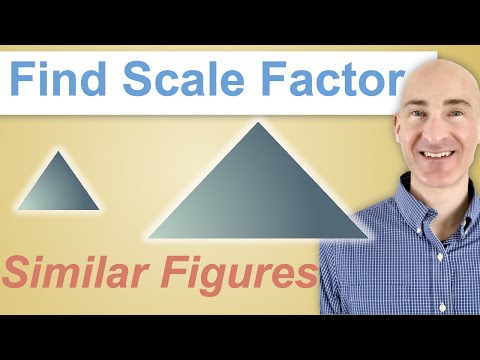
The (linear) scale factor is the ratio of two corresponding sides of figures with the same shape. Similar figures have the same shape but different dimensions. The scale factor is used to solve simple geometric problems. You can use the scale factor to determine the unknown sides of a figure. Conversely, you can use the side length of two similar digits to calculate the scale factor. For such exercises you have to multiply or simplify fractions.
To step
Method 1 of 4: Determining the scaling factor of a scaled figure
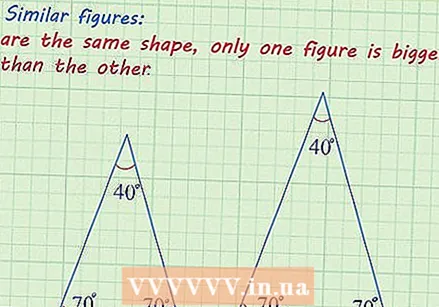 Check that the figures are comparable. Figures of the same shape have the same angles and the lengths of the sides are proportional. Similar figures have the same shape, but one figure is larger than the other.
Check that the figures are comparable. Figures of the same shape have the same angles and the lengths of the sides are proportional. Similar figures have the same shape, but one figure is larger than the other. - The statement should state that the shapes are the same, or show that the angles are the same, and otherwise indicate that the length ratio of the sides is proportional, to scale, or that they correspond to each other.
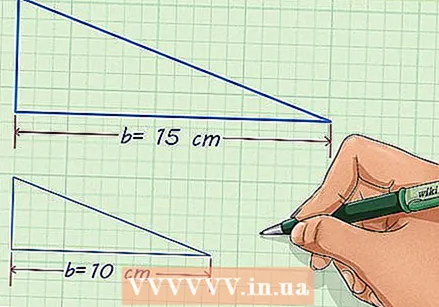 Find a corresponding side of each figure. You may need to rotate or flip the figure so that the two shapes line up and you recognize the corresponding sides. The length of these two sides must be given, or you must be able to measure them. If no side length of each figure is known, you cannot find the scale factor.
Find a corresponding side of each figure. You may need to rotate or flip the figure so that the two shapes line up and you recognize the corresponding sides. The length of these two sides must be given, or you must be able to measure them. If no side length of each figure is known, you cannot find the scale factor. - For example, you have a triangle with a base of 6 inches, and a corresponding triangle with a base that is 4 inches long.
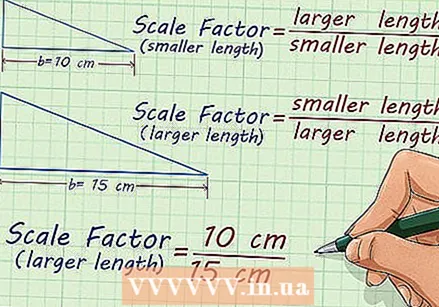 Determine the ratio. For each pair of matching figures, there are two scaling factors: one that you use when you enlarge a figure and one that you use for resizing. If you are enlarging to a larger version, use the ratio
Determine the ratio. For each pair of matching figures, there are two scaling factors: one that you use when you enlarge a figure and one that you use for resizing. If you are enlarging to a larger version, use the ratio 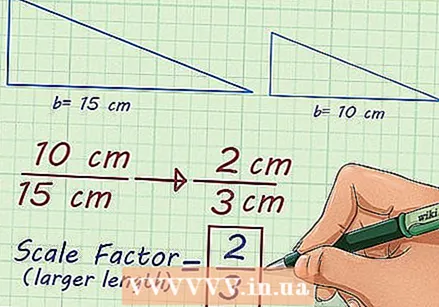 Simplify the ratio. The simplified ratio, or fraction, gives you the scale factor. If you decrease, the scale factor will be a regular fraction. When you increase, it becomes an integer or an improper fraction, which you can convert to a decimal number.
Simplify the ratio. The simplified ratio, or fraction, gives you the scale factor. If you decrease, the scale factor will be a regular fraction. When you increase, it becomes an integer or an improper fraction, which you can convert to a decimal number. - For example: the ratio
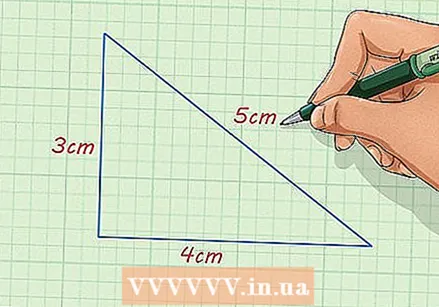 Determine the length of the side of the figure. You need one figure whose sides are given or measurable. If you cannot determine the side length of the image, you cannot create a scaled figure.
Determine the length of the side of the figure. You need one figure whose sides are given or measurable. If you cannot determine the side length of the image, you cannot create a scaled figure. - For example: you have a right triangle with sides of 4 cm and 3 cm and a sloping side of 5 cm.
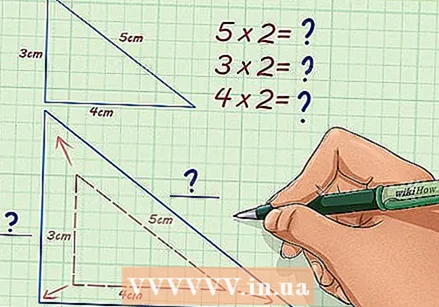 Decide whether you are going to enlarge or reduce. If you increase, your missing figure will become larger and the scale factor will be an integer, improper fraction or decimal. If you are going to shrink, the figure gets smaller, and your scaling factor is most likely an ordinary fraction.
Decide whether you are going to enlarge or reduce. If you increase, your missing figure will become larger and the scale factor will be an integer, improper fraction or decimal. If you are going to shrink, the figure gets smaller, and your scaling factor is most likely an ordinary fraction. - For example, with a scale factor of 2 you enlarge the figure.
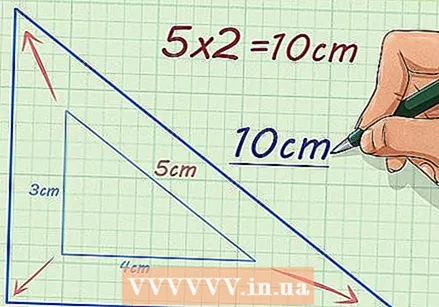 Multiply the length of one side by the scale factor. The scale factor must be given. When you multiply the length of the side by the scaling factor, it returns the missing side of the scaled figure.
Multiply the length of one side by the scale factor. The scale factor must be given. When you multiply the length of the side by the scaling factor, it returns the missing side of the scaled figure. - For example, if the hypotenuse of a right triangle is 5 centimeters long and the scale factor is 2, then you calculate to find the hypotenuse of the corresponding triangle
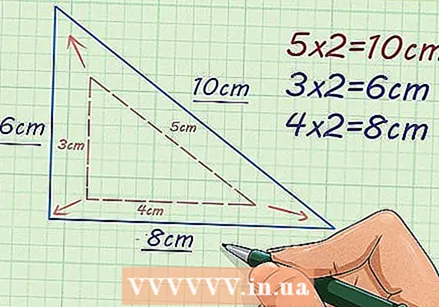 Determine the other sides of the figure. Continue to multiply each side by the scale factor. This will give you the corresponding sides of the missing figure.
Determine the other sides of the figure. Continue to multiply each side by the scale factor. This will give you the corresponding sides of the missing figure. - For example, if the base of a right triangle is 3 cm, with a scale factor of 2, then you calculate
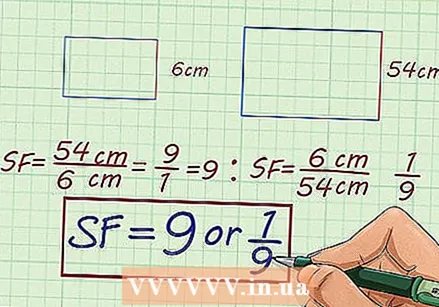 Determine the scale factor of these corresponding figures: a rectangle with a height of 6 cm, and a rectangle with a height of 54 cm.
Determine the scale factor of these corresponding figures: a rectangle with a height of 6 cm, and a rectangle with a height of 54 cm. - Compare the two heights. To increase, the ratio is
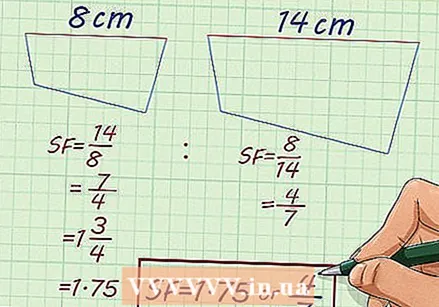 Try the following problem. An irregular polygon is 14 cm long at its widest point. A corresponding irregular polygon is 8 cm at its widest part. What is the scale factor?
Try the following problem. An irregular polygon is 14 cm long at its widest point. A corresponding irregular polygon is 8 cm at its widest part. What is the scale factor? - Irregular figures can be scaled if their sides are all proportional. So you can calculate a scale factor using any dimension that is given.
- Since you know the width of each polygon, you can make a ratio equation. You use the ratio to enlarge
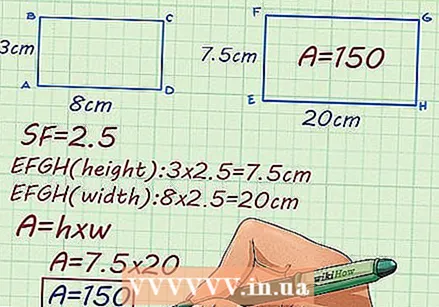 Use the scale factor to answer the following problem. Rectangle ABCD is 8 cm x 3 cm. rectangle EFGH is a larger, corresponding rectangle. A scale factor of 2.5 is given. What is the area of the rectangle EFGH?
Use the scale factor to answer the following problem. Rectangle ABCD is 8 cm x 3 cm. rectangle EFGH is a larger, corresponding rectangle. A scale factor of 2.5 is given. What is the area of the rectangle EFGH? - Multiply the height of the rectangle ABCD by the scale factor. This will give you the height of the rectangle EFGH:
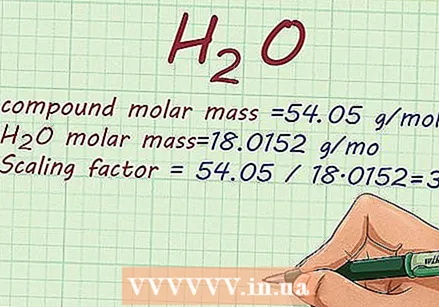 Divide the molar mass of a substance by that of the empirical formula. When you know the empirical formula of a chemical compound and you need the molecular formula of the same chemical, you can find the scale factor you need by dividing the molar mass of the substance by the molar mass of the empirical formula.
Divide the molar mass of a substance by that of the empirical formula. When you know the empirical formula of a chemical compound and you need the molecular formula of the same chemical, you can find the scale factor you need by dividing the molar mass of the substance by the molar mass of the empirical formula. - For example, you want to know the molar mass of an H2O compound with a molar mass of 54.05 g / mol.
- The molar mass of H2O is 18.0152 g / mol.
- Find the scale factor by dividing the molar mass of the compound by the molar mass of the empirical formula:
- Scale factor = 54.05 / 18.0152 = 3
- For example, you want to know the molar mass of an H2O compound with a molar mass of 54.05 g / mol.
 Multiply the empirical formula by the scale factor. Multiply the subscript of each element within the empirical formula by the scaling factor you just calculated. This will give you the molecular formula of the compound.
Multiply the empirical formula by the scale factor. Multiply the subscript of each element within the empirical formula by the scaling factor you just calculated. This will give you the molecular formula of the compound. - For example: to determine the molecular formula of the substance in question, multiply the subscript of H2O by the scale factor of 3.
- H2O * 3 = H6O3
- For example: to determine the molecular formula of the substance in question, multiply the subscript of H2O by the scale factor of 3.
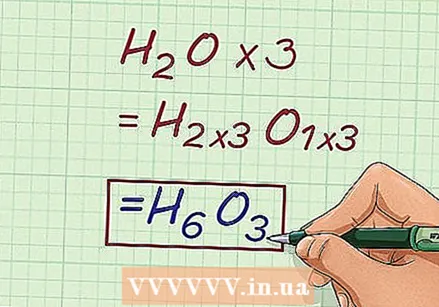 Write down the answer. With this answer, you have found the correct answer for the empirical formula, as well as the molecular formula of the chemical bond.
Write down the answer. With this answer, you have found the correct answer for the empirical formula, as well as the molecular formula of the chemical bond. - For example, the scale factor for the compound is 3. The molecular formula of the substance is H6O3.
- Multiply the height of the rectangle ABCD by the scale factor. This will give you the height of the rectangle EFGH:
- Compare the two heights. To increase, the ratio is
- For example, if the base of a right triangle is 3 cm, with a scale factor of 2, then you calculate
- For example, if the hypotenuse of a right triangle is 5 centimeters long and the scale factor is 2, then you calculate to find the hypotenuse of the corresponding triangle
- For example: the ratio