Author:
Bobbie Johnson
Date Of Creation:
4 April 2021
Update Date:
26 June 2024

Content
Have you ever been somewhere and got really badly injured, but did not know how you can provide effective first aid? These tips will help you keep yourself safe.
Steps
 1 Try to find something clean (or as clean as possible). If you cannot find anything such as a clean rag, towel, pack of napkins, or paper towel, use your hand.
1 Try to find something clean (or as clean as possible). If you cannot find anything such as a clean rag, towel, pack of napkins, or paper towel, use your hand. 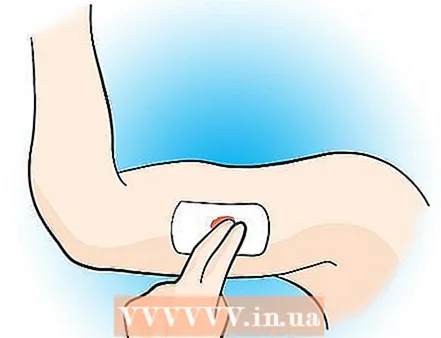 2 Cover the wound with a clean object and apply pressure. You must apply constant pressure for at least 4 (four) minutes - if it's a small wound. If the wound is large, especially if you cut or ruptured a vein or artery, then even longer.
2 Cover the wound with a clean object and apply pressure. You must apply constant pressure for at least 4 (four) minutes - if it's a small wound. If the wound is large, especially if you cut or ruptured a vein or artery, then even longer.  3 If you have injured a large vessel and the bleeding does not stop, and the wound is on the arm or leg, then a tourniquet must be applied. Find a piece of cloth, rope, or similar material (but not nothing like a narrow wire that can cut or break the wound when tightened ...) that you can easily tie around the limb, between the heart and the wound. If you can't tighten it tight enough to manually stop the blood flow, make a loop and push something (like a sturdy branch) through it. Use this device as a handle to twist and tighten the bandage until the bleeding stops.
3 If you have injured a large vessel and the bleeding does not stop, and the wound is on the arm or leg, then a tourniquet must be applied. Find a piece of cloth, rope, or similar material (but not nothing like a narrow wire that can cut or break the wound when tightened ...) that you can easily tie around the limb, between the heart and the wound. If you can't tighten it tight enough to manually stop the blood flow, make a loop and push something (like a sturdy branch) through it. Use this device as a handle to twist and tighten the bandage until the bleeding stops. 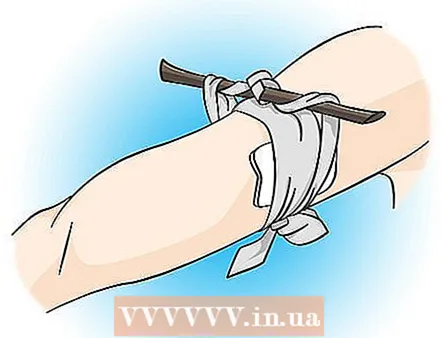 4 The tourniquet can only be used to save lives. How and when to use the tourniquet. If you put on a tourniquet not properly, it can lead to injury, and even loss legs or arms. Attention: This method of stopping bleeding is really used as a last resort, and only if the wound is so serious that you are in danger, bleeding and cannot stop the bleeding. Then get help immediately.
4 The tourniquet can only be used to save lives. How and when to use the tourniquet. If you put on a tourniquet not properly, it can lead to injury, and even loss legs or arms. Attention: This method of stopping bleeding is really used as a last resort, and only if the wound is so serious that you are in danger, bleeding and cannot stop the bleeding. Then get help immediately. 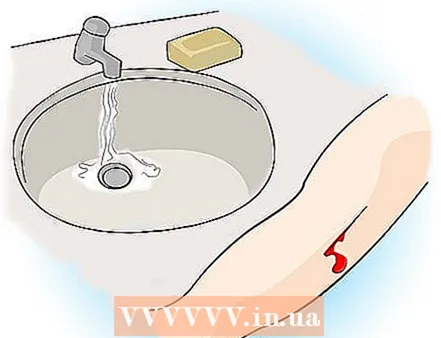 5 If you are in the woods or near any kind of water source, wash the wound thoroughly, but do not rub it. * * See note below.
5 If you are in the woods or near any kind of water source, wash the wound thoroughly, but do not rub it. * * See note below. 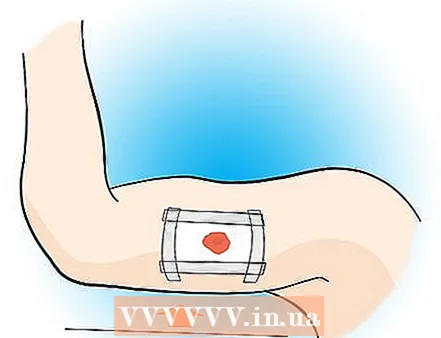 6 Keeping the wound elevated will reduce bleeding and normalize blood pressure.
6 Keeping the wound elevated will reduce bleeding and normalize blood pressure. 7 Hurry to the nearest pay phone, highway, or trail that is likely to lead to some civilization.
7 Hurry to the nearest pay phone, highway, or trail that is likely to lead to some civilization. 8 Call or ask someone to call emergency services or dial 112 yourself if you can reach the phone.
8 Call or ask someone to call emergency services or dial 112 yourself if you can reach the phone.
Tips
- Always carry a first aid kit with you when traveling with your own car / scooter, etc. Useful (and very simple) things: a roll of gauze, surgical tape, bandage, adhesive plaster, antibiotic ointment, antiseptic wipes.
- There is some controversy regarding the advice to clean the wound in the wild. If you have a profusely bleeding wound and your companion (or you yourself can see it) tells you that there are no foreign objects in the wound, it may be better not wash it, especially if the water is stagnant (possibly stagnant). The blood that comes out of your body is sterile, and you can introduce bacteria or parasites into the wound by flushing it with water that may be contaminated. If the wound is dirty, then of course try to clean it, but it may be better to use a small amount of drinking water for this, especially if there is water nearby that you have boiled so that there is clean water.
- Use an old shirt or even a last shirt.
- If you have nothing but a book cover, then use it.
Warnings
- Any wound on the hands or face should be examined by a doctor.
- Any wound with deep, uneven edges must be examined. Most likely, stitches will be needed!
- Use the tourniquet only in extreme circumstances where life and death are involved, to avoid unnecessary, serious damage and harm from the tourniquet itself.
- If bleeding does not stop after ten minutes, induce ambulance! You may have a ruptured artery, in which case you not you can help yourself.
- Using a tourniquet can lead to gangrene, tissue death, or loss of a limb.