Author:
Joan Hall
Date Of Creation:
1 July 2021
Update Date:
11 May 2024

Content
- Steps
- Method 1 of 3: Herpes Symptoms
- Method 2 of 3: Getting Medical Help
- Method 3 of 3: Risk Factors for Herpes
The disease caused by the herpes simplex virus is sexually transmitted. Treatment can help relieve symptoms, relieve pain, and reduce the spread of infection, but there is no way to completely recover from herpes. The virus remains latent in the human body, but symptoms can come back again and again. Read our article to find out if you have this condition.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Herpes Symptoms
 1 Herpes virus. There are two strains of the herpes simplex virus - HSV-1 and HSV-2. Both are considered genital. HSV-1 most commonly affects the lips, mouth and spreads through oral sex, just like HSV-2. Both strains of the herpes virus are treatable.
1 Herpes virus. There are two strains of the herpes simplex virus - HSV-1 and HSV-2. Both are considered genital. HSV-1 most commonly affects the lips, mouth and spreads through oral sex, just like HSV-2. Both strains of the herpes virus are treatable. - It is necessary to treat the symptoms of the disease. If left untreated, genital herpes can spread to other people (including a baby during pregnancy) and can affect the bladder, rectum, and in severe cases, meningitis.
 2 Pay attention to symptoms 2 weeks after getting herpes. The first manifestations may appear in the near future. It is usually impossible to know for sure when the infection occurred, so watch out for any unusual symptoms. Herpes symptoms include fever, muscle aches, decreased appetite, and fatigue. See your doctor at the first symptoms of herpes.
2 Pay attention to symptoms 2 weeks after getting herpes. The first manifestations may appear in the near future. It is usually impossible to know for sure when the infection occurred, so watch out for any unusual symptoms. Herpes symptoms include fever, muscle aches, decreased appetite, and fatigue. See your doctor at the first symptoms of herpes. - The moment of herpes infection is difficult to determine, as the symptoms appear after a while. Infection with herpes can occur from a person who does not even have visible symptoms of the disease.
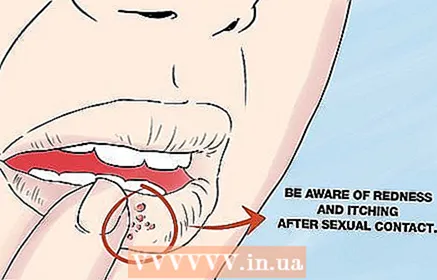 3 Pay attention to redness and itching. After sexual intercourse, look for any redness or itching in the genital area and around the mouth. Tingling and heat may be felt in the affected area. After a few days, a rash and herpetic blisters appear on the skin. Be aware of the risk factors that can contribute to the development of infection. These factors include:
3 Pay attention to redness and itching. After sexual intercourse, look for any redness or itching in the genital area and around the mouth. Tingling and heat may be felt in the affected area. After a few days, a rash and herpetic blisters appear on the skin. Be aware of the risk factors that can contribute to the development of infection. These factors include: - Trauma, stress, menstruation - these conditions lead to a sharp increase in cortisol, adrenaline and other stress hormones that reduce the defense mechanisms of the immune system. This gives the herpes virus the opportunity to activate.
- Burning and itching before blistering (prodrome). Try not to scratch the rash, as this will spread the virus and create new lesions of damaged skin.
- Sunburn or overheating. Solar radiation damages the skin and gives the herpes infection the opportunity to develop. Overheating or hypothermia weakens the immune system, so at times like these, herpes can wake up again.
 4 Look for blisters in the genital area. Look for blisters (bullae or vesicles) that appear 6 to 48 hours after other symptoms. After opening the bubbles, a yellow liquid flows out of them, and ulcers are formed. Bubbles can be found on lips, mouth, eyes, tongue, and other parts of the body. Before the bubbles appear, a tingling sensation usually occurs.
4 Look for blisters in the genital area. Look for blisters (bullae or vesicles) that appear 6 to 48 hours after other symptoms. After opening the bubbles, a yellow liquid flows out of them, and ulcers are formed. Bubbles can be found on lips, mouth, eyes, tongue, and other parts of the body. Before the bubbles appear, a tingling sensation usually occurs. - In women, bubbles appear on the lips, vagina, anus, cervix, buttocks, and thighs. The ulcers heal in 7-14 days.
- In men, vesicles appear on the scrotum, penis, buttocks, and thighs.
 5 Painful urination. During an exacerbation of herpes, urination may become painful. If you experience painful urination against the background of an exacerbation of herpes infection, you should consult a doctor. Women should look for unusual vaginal discharge (any abnormal or strange discharge). In some situations, vaginal discharge becomes clear, white, or yellowish-white.
5 Painful urination. During an exacerbation of herpes, urination may become painful. If you experience painful urination against the background of an exacerbation of herpes infection, you should consult a doctor. Women should look for unusual vaginal discharge (any abnormal or strange discharge). In some situations, vaginal discharge becomes clear, white, or yellowish-white. - Remember that vaginal discharge may not appear in all cases, that is, they are a possible symptom of herpes, and not a diagnostic one.
Method 2 of 3: Getting Medical Help
 1 See a doctor and get tested. During an exacerbation, your doctor may order tests for STIs or a study of fluid from the vesicles. These tests help detect the herpes virus.
1 See a doctor and get tested. During an exacerbation, your doctor may order tests for STIs or a study of fluid from the vesicles. These tests help detect the herpes virus. - Usually, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is used to diagnose herpes. A swab is collected from the affected area of the skin with a synthetic swab - it is placed in a test tube with liquid and sent to the laboratory. The laboratory uses special techniques to multiply genetic material and detect the herpes virus.
- In some cases, it is necessary to detect type-specific antibodies. This test can detect HSV-1 or HSV-2 infection. In 50% of infected people, this test is positive 4 weeks after infection. If the infection occurred more than 16 weeks ago, then the test gives a positive result in almost all cases.
- The doctor prescribes a PCR study of the vesicle. In this analysis, a smear of the epithelium and the contents of the vesicle is collected using a sterile swab. For diagnosis, the sample is sent to the laboratory.
 2 Treating symptoms with antiviral drugs. If the test is positive, your doctor may prescribe medications to suppress the infection and treat symptoms. These drugs prevent the spread of herpes infection to others. It is necessary to start treatment as soon as possible in accordance with the instructions of the doctor. Antiviral drugs include:
2 Treating symptoms with antiviral drugs. If the test is positive, your doctor may prescribe medications to suppress the infection and treat symptoms. These drugs prevent the spread of herpes infection to others. It is necessary to start treatment as soon as possible in accordance with the instructions of the doctor. Antiviral drugs include: - Acyclovir. This drug is most commonly used to treat genital herpes and relapsing labial infections. The drug is also available in a form for topical treatment of herpetic lesions of the eyes. Acyclovir is considered safe for use in pregnant and lactating women and children.
- Penciclovir. This medication is used for the topical treatment of lip herpes.
- Valacyclovir. This drug is used to treat primary or recurrent cases of genital herpes.
- Foscarnet. This is a second-line drug, it is prescribed when acyclovir is ineffective, in cases of immunodeficiency with systemic herpes infection.
 3 Learn more about herpes. Explore the available information about infection and the herpes virus. The better you understand the infection, the easier it is to prevent recurrence of herpes. Herpes infection is well understood. Currently, new methods of treatment are constantly emerging.
3 Learn more about herpes. Explore the available information about infection and the herpes virus. The better you understand the infection, the easier it is to prevent recurrence of herpes. Herpes infection is well understood. Currently, new methods of treatment are constantly emerging. - See your doctor, and he will give recommendations on the prevention of relapse, prescribe modern treatment for you.
 4 Avoid spreading the infection. Take a moment to inform your sexual partner about your health. Take steps to prevent the spread of the infection. Most likely, you will need to change your lifestyle and habits. For example, it is necessary to exclude sex with multiple partners, it is necessary to use condoms when the infection subsides, and to avoid sex during an exacerbation.
4 Avoid spreading the infection. Take a moment to inform your sexual partner about your health. Take steps to prevent the spread of the infection. Most likely, you will need to change your lifestyle and habits. For example, it is necessary to exclude sex with multiple partners, it is necessary to use condoms when the infection subsides, and to avoid sex during an exacerbation. - Don't touch herpes sores! If you touch a herpes bladder, wash your hands immediately with soap and water to get rid of the virus. Avoid kissing during a flare-up of labial herpes (on the lips).
Method 3 of 3: Risk Factors for Herpes
 1 Assess your risk factors. Understand that many people live with genital herpes for a long time without any symptoms. Become familiar with the risk factors that require early treatment. Risk factors for contracting herpes include:
1 Assess your risk factors. Understand that many people live with genital herpes for a long time without any symptoms. Become familiar with the risk factors that require early treatment. Risk factors for contracting herpes include: - Immunodeficiency states. A weakened immune system will make your herpes infection more severe. Soreness, stress, AIDS, tumors, diabetes, and old age are factors that make it easier to contract HSV-1 and HSV-2.
- Atopic dermatitis in children. Atopic dermatitis is manifested by itchy skin. When herpes joins atopic dermatitis, a serious skin lesion develops.
- Harmful factors of labor. Some professions are more susceptible to infection with the herpes virus.For example, a dentist has a higher risk of contracting HSV-1, which leads to a painful hand skin infection.
 2 Think back if you have had unprotected sex lately. HSV-2 infection occurs during sexual intercourse. During an exacerbation of the infection, even a condom does not provide sufficient protection. Herpes is most likely to contract through contact with mucous membranes, in particular through contact with the mouth, anus, penis and vagina. When the mucous membrane of a sick person comes into contact with the mucous membrane of a healthy person, a healthy person becomes infected.
2 Think back if you have had unprotected sex lately. HSV-2 infection occurs during sexual intercourse. During an exacerbation of the infection, even a condom does not provide sufficient protection. Herpes is most likely to contract through contact with mucous membranes, in particular through contact with the mouth, anus, penis and vagina. When the mucous membrane of a sick person comes into contact with the mucous membrane of a healthy person, a healthy person becomes infected. - Herpes is easily transmitted during the following contacts: oral, anal, vaginal sex (and any other combination of mucous membranes).
 3 Determine the number of sexual partners. Since herpes spreads through oral and genital contact, the risk of getting herpes increases with each new sexual partner.
3 Determine the number of sexual partners. Since herpes spreads through oral and genital contact, the risk of getting herpes increases with each new sexual partner.  4 The risk of infection in women is higher. Women have a higher risk of getting herpes than men. This is due to the fact that the transmission of herpes occurs more easily from man to woman, and not vice versa. For example, 20.3% of women are infected with HSV-2, while among men this figure reaches 10.6%.
4 The risk of infection in women is higher. Women have a higher risk of getting herpes than men. This is due to the fact that the transmission of herpes occurs more easily from man to woman, and not vice versa. For example, 20.3% of women are infected with HSV-2, while among men this figure reaches 10.6%. - According to the American Centers for Disease Control, one in six people in the United States between the ages of 14 and 49 has genital herpes.



