Author:
Lewis Jackson
Date Of Creation:
5 May 2021
Update Date:
25 June 2024

Content
If you have an inguinal hernia, one of the things you will notice is a bulge in your abdomen or groin. This bulge is the intestine or part of the intestine that pushes through the abdominal muscles. Inguinal hernia is diagnosed quite simply and surgery is the main treatment. A hernia is usually not life-threatening, but complications can occur if you don't treat it.An inguinal hernia can cause such dangers as intestinal ligation, where part of the intestine twists and ruptures due to a herniated sac. This can lead to intestinal congestion, abdominal pain and fever if left untreated, and ultimately emergency. You should learn to recognize the signs and to treat an inguinal hernia, but it's best to prevent it than cure it.
Steps
Part 1 of 3: Look for signs of an inguinal hernia

Look in the mirror for signs of a hernia. Take off your clothes from waist down and look in the mirror. Place 2 fingers on the area you think has influence. Try to cough and notice if you feel or see a bulge coming out of this area. You can also hold your breath and pull your stomach in, like you're going to the toilet. Use your fingers to feel the bulge. A hernia gets worse each time you do things that put pressure on your abdomen. You should also look for:- Bulges in the groin area: If this happens, you will have a hernia, either directly or indirectly.
- You will find that your lower abdomen is swollen, extending as far as the scrotum or even the scrotum.
- Bulges on thighs and under groin: An almost certain sign of thigh herniation.
- One testicle is larger than the other or swollen: This could be an indication of an indirect hernia.
- Hot, painful, or very painful groin: These symptoms indicate a hernia because the intestines are stuck and constricted, causing pain.
- If the swollen site is oval but not in the scrotum, it is likely a direct inguinal hernia rather than indirect.

Check to see if the hernia can be pushed back up. Touch with your hands to see if you can retract or repel the herniation back into position. Lie down so that gravity helps relax the tension at the herniation. Slowly press the bulge with your index finger and try to push the contents back up. Not harsh because it can break the herniated component or tear the mouth of the groin. If you cannot recover the hernia, seek medical attention immediately.- Tell your doctor if you feel nauseous, in addition to not being able to push the bulge back in, it could be a complication of hernias, constriction.
- See your doctor right away if stomach upset or fever.
- The stuffy bowel phenomenon makes the blood vessels unable to supply enough nutrients to the intestine, causing tissue death and intestinal failure. You need surgery to remove dead cells so that digested products can pass through.

Medical examination. Patients need to see a doctor regardless of the type of hernia. At the clinic you have to undress all the way down from the waist, the doctor and their assistant will examine the abdomen and genitals for imbalances and bulges. They ask you to hold your stomach down as if you were coughing, or pull your stomach in while holding your breath. If there is a bulge there is a hernia. The doctor also checks to see if the hernia can be retrieved by touching the area with your index finger.- They used a stethoscope to hear the sounds made by the intestines inside the bulge. If there is no sound, then tissue is dead or choked.
Learn about types of inguinal hernia. Inguinal hernia is differentiated based on location and cause of the disease. There are the following types of inguinal hernias: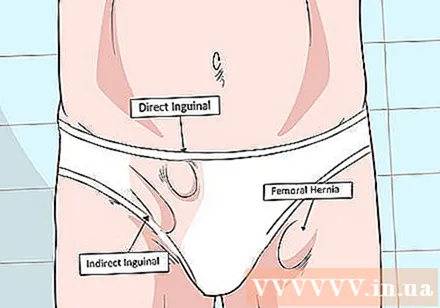
- Indirect inguinal hernia: This is a birth defect that causes the intestines and / or the intestinal wall to slide into the position where the male fetus' testicles descend before birth. In most cases this is because the area does not close tightly after the baby is born and the intestines slide in.
- Direct inguinal hernia: This type of herniation occurs when trauma enters the area, resembling constant pressure when lifting heavy objects, coughing a lot, squeezing while using the bathroom, or pregnant. The intestine, intestinal wall, or intestinal fat slides through weak muscles near the groin and genitals, but not into the scrotum or testicle. This condition usually occurs in men over 40 years old, but can also occur in women.
- Throat hernia: This disease usually occurs during pregnancy or childbirth. The intestinal components slide through the weak point in the lower part of the groin, where blood vessels pass to supply blood to the thighs and legs. A thigh hernia has a higher risk of complications, so it's important to let your doctor know if your symptoms change.
Part 2 of 3: Treatment of inguinal hernia and rehabilitation
Discuss treatment options with your doctor. Surgery is the most recognized and widely used treatment for hernias. But if no symptoms appear yet and the hernia can be repelled, you may still want to wait. Whether you have surgery or not, you must make an appointment with your doctor for expert opinion. If you want surgery but your doctor advises you not because there are no symptoms, then you still have the right to choose surgery for cosmetic reasons. After making that decision, you must make an appointment to see the surgeon.
- Follow-up work is to perform tests, including: testing of blood readings (PT, PTT, INR, and CBC), the content of electrolytes such as sodium, potassium and glucose, and recording an electrocardiogram. an ECG to detect heart abnormalities. Make an appointment with your doctor to arrange testing, then bring the results to the surgeon.
Endoscopic surgery. For this method you will need to take anesthetics to relieve pain and discomfort. The surgeon will blow air into the abdomen to expand the tissues before starting the work. Next they inserted a camera probe inward to instruct other devices when cutting and stitching. They used devices to push the hernia back into place, and at the same time inserted an artificial net to strengthen the weak muscles on the abdominal wall. This procedure prevents future hernia. Finally the doctor sutured the cut where the transducer was inserted.
- Because it is a less invasive form of surgery, laparoscopic surgery leaves only a small scar later, does not lose much blood, so it does not cause much pain after surgery.
- Laparoscopic surgery is preferred over open surgery if the hernia occurs on both sides, recurrent, or thigh herniation.
Open surgery. If this type of surgery is chosen, the doctor will make an incision along the groin to open the area. They then used their hands to push the hernia back into the abdomen and look for an air leak from the intestine. Eventually the doctor will insert a mesh around the weak abdominal muscles or tie the muscles together, thus preventing a hernia in the future. The cut will be stitched again after completion.
- If you have a severe hernia and want to find a relatively inexpensive surgical procedure, you might consider open surgery.
- Open surgery is preferred over laparoscopic surgery if the site has been operated on, if this is the first time you have an inguinal hernia, if the herniation is large, or if you are concerned about infection.
Care after surgery. Since the pain may last for several weeks after surgery, take whatever pain reliever your doctor has prescribed. Be sure to eat plenty of fiber-rich foods or drink 2 tablespoons of magnesium milk twice daily after surgery. It takes about 1-5 days after surgery to have a bowel movement and a high-fiber diet will make it easier for you to have bowel movements.
- To relieve pain, place an ice pack around the operating area for 20 minutes at a time (remember to wrap a towel over the ice pack).
Clean the wound. Leave the bandage on the wound for 2 days. You may see a little blood or discharge from the wound, which is normal. After 36 hours you are allowed to shower, however remember to take off the gauze and only gently rub soap on it. When you have finished bathing, gently dry the wound and change a new gauze pad after each shower.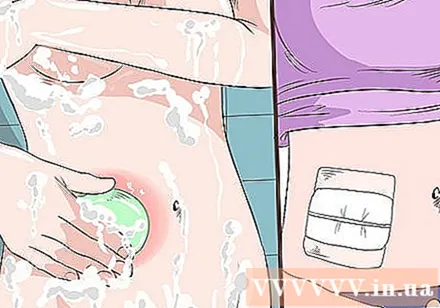
- Avoid bathing or soaking the wound in swimming pools or hot tubs for at least 2 weeks.
Gently move back. After surgery there are no restrictions on physical activity but the area is still quite weak, so avoid activities that put pressure on your abdomen for a week. Examples include exercise, jogging, or swimming.
- You should also not lift anything heavier than 5 kg for the first 6 weeks, or wait until your doctor says it is OK. Heavy lifting can cause a new hernia at the same site.
- You should not drive for the first two weeks after surgery.
- You can have sex as long as it doesn't feel pain or discomfort.
- Most patients recover and return to work within a month of treatment.
Watch for complications. Let your doctor know if you experience any of the following complications following surgery:
- Fever (38.3 C) and chills: Bacteria may have entered the wound.
- Drainage from a wound that has a pus-like odor and color (usually brown or green): A bacterial infection produces a foul-smelling mucus.
- Continuous bleeding from the wound: it is possible that a blood vessel is ruptured and not sealed during surgery.
- Problems urinating: It is normal to have fluid and inflammation after surgery, but too much fluid can lead to bladder or urethral insertion and make urinating difficult. This may cause urine to retain or the inability to empty the bladder.
- Swelling or pain is worse and worse in the testicles.
- The most common complication is recurrent hernia.
Part 3 of 3: Prevent inguinal hernia
Weight loss. If you are overweight or obese, you should lose weight by eating fewer calories and exercising moderately. Being overweight causes the already weak areas in the abdomen to carry more weight than usual, which in turn leads to an increased chance of herniation at these weak spots.
- Remember to choose an exercise that doesn't put much pressure on the abdominal wall. Try moderate exercises like walking, running, swimming, and cycling.
Eat more fiber. Dietary fiber helps improve digestion and empty the bowels, a high-fiber diet also softens stools and makes you less urge to urinate. Eat high-fiber foods like bread, fruits, and vegetables. You should also drink plenty of fluids throughout the day to keep bowel functioning better.
- Fiber is especially important if you've just had a herniation surgery, as surgery and painkillers by themselves slow down bowel movements. This leads to constipation and puts pressure on the abdomen.
Learn how to lift objects. Avoid or be careful when lifting heavy objects. You can start lifting heavy objects over 5 kg about 6 weeks after surgery. To lift properly, you have to bend your knees to lower your body first, pull the object closer and lift, use your knees to lift instead of using your waist. This lift reduces the weight and pressure placed on the abdomen when bent.
- You can wear exercise support around the waist, it helps to support the abdominal muscles especially when lifting.
Stop smoking. Smoking is a direct cause of chronic cough, leading to and exacerbating the inguinal hernia problem. If you have had an inguinal hernia in the past, you should avoid activities that may cause the problem, such as smoking. advertisement
Advice
- The possibility of an inguinal hernia is not excluded even if you feel pain, as inguinal hernia may not be painful.
- Risk factors for inguinal hernia in adults include: having had it in childhood, old age, men, chronic cough, chronic constipation, abdominal wall injury, smoking or having a family a history of this disease.
- Most hernias need surgical treatment. Ask your general practitioner to refer a surgeon to your treatment.
- If you choose to have surgery, don't eat or drink anything after midnight the day before the surgery. The purpose is to prevent inhalation of food from the stomach into the lungs during anesthesia.
- Quit smoking to avoid coughing because coughing causes the abdominal muscles to contract.
Warning
- If you have ever had a hernia, strictly follow the above prevention methods.
- Bowel obstruction and obstruction can occur if you don't treat an inguinal hernia. These complications are very dangerous and can lead to death.
- If you feel a sharp pain during the self-examination, see your doctor immediately. That could be a sign of the torsion of the blood vessels leading to the testicles, reducing blood flow to the testicles. Without timely intervention, anemia to the two testicles will damage and even have to remove the testicles.