Author:
Clyde Lopez
Date Of Creation:
18 June 2021
Update Date:
22 June 2024
Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 3: Defragment
- Method 2 of 3: Defragment Windows XP
- Method 3 of 3: Defragmenting from the Command Window
- Warnings
If your computer starts to run slowly, then it might be time to defragment your hard drive. Fragmentation can slow down your computer and wastes your hard drive space.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Defragment
 1 The reasons for the fragmentation of the hard drive. On a formatted hard drive, the system files are located at the beginning of the hard drive, followed by a block of free space. This space is optimally filled when installing new programs. When files are erased, modified, or moved on the hard disk, chunks of data and small blocks of free disk space remain.
1 The reasons for the fragmentation of the hard drive. On a formatted hard drive, the system files are located at the beginning of the hard drive, followed by a block of free space. This space is optimally filled when installing new programs. When files are erased, modified, or moved on the hard disk, chunks of data and small blocks of free disk space remain. 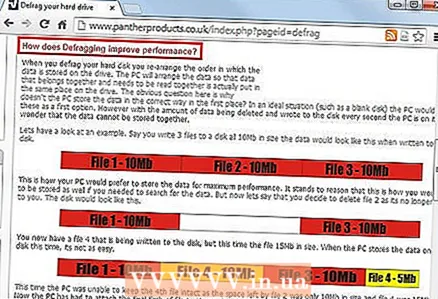 2 The impact of fragmentation on performance. As the number of fragments increases, performance degrades. The hard disk takes more time to find the files it needs, and the free space on the disk is not located in an optimal way.
2 The impact of fragmentation on performance. As the number of fragments increases, performance degrades. The hard disk takes more time to find the files it needs, and the free space on the disk is not located in an optimal way.  3 Prevention of fragmentation. Many modern file systems are designed to limit the amount of fragmentation. If you notice that your system is starting to slow down, defragmenting can help speed up your hard drive.
3 Prevention of fragmentation. Many modern file systems are designed to limit the amount of fragmentation. If you notice that your system is starting to slow down, defragmenting can help speed up your hard drive. - Solid state drives (flash memory) do not require defragmentation as they have no mechanical parts. Defragmenting an SSD can reduce its useful life because data can only be written to it a certain number of times.
Method 2 of 3: Defragment Windows XP
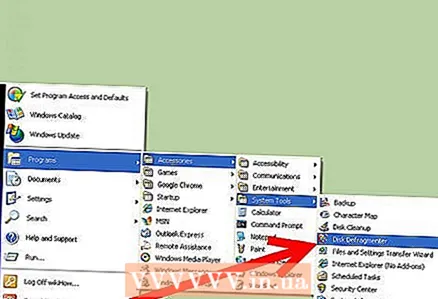 1 Open the Disk Defragmenter utility. Click Start - All Programs - Accessories - System Tools. Select Disk Defragmenter from the list. You must have administrator access to run the Disk Defragmenter utility.
1 Open the Disk Defragmenter utility. Click Start - All Programs - Accessories - System Tools. Select Disk Defragmenter from the list. You must have administrator access to run the Disk Defragmenter utility. 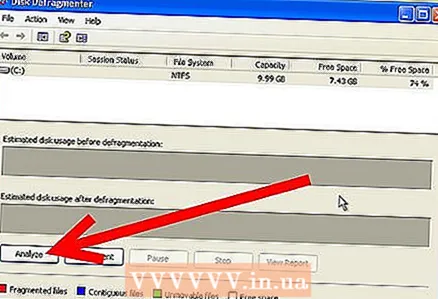 2 Select your device. A list of local drives that are installed on the computer will open. Select the drive you want to defragment. Typically, this is the C: or D: drive. Click Analyze to see that the disk needs defragmentation.
2 Select your device. A list of local drives that are installed on the computer will open. Select the drive you want to defragment. Typically, this is the C: or D: drive. Click Analyze to see that the disk needs defragmentation. - You can look at the graphs below the disc list. They show the effect of defragmentation on the allocation of used and free space. If you see a lot of red lines, then the amount of fragmentation is significant.
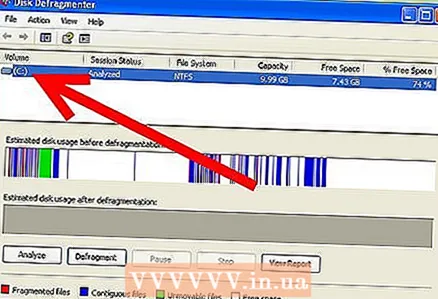
- You must have at least 15% free space to defragment the disk because files will be moved in order to optimize space and therefore the system needs free space to temporarily store the files being moved.
- You can look at the graphs below the disc list. They show the effect of defragmentation on the allocation of used and free space. If you see a lot of red lines, then the amount of fragmentation is significant.
 3 Disk Defragmenter. Select the drive and click Defragment. After defragmentation is complete, you will receive a report in a new window. It will inform you about which files have been moved and which cannot be moved, as well as the amount of free space.
3 Disk Defragmenter. Select the drive and click Defragment. After defragmentation is complete, you will receive a report in a new window. It will inform you about which files have been moved and which cannot be moved, as well as the amount of free space. - Do not use a computer to defragment a disk. If you change any files, defragmentation may need to be repeated.
- You can watch the progress in the status bar at the bottom of the window.
Method 3 of 3: Defragmenting from the Command Window
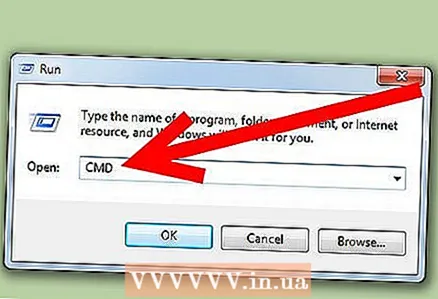 1 Open a command window. Click Start - Run. In the new window, type "cmd" and press Enter. This will open a command window.
1 Open a command window. Click Start - Run. In the new window, type "cmd" and press Enter. This will open a command window.  2 Disk analysis. To verify that the disk is fragmented, enter the following command in a command window. Replace "C" with the letter of your logical drive that you want to analyze:
2 Disk analysis. To verify that the disk is fragmented, enter the following command in a command window. Replace "C" with the letter of your logical drive that you want to analyze:
defrag C: / a 3 Disk Defragmenter. To start the defragmentation process, enter the following command in the command window. Replace "C" with the letter of your logical drive that you want to defragment:
3 Disk Defragmenter. To start the defragmentation process, enter the following command in the command window. Replace "C" with the letter of your logical drive that you want to defragment:
defrag C:- You can force defragmentation by adding / f at the end of the defrag command.
- A blinking cursor is displayed in the command window while defragmentation is in progress. When the process is complete, a report will be displayed. You can save the report to a text file by running defragmentation with the following command:
defrag C: / v> filename.txt.. - You can interrupt the defragmentation process by pressing Ctrl + C.
- You can force defragmentation by adding / f at the end of the defrag command.
Warnings
- Do not defragment solid state drives. This will reduce the resource of their performance.