Author:
Randy Alexander
Date Of Creation:
27 April 2021
Update Date:
14 May 2024

Content
Bleeding is the way the blood leaves the blood vessels in any part of the body. When injured and bleeding, it's important for us to stop blood loss quickly. Usually, it is not difficult to stop the bleeding. However, in severe cases, heavy and persistent bleeding can lead to shock, blood circulation disturbances, or other serious consequences. In some cases, uncontrolled bleeding can damage vital tissues and organs, leading to the risk of death. You need to consider the location of the bleeding and the severity, and take the right first aid measures. In the event of a massive or unstoppable bleeding, seek immediate medical attention.
Steps
Method 1 of 3: Stop bleeding for small cuts

Rinse the cut with water. The running water will help clean the wound and stop the bleeding. You can run cold tap water over the cut to constrict blood vessels and stop bleeding, or turn on hot water to bottle the wound and help blood clot. Don't use both hot and cold water - use only one method for best results.- You can use ice instead of cold water to constrict blood vessels. Apply an ice cube to the cut for a few seconds until the wound closes and the bleeding stops.
- If there are many small cuts on your body, you can take a hot shower to wash and bottle multiple wounds at the same time.
- Apply pressure to the wound. Apply pressure to the wound with a clean gauze pad or paper towel after it has been washed. Hold for a few minutes, then check to see if the bleeding has stopped.
- If the blood seeps through the gauze, replace it with a new, clean, dry gauze pad.

Use a pen to stop bleeding. Originally used to treat scratches and burns from shaving, this wax pen is also great for small cuts. You can rub it on your skin with a pen and let the astringent minerals work. It may feel a bit painful at first, but after a few seconds you should stop the pain and stop bleeding.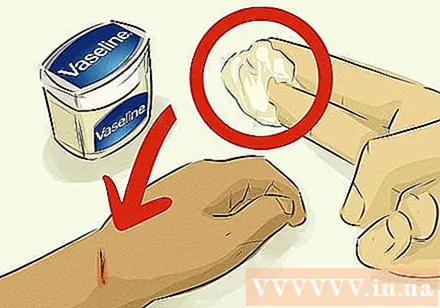
Apply Vaseline cream to stimulate blood clotting. Apply a thin layer of Vaseline to the wound. With a waxy texture, Vaseline cream can block blood flow to the skin and help create blood clots. Regular lip balm is also effective if you don't already have Vaseline.
Use antiperspirants. Similar to hemostasis pens, antiperspirants contain aluminum chloride, which acts as an astringent, helping to prevent bleeding. You can take some of the antiperspirant on your finger and rub it on the cut or roll it directly onto the wound.
Dab the Listerine solution on the cut. Originally a product used after shaving, Listerine solution can disinfect wounds and help stop bleeding. You can either pour Listerine directly onto the cut or dip a cotton ball into Listerin and dab it on the wound. You should notice less bleeding after 1-2 minutes.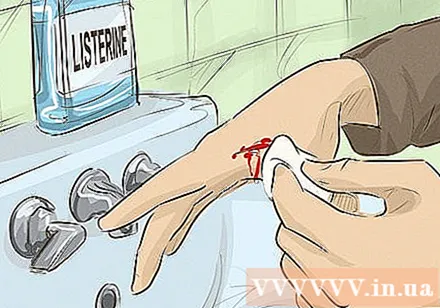
Use aluminum block (alum block). This product comes in the form of a soap cake made from minerals that can help stop bleeding. Dip the aluminum block in water to wet it and rub it gently over the cut. You do not need to press the aluminum block into the wound; minerals in it will exert its effects.
Apply white vinegar to disinfect the wound. The astringent properties of vinegar will help disinfect and coagulate the cut. Soak a little white vinegar in a cotton ball, dab it on the cut, and wait for the bleeding to stop.
Try witch hazel to stop the bleeding. Similar to white vinegar, witch hazel acts as a natural astringent that is very effective in clotting blood on wounds. Pour witch hazel directly over the wound or use a cotton ball soaked in witch hazel.
Sprinkle cornstarch on the wound. Sprinkle a little bit of cornstarch on the cut, being careful not to rub or scratch any more. You can press lightly on the cut to give the cornstarch a quicker effect. Rinse the cornstarch under running water once the bleeding has stopped.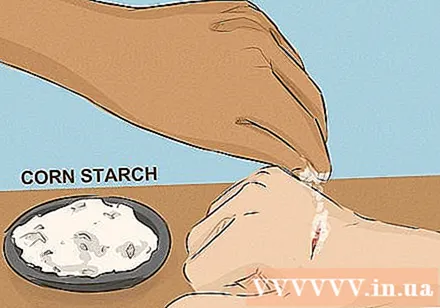
Use a spider web in an emergency. This is a great choice while you are on a picnic or are outdoors. Pick up some webs (make sure no spiders!) And cover the wound, wrapping it up if necessary. The spider web will stop bleeding and help the wound to clot inside.
Cover the cut when bleeding has been controlled. Cover the wound with a clean bandage or gauze to prevent dirt and further bleeding. You can use a simple bandage or a clean gauze pad. advertisement
Method 2 of 3: Treating serious injuries
Lay. You can reduce the risk of shock by raising your legs or lying head lower than your torso. If you are helping someone else, check the victim's breathing and circulation before handling.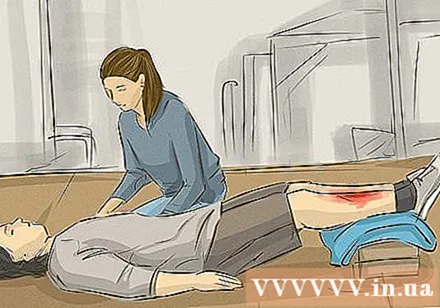
- If you suspect the victim is in shock, call an ambulance or seek medical attention right away.
Raise the injured hand or leg. Raising the injured hand / leg (assuming the wound is in the arm / leg) will help reduce massive bleeding. However, do not attempt to move your limbs if you suspect a fracture.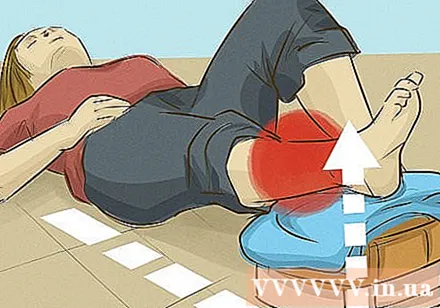
Remove any debris from the wound. Clean up dirt and visible objects, but do not wash the wound too thoroughly to avoid aggravating the wound. The urgent priority now is to prevent excessive bleeding. The wound cleaning can be done later.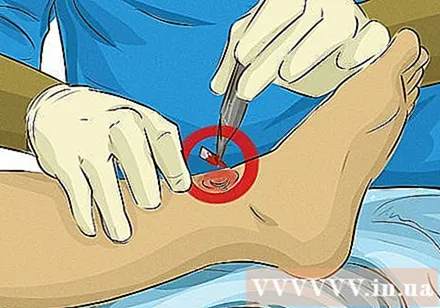
- However, you need to leave the foreign body in place if it is a large size (a large piece of glass, a knife or similar). The foreign body itself also works to prevent bleeding. Just press around the object, be careful not to press any further.
Press firmly on the wound until the bleeding stops. Press a clean gauze pad or cloth on the wound. Place your hand on the gauze and press firmly. You can use your bare hands to press on the wound if there is nothing else.
Create stable pressure on the wound. If the wound is on the arm or leg, you can wrap the wound with a bandage or cloth to maintain pressure (a triangular fold over the wound and tying it is ideal). For groin wounds or other parts that cannot be wrapped, you can place a thick gauze pad over the wound and press it down with your hand.
Notice if blood is leaking from the wound. Apply additional gauze or bandages to the wound if the blood has seeped through the gauze / dressing earlier. However, do not wrap the wound too many times, as thick layers of fabric will reduce the pressure on the wound. If you suspect that the dressing is not working, remove the bandage and gauze to review. If the bleeding appears to be controlled, you can maintain the pressure until you are sure the bleeding has stopped or until emergency personnel arrive.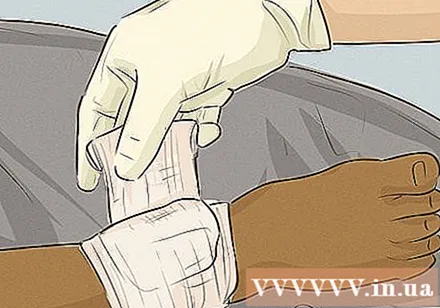
Use pressure point, if necessary. If you cannot stop the bleeding with just pressure, you can combine the pressure directly on the wound with pressure on one of the pressure points. Use your fingers to press down on the blood vessels. The most common pressure points required are described as follows:
- Arm artery for handling forearm injuries. This artery runs down the inside of the arm, from the armpit to the elbow.
- The femoral artery to treat thigh wounds. This artery is located in the groin area, near the groin.
- The artery is used to treat a leg wound. This artery is located at the arch of the leg, behind the knee.
Maintain pressure until the bleeding stops or emergency personnel arrive. Don't stop pressing when you're not sure that the bleeding has stopped. If you don't see any blood seeping through the gauze, check the wound from time to time for bleeding.
- Do not press on the artery more than 5 minutes after the bleeding has stopped.
- Use garnet if the bleeding becomes life-threatening. Garlic usually stops bleeding immediately when used correctly, but can harm the victim if used incorrectly.
Keep track of the victim's breathing. Check to make sure the tape is not too tight. If the victim has chills, pale skin, toes or fingers that do not return to their original color when pressed down, or if the victim complains of numbness or stinging sensation, the bandage may be too tight. advertisement
Method 3 of 3: Handling internal bleeding
Call an ambulance right away if you suspect the victim has internal bleeding. Get the victim of internal bleeding to the hospital as soon as possible. This condition cannot be treated at home, and only a doctor can handle it. Symptoms of internal bleeding include:
- Heart beat fast
- Hypotension
- The skin is cold sweat
- Dizziness or confusion
- Pain and inflammation near the wound site
- There are bruises on the skin
Relax in a comfortable position. Don't try to move and keep lying down if possible. If you are helping a victim with suspected internal bleeding, reassure them and rest them in a comfortable position to prevent further injury.
Check for breathing conditions. Monitor airway, breath and blood circulation. Stop bleeding if bleeding comes out.
Maintain normal body temperature. Keep the victim from getting too hot or too cold by applying a washcloth to the forehead. advertisement
Advice
- If possible, you should wear latex or rubber gloves before coming into contact with someone else's blood. In an emergency, you can use a clean plastic bag to protect your hands.
- When applying pressure on a bleeding wound, do not lift the gauze to see if the bleeding has stopped. Please continue to press on the wound.
- Avoid the use of hydrogen peroxide or iodine solution when handling the wound, as these can cause tissue damage.
- If you are taking an anticoagulant, it may take longer and more pressure to stop the bleeding. If you are helping someone, look for a medical necklace or bracelet to see if the victim is taking anticoagulants.
- For serious bleeding cases, you need to call an ambulance or have an ambulance caller as soon as possible.
- Arterial bleeding requires more precise pressure than general pressure on venous bleeding wounds. You may need to press your fingertips on the starting point of the bleeding - not general pressure on the wound.This is the artery with high blood pressure. In the event of an arterial bleeding, seek medical attention as quickly as possible.
- If the bleeding is not too bad, simply wash the wound with water and cover it.
- If the victim has serious abdominal injuries, do not return the internal organs to the abdomen. Cover the wound with gauze and wait for the ambulance to come and move the victim.
Warning
- If you have a stab or deep cut that hasn't been vaccinated against tetanus in the past 5 years, see your general practitioner.
- To prevent infection between you and the victim, you need to take the following precautions:
- Use quarantine when in contact with blood. Wear gloves (preferably latex-free gloves, as some people are allergic to latex), or use a clean, folded cloth.
- Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water after contact with bleeding victim. Use the sink for your hands, not the basin used to prepare food.
- Do not eat, drink or touch the nose / mouth / eyes without washing hands thoroughly after coming into contact with the bleeding victim.
- The garnet method is not recommended. However, in the event of a serious injury, you may need to use a garland to save your life. However, be aware that this can lead to loss of limbs.