Author:
Lewis Jackson
Date Of Creation:
8 May 2021
Update Date:
1 July 2024

Content
There are two forms of energy: potential energy and kinetic energy. Potential energy is the energy that an object has due to its relative position to another. For example, if you are standing on top of a hill, you have greater potential energy than if you are standing at the bottom of the hill. Kinetic energy is the energy that an object has when it moves. Kinetic energy can be produced by vibration, rotation or movement (moving from one place to another). We can easily calculate the kinetic energy of any object by equating its mass and velocity.
Steps
Part 1 of 3: Understanding dynamism
Know the dynamic formula. We have the formula for calculating kinetic energy (KE) is KE = 0.5 x mv. In this recipe m mass - a measure of the amount of matter in an object, and v is the speed of the object, or the rate at which it changes position.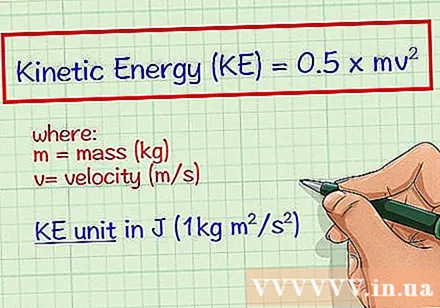
- The answer is always expressed in joule (J), which is the standard unit of measurement for kinetic energy. It is equivalent to 1 kg * m / s.
Determine the mass of the object. If the problem does not give weight, you will have to determine the weight yourself. You can weigh the object and get a value of its mass in kilograms (kg).- Balance adjustment. Before weighing an object, you must adjust the scale to zero.
- Place the object on the scale. Gently place the object on the scale and record the mass in kilograms.
- If necessary, convert from grams to kilograms. To make the final calculation, the mass must be in kilograms.

Calculate the velocity of the object. Usually the problem will give you the velocity of the object. If not, you can determine the speed by using the distance the object has traveled and the time it takes it to go all the way. The unit for speed is meters per second (m / s).- Velocity is defined by displacement divided by time: V = d / t. Velocity is a vector quantity, meaning it has the magnitude and direction of motion. Magnitude is the numerical value that quantifies speed, while the direction of motion is the direction in which speed takes place during motion.
- For example, the speed of an object can be 80m / s or -80m / s, depending on the direction of motion.
- To calculate the velocity, you divide the distance the object has to travel by the time it takes it to travel that distance.
Part 2 of 3: Dynamism
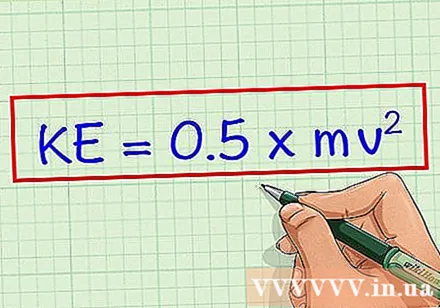
Write down the formula. We have the formula for calculating kinetic energy (KE) is KE = 0.5 x mv. In this recipe m mass - a measure of the amount of matter in an object, and v is the speed of the object, or the rate at which it changes position.- The answer is always expressed in joule (J), which is the standard unit of measurement for kinetic energy. It is equivalent to 1 kg * m / s.
Replace mass and velocity in the equation. If you don't know the mass or speed of the object, you have to find it. But suppose that you know these two values and are solving the following problem: Determine the kinetic energy of a woman weighing 55kg running at a speed of 3.87m / s. Since you know the person's mass and velocity, you'd plug them into the equation:
- KE = 0.5 x mv
- KE = 0.5 x 55 x (3.87)
Solve the equation. After you plug the mass and velocity into the equation, you will find the kinetic energy (KE). Square the velocity and then multiply all the variables together. Remember to write your answers in joule (J).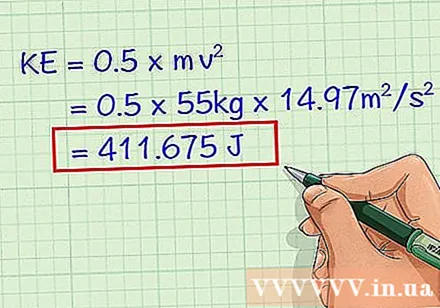
- KE = 0.5 x 55 x (3.87)
- KE = 0.5 x 55 x 14.97
- KE = 411,675 J
Part 3 of 3: Using kinetic energy to find speed or mass
Write down the formula. We have the formula for calculating kinetic energy (KE) is KE = 0.5 x mv. In this recipe m mass - a measure of the amount of matter in an object, and v is the speed of the object, or the rate at which it changes position.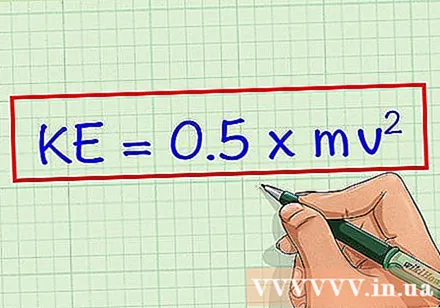
- The answer is always expressed in joule (J), which is the standard unit of measurement for kinetic energy. It is equivalent to 1 kg * m / s.
Replace the known variables. Some problems can tell you whether kinetic energy versus mass, or kinetic energy versus speed. The first step in solving this problem is to plug all known variables into the equation.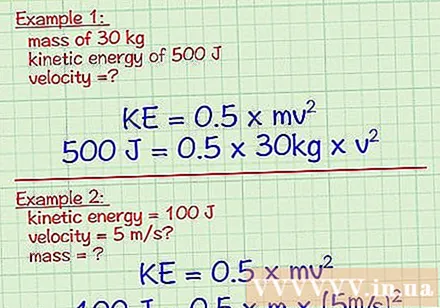
- Example 1: What is the velocity of an object with a mass of 30 kg and a kinetic energy of 500J?
- KE = 0.5 x mv
- 500 J = 0.5 x 30 x v
- Example 2: What is its mass if an object has a kinetic energy of 100 J and a velocity of 5 m / s?
- KE = 0.5 x mv
- 100 J = 0.5 x m x 5
- Example 1: What is the velocity of an object with a mass of 30 kg and a kinetic energy of 500J?
Switch to the equation to find unknown variables. Use the algebraic method to solve for unknown variables by shifting all known variables to one side of the equation.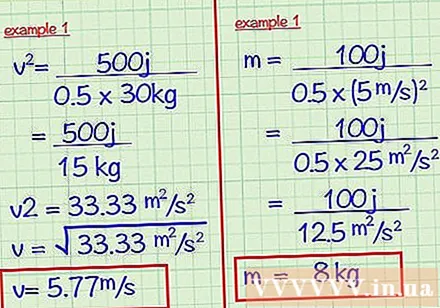
- Example 1: What is the velocity of an object with a mass of 30 kg and a kinetic energy of 500J?
- KE = 0.5 x mv
- 500 J = 0.5 x 30 x v
- Multiply mass by 0.5: 0.5 x 30 = 15
- Divide the kinetic energy by the result you just found: 500/15 = 33.33
- Get the square root to find the velocity: 5.77 m / s
- Example 2: What is its mass if an object has a kinetic energy of 100 J and a velocity of 5 m / s?
- KE = 0.5 x mv
- 100 J = 0.5 x m x 5
- Square the velocity: 5 = 25
- Multiply by 0.5: 0.5 x 25 = 12.5
- Divide the kinetic energy by the result you just found: 100 / 12,5 = 8 kg
- Example 1: What is the velocity of an object with a mass of 30 kg and a kinetic energy of 500J?