Author:
Florence Bailey
Date Of Creation:
22 March 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 5: Drug Treatment
- Method 2 of 5: Review Your Diet
- Method 3 of 5: Treating with Home Remedies
- Method 4 of 5: Preventing a fungal infection
- Method 5 of 5: When to see a doctor
Candidiasis, or thrush, is an infection caused by a yeast of the genus Candida albicans (diploid fungus), which can affect the mouth, vagina, skin, stomach, and urinary tract. Vaginal infection is especially common. People with weakened immune systems are also at risk (for both vaginal and oral candidiasis). Most of these infections can be treated at home, but see a doctor if symptoms first appear or persist for a long time.
Attention:the information in this article is for informational purposes only. Before using any methods, consult your doctor.
Steps
Method 1 of 5: Drug Treatment
 1 Pay attention to the symptoms. The risk of contracting candidiasis may increase in people taking antibiotics, in pregnant women, in people who are overweight, have diabetes, or a weakened immune system. So, the symptoms of candidiasis include:
1 Pay attention to the symptoms. The risk of contracting candidiasis may increase in people taking antibiotics, in pregnant women, in people who are overweight, have diabetes, or a weakened immune system. So, the symptoms of candidiasis include: - itching, irritation, soreness, and burning in the vagina;
- odorless white cheesy discharge;
- skin rash, spots and blisters in the groin area.
 2 Buy an over-the-counter antifungal cream. Your doctor may prescribe an antifungal agent that will cure the infection, and it may be available with or without a prescription. Fungal infections are caused by fungi, which is why over-the-counter antifungals are one of the most popular remedies for candidiasis.
2 Buy an over-the-counter antifungal cream. Your doctor may prescribe an antifungal agent that will cure the infection, and it may be available with or without a prescription. Fungal infections are caused by fungi, which is why over-the-counter antifungals are one of the most popular remedies for candidiasis. - If you do not notice any improvement within 3-4 days, seek the advice of your doctor.
- DO NOT USE antifungal medications if you are pregnant or if you have had a relapse of the infection. In this case, you should see a doctor to help cure the fungal infection.
- Check the instructions for the antifungal cream that it is for yeast infection (candidiasis). Other antifungal medications are not recommended for use in the groin or vaginal area.
- Over-the-counter creams are used for 1 to 7 days. Follow the directions given in the instructions for use.
 3 Buy vaginal suppositories. Like an antifungal ointment, vaginal suppositories help treat thrush by coming into direct contact with the fungus that caused the infection. The composition of the suppositories is slightly different from the composition of the ointment, but usually they contain antifungal agents (such as clotrimazole, butoconazole, miconazole, or thioconazole).
3 Buy vaginal suppositories. Like an antifungal ointment, vaginal suppositories help treat thrush by coming into direct contact with the fungus that caused the infection. The composition of the suppositories is slightly different from the composition of the ointment, but usually they contain antifungal agents (such as clotrimazole, butoconazole, miconazole, or thioconazole). - Over-the-counter suppositories can also be used for 1 to 7 days. Before use, be sure to read the instructions that come with the drug in order to know how often to use candles, as well as how to insert them correctly.
- Typically, candles are produced in conical, cylindrical and wedge-shaped shapes. They need to be inserted directly into the vagina.
 4 Buy over-the-counter pills. Oral medications can be purchased without a prescription, but you should consult your doctor first. Some drugs have side effects, especially when combined with other drugs, herbs, or supplements.
4 Buy over-the-counter pills. Oral medications can be purchased without a prescription, but you should consult your doctor first. Some drugs have side effects, especially when combined with other drugs, herbs, or supplements. - To find out the optimal dosage and frequency of administration, read the instructions that came with the medicine. The pill treatment may take 1 to 7 days.
- These tablets contain antifungal medications that are safe to take by mouth.
- Excessive antibiotics should be avoided because they destroy the normal vaginal microflora that inhibits reproduction Candida.
 5 Apply an anti-itch cream to your skin. These ointments should only be applied around the vulva, not inside the vagina. Vaginal creams can be combined with corticosteroids to relieve inflammation and itching and are usually sold with a special applicator to accurately measure the amount of cream used.
5 Apply an anti-itch cream to your skin. These ointments should only be applied around the vulva, not inside the vagina. Vaginal creams can be combined with corticosteroids to relieve inflammation and itching and are usually sold with a special applicator to accurately measure the amount of cream used. - Even if these creams are available without a prescription, you should consult your doctor before using them.
- Creams are thicker than lotions, but they can leak, so a sanitary pad or panty liner should be used. However, do not use a tampon because it will absorb the ointment, reducing the effectiveness of the treatment.
- An anti-itch cream does not treat the infection itself, but it does help relieve symptoms that are associated with a fungal infection. It should be used in combination with an antifungal cream, vaginal suppository or pill.
- You should use a cream that is intended for the vaginal area. Other anti-itch medications can upset the acid balance, thereby contributing to infection.
Method 2 of 5: Review Your Diet
 1 Remove certain foods and drinks from your diet. Eating the right diet will help reduce the growth of fungi that cause thrush. Experts suggest removing alcohol, foods and beverages that contain a lot of sugar or artificial sweeteners, refined carbohydrates and foods with a high concentration of yeast from the diet.
1 Remove certain foods and drinks from your diet. Eating the right diet will help reduce the growth of fungi that cause thrush. Experts suggest removing alcohol, foods and beverages that contain a lot of sugar or artificial sweeteners, refined carbohydrates and foods with a high concentration of yeast from the diet. - Certain types of dairy products (such as cheese and butter) can also contribute to the development of candidiasis, but this issue has not yet been adequately researched.
- If you have low blood sugar or are unsure of what foods you should cut out of your diet, ask a therapist or nutritionist for a personalized diet plan for you.
 2 Take vitamin C. Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid) is an important natural antioxidant that contributes to the development of the body's immune function. Vitamin C can be taken as a dietary supplement. The recommended dose is 500 to 1000 mg per day, divided into 2-3 doses. You can also add vitamin C-rich foods to your diet. Before taking vitamin C supplements, be sure to check with your doctor, especially if you are taking immunosuppressants or have a weakened immune system. However, natural sources of vitamin C have no side effects (unless you are allergic to these foods, of course). Foods rich in vitamin C include:
2 Take vitamin C. Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid) is an important natural antioxidant that contributes to the development of the body's immune function. Vitamin C can be taken as a dietary supplement. The recommended dose is 500 to 1000 mg per day, divided into 2-3 doses. You can also add vitamin C-rich foods to your diet. Before taking vitamin C supplements, be sure to check with your doctor, especially if you are taking immunosuppressants or have a weakened immune system. However, natural sources of vitamin C have no side effects (unless you are allergic to these foods, of course). Foods rich in vitamin C include: - sweet red or green peppers;
- citrus fruits (orange, pomelo, grapefruit, lime), non-concentrated citrus juices);
- spinach, broccoli, Brussels sprouts;
- strawberries and raspberries;
- tomatoes;
- mango, papaya, cantaloupe melon.
 3 Supplement your diet with vitamin E. Vitamin E is also an antioxidant that stimulates the immune system and is effective in fighting fungal infections caused by a weakened immune system. The recommended adult dose is 15 mg per day. Vitamin E is found in foods such as:
3 Supplement your diet with vitamin E. Vitamin E is also an antioxidant that stimulates the immune system and is effective in fighting fungal infections caused by a weakened immune system. The recommended adult dose is 15 mg per day. Vitamin E is found in foods such as: - vegetable oils;
- almond;
- peanut;
- hazelnut;
- sunflower seeds;
- spinach;
- broccoli.
 4 Eat more foods that contain omega-3 fatty acids. Essential fatty acids can help reduce inflammation and relieve the burning sensation that often occurs in people with thrush. It is recommended to take omega-6s, which are found in evening primrose extract (also known as evening primrose), while omega-3s can be found in fish and flaxseed oil. Take 2 tablespoons of oil a day or 1000-1500 mg in separate doses 2 times a day.
4 Eat more foods that contain omega-3 fatty acids. Essential fatty acids can help reduce inflammation and relieve the burning sensation that often occurs in people with thrush. It is recommended to take omega-6s, which are found in evening primrose extract (also known as evening primrose), while omega-3s can be found in fish and flaxseed oil. Take 2 tablespoons of oil a day or 1000-1500 mg in separate doses 2 times a day. - eggs;
- pinto beans, soybeans and black-eyed peas;
- tofu;
- wild salmon and sardines;
- walnuts, almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds;
- rapeseed oil, fish oil and flaxseed oil.
 5 Take probiotics. Probiotics contain bacteria that are beneficial to our body, which usually live on the inner walls of the intestines. They act as antifungal agents that control reproduction Candida and increase the body's immune defenses. Some studies show that yogurt containing active probiotic cultures helps prevent fungal infections. Here are some ways to increase your probiotic intake:
5 Take probiotics. Probiotics contain bacteria that are beneficial to our body, which usually live on the inner walls of the intestines. They act as antifungal agents that control reproduction Candida and increase the body's immune defenses. Some studies show that yogurt containing active probiotic cultures helps prevent fungal infections. Here are some ways to increase your probiotic intake: - Try probiotic supplements with a concentration of 1 to 10 billion Bifidobacteria (up to twice a day).
- Talk to your doctor before taking probiotics (especially if you are taking immunosuppressive medications or antibiotics).
- Consume a glass (250 ml) of plain unsweetened yogurt daily to prevent fungal infections.
- You can buy probiotic vaginal suppositories that help restore the balance of microflora in the vagina.
Method 3 of 5: Treating with Home Remedies
 1 Eat more garlic. Garlic is widely recognized for its antibacterial and antifungal properties thanks to allicin. Consider eating one raw garlic clove a day, or adding 2-3 grated cloves to meals. An alternative to this is a food supplement containing 4000-5000 mcg of allicin.
1 Eat more garlic. Garlic is widely recognized for its antibacterial and antifungal properties thanks to allicin. Consider eating one raw garlic clove a day, or adding 2-3 grated cloves to meals. An alternative to this is a food supplement containing 4000-5000 mcg of allicin. - Garlic can interact with a number of medications, including drugs used to treat HIV. Garlic may increase the risk of bleeding in people with weak immune systems, those who take blood thinners, or have recently had an injury or surgery. Talk to your doctor before taking garlic in natural or supplement form.
 2 Drink echinacea extract. Echinacea is a herb with antiviral and antioxidant effects that help boost immune function, reduce inflammation, and restore hormonal balance. Echinacea is useful when combined with econazole, an antifungal agent used to treat fungal infections, by helping to reduce the frequency of re-infections. Studies show that drinking 2-9 ml of echinacea juice or 1 cup of echinacea tea helps prevent fungal infections caused by fungus Candida.
2 Drink echinacea extract. Echinacea is a herb with antiviral and antioxidant effects that help boost immune function, reduce inflammation, and restore hormonal balance. Echinacea is useful when combined with econazole, an antifungal agent used to treat fungal infections, by helping to reduce the frequency of re-infections. Studies show that drinking 2-9 ml of echinacea juice or 1 cup of echinacea tea helps prevent fungal infections caused by fungus Candida. - To make echinacea tea, simply steep 1-2 grams of dry echinacea root or herb extract in warm water for 5 minutes, then strain and drink.
- Echinacea also has the ability to interact with a number of medications, so check with your doctor before taking it.
- Some people experience minor side effects of this supplement (these include upset stomach, nausea, dizziness, and dry eyes). Do not take echinacea on an empty stomach.
- Do not take echinacea if you have multiple sclerosis, tuberculosis, connective tissue disease, leukemia, diabetes, HIV or AIDS, any autoimmune disease, or liver disease.
 3 Take a tea tree oil bath. Tea tree oil is known for its antiviral and antifungal properties.Research results indicate that tea tree oil may be effective in treating vaginal fungal infections, but injecting tea tree oil directly into the vagina is not recommended. Try taking a tea tree oil bath instead.
3 Take a tea tree oil bath. Tea tree oil is known for its antiviral and antifungal properties.Research results indicate that tea tree oil may be effective in treating vaginal fungal infections, but injecting tea tree oil directly into the vagina is not recommended. Try taking a tea tree oil bath instead. - Add 10-15 drops of tea tree oil to a warm bath and sit in it for at least 15 minutes. Repeat this procedure 2-3 times a week. This will help maintain the balance of microflora and prevent vaginal fungal infections.
Method 4 of 5: Preventing a fungal infection
 1 Take care of your personal hygiene. The best prevention of recurrent fungal infections is to maintain personal hygiene and keep the genital area clean and dry. Here are some more tips to help prevent fungal infection:
1 Take care of your personal hygiene. The best prevention of recurrent fungal infections is to maintain personal hygiene and keep the genital area clean and dry. Here are some more tips to help prevent fungal infection: - Do not wash your genital area with soap - limit yourself to plain lukewarm water.
- Always wipe from front to back after using the toilet.
- Do not apply cosmetic products (perfume, feminine hygiene spray, powder) to the intimate area.
- Remember to change sanitary pads, menstrual cups, and tampons every 2 to 4 hours.
 2 Wear comfortable clothing. Avoid wearing tight-fitting items such as tight pants, leggings, or tights every day. Clothing that is too tight can lead to irritation and worsen symptoms. In addition, you should spend as little time as possible in a wet swimsuit and workout clothes. Items soaked with water or sweat should be replaced with clean and dry items as soon as possible.
2 Wear comfortable clothing. Avoid wearing tight-fitting items such as tight pants, leggings, or tights every day. Clothing that is too tight can lead to irritation and worsen symptoms. In addition, you should spend as little time as possible in a wet swimsuit and workout clothes. Items soaked with water or sweat should be replaced with clean and dry items as soon as possible. - Instead of nylon or silk underwear or tights, it is better to wear cotton underwear, because nylon and silk underwear increases sweating in the genital area, causing irritation.
 3 Do not use douching. Some women find that douching can help cleanse and freshen the vaginal area, but in fact, the douching process can contribute to the development of a fungal infection. Douching can change the natural pH balance in the vagina and irritate and damage the skin and mucous membranes (regardless of whether you use herbal or medicinal products). Douching increases the risk of vaginal infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, and pregnancy complications.
3 Do not use douching. Some women find that douching can help cleanse and freshen the vaginal area, but in fact, the douching process can contribute to the development of a fungal infection. Douching can change the natural pH balance in the vagina and irritate and damage the skin and mucous membranes (regardless of whether you use herbal or medicinal products). Douching increases the risk of vaginal infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, and pregnancy complications.
Method 5 of 5: When to see a doctor
 1 See your doctor if you first experience symptoms of candidiasis. Since the symptoms of a yeast infection may overlap with signs of other diseases, you need to know the exact diagnosis from your gynecologist. To begin with, the doctor may recommend one of the weaker drugs or immediately choose a potent remedy.
1 See your doctor if you first experience symptoms of candidiasis. Since the symptoms of a yeast infection may overlap with signs of other diseases, you need to know the exact diagnosis from your gynecologist. To begin with, the doctor may recommend one of the weaker drugs or immediately choose a potent remedy. - Your doctor will help you find the best treatment for you.
 2 See your doctor if over-the-counter drugs don't work. If symptoms persist or worsen with treatment, you may need a stronger remedy - or the symptoms may have a different cause. The doctor will be able to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment that will help you.
2 See your doctor if over-the-counter drugs don't work. If symptoms persist or worsen with treatment, you may need a stronger remedy - or the symptoms may have a different cause. The doctor will be able to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment that will help you. - Do not use over-the-counter products for more than 5-7 days without consulting your doctor.
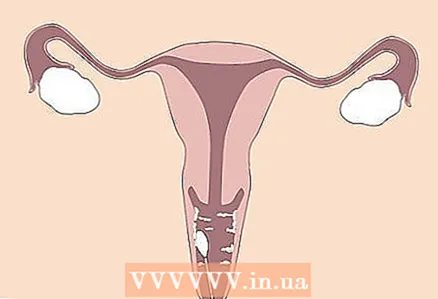 3 Be aware that your doctor will need to examine and take a swab from your vagina. To detect candidiasis, a vaginal swab is usually taken and sent for analysis. The test will show if you have a yeast infection, and if so, which one. In addition, the gynecologist may do an examination to look for other signs of infection.
3 Be aware that your doctor will need to examine and take a swab from your vagina. To detect candidiasis, a vaginal swab is usually taken and sent for analysis. The test will show if you have a yeast infection, and if so, which one. In addition, the gynecologist may do an examination to look for other signs of infection. - Your doctor can also discuss possible risk factors with you.
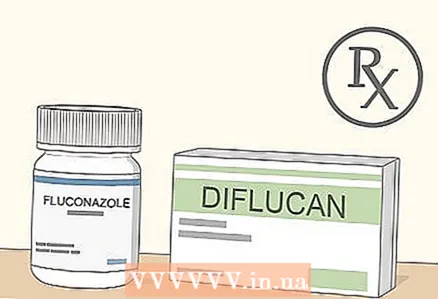 4 Talk with your doctor about taking a prescription antifungal medication. Such drugs are usually strong, and even if they can actually be obtained without a prescription, you should not prescribe them yourself. Your doctor may prescribe one of the drugs, which are taken in a 3–7 day course, or fluconazole (Diflucan), which is usually taken as a single dose.
4 Talk with your doctor about taking a prescription antifungal medication. Such drugs are usually strong, and even if they can actually be obtained without a prescription, you should not prescribe them yourself. Your doctor may prescribe one of the drugs, which are taken in a 3–7 day course, or fluconazole (Diflucan), which is usually taken as a single dose. - For severe infections, your doctor may prescribe a single dose followed by another 3 days later, or recommend a long-term course of treatment.
- A short-term course of treatment may include ointments, creams, suppositories, or pills.
- Be sure to take your medications as directed by your doctor or the infection may return.
- If you are pregnant or think you might be pregnant, tell your doctor, as oral medications should not be taken during pregnancy. Creams and ointments can be applied if approved by your doctor.