Author:
Monica Porter
Date Of Creation:
16 March 2021
Update Date:
14 May 2024

Content
Many women experience vaginal bleeding at some point in their pregnancy, especially the first 3 months of pregnancy. In many cases (especially in the early stages, and if the amount of blood is not much), this is completely normal. However, persistent bleeding can be quite worrying and it can guarantee that you will need to see a doctor, especially if the bleeding is accompanied by pain, cramps, fever, dizziness or fainting. It's important to have a good understanding of strategies for how to deal with and manage your bleeding, and also be aware of when you need to see your doctor for help and treatment.
Steps
Method 1 of 2: Assessment and Management of Vaginal Bleeding
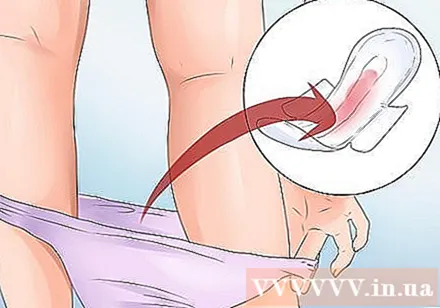
Watch for bleeding. It is important to be aware of the amount of blood you lose during this process. This method will help your doctor make a diagnosis as well as create a management plan. Start monitoring the amount of blood you lose as soon as you become aware of the problem.- You can do this by placing a tampon on your underwear until the dressing is completely wet. Count the number of tampons you used from 8:00 am today until 8:00 am the next morning. Record these numbers, then bring them to the hospital for evaluation by your doctor.
- Also be sure to watch for other symptoms of the bleeding, such as whether bleeding is accompanied by pain, and bleeding that is constant or intermittent. This information will help describe your condition so that your doctor can easily find out the cause.
- Note the color of the blood (pink or red or brown), as well as see if you notice the presence of a blood clot or other "mass of tissue" that escapes with the blood. If so, you should collect them in a container for your doctor to see, as it may help your doctor diagnose the cause of your problem.

Rest much. For low bleeding in early pregnancy, rest is the most ideal treatment. Your doctor will usually recommend that you lie down in bed for the first few days after experiencing vaginal bleeding.- If the problem does not go away or goes away after you have rested, you may need to see your doctor for a more detailed assessment.

Avoid heavy work. Your doctor will definitely advise you to avoid heavy or stressful work such as lifting weights, regularly climbing ladders, jogging, cycling, etc. These activities will shock the uterus and can destroy the fragile, newly formed blood vessels in the placenta. Avoiding these activities is essential, even if you have only mild vaginal bleeding.- Limit physical activity and avoid heavy work for at least 2 weeks after the bleeding has stopped.
Don't have sex in this moment. Sometimes, having sex can take shape or make problems worse.
- If you bleed during pregnancy, you should avoid having sex until your doctor says it is okay. Usually, you will need to wait at least 2 - 4 weeks after the condition ends.
Do not use tampons (tampons) or douche. Do not insert anything into the vagina after bleeding. Douching or using tampons should be avoided entirely, as this can damage the cervix or vaginal wall and cause more bleeding. Douching will also allow bacteria and other microorganisms to enter the vagina, causing serious infections.
Drink enough water. It is important that you drink enough fluids during the time you experience vaginal bleeding. This is especially true if you have severe bleeding.
- You should drink at least 8 glasses of water per day to stay hydrated and provide many other benefits. Bleeding is correlated with dehydration, so you'll need to drink more water than usual to make up for the lost water.
- Staying hydrated is also important for the health and well-being of your baby.
Understand what causes vaginal bleeding during pregnancy. This can help you make a difference to the problem that might be happening in your case.
- Vaginal bleeding is actually quite normal in the first 3 months (during the first 12 weeks of pregnancy) and about 20-30% of women experience this problem. In many cases, bleeding is not dangerous, which means it does not affect the mother and baby and can be due to the fetus being implanted in the uterus or the effects of other physiological changes during the pregnancy. course of pregnancy.
- However, heavy bleeding and / or pain during the first 3 months of pregnancy can also be due to a more serious problem, such as an "ectopic pregnancy" (a fetus implanted in a replacement fallopian tube. because of the uterus), "false pregnancy" (this is a fairly rare condition in which an abnormal tissue will develop in the uterus instead of a fetus), or miscarriage.
- 50% of vaginal bleeding within the first 20 weeks of pregnancy is a sign that you have miscarried.
- Bleeding later in pregnancy (in the second and third trimester) is often of great concern. Causes include problems with the placenta, with the uterus (especially if you have had a cesarean section before), preterm labor (determined by labor before 37 weeks), and of course the process itself. labor process (if you are close to your due date).
- Other causes of bleeding that may not be related to pregnancy include "trauma" (or damage to the vaginal wall) from the act of sex, cervical polyps (tumors around the cervix that cause bleeding and can occur in a woman's uterus regardless of whether they are pregnant or not), cervical dysplasia (abnormal cell appearance that can cause cancer), and / or cervical cancer (one of The most common forms of cancer are in people who don't usually have a Pap test).
Calculate the date of birth and consider whether bleeding is due to the onset of labor. Pregnancy usually lasts for 40 weeks or 280 days. You can use this information to calculate the date of your baby's birth - just add 9 calendar months and 7 days from the first day of your last menstrual cycle. For example, if your last menstrual cycle started January 1, 2016, your baby's date of birth would be October 8, 2016.
- Bleeding closer to your due date can be a sign that you're starting labor. This usually takes place 10 days before or after 10 days of your expected delivery. You should report it to your doctor right away if you suspect that you are in labor.
Know when to seek help from a medical professional. You should notify your doctor promptly if you experience any bleeding during pregnancy. If your bleeding is associated with one of the following symptoms, you should see your doctor as soon as possible so that your doctor can evaluate and treat:
- Severe pain or cramps
- Dizziness or fainting (signs of heavy blood loss)
- Mass of tissue (blood clot) leaving the vagina with blood (may indicate miscarriage)
- Fever and / or chills (could be signs of infection)
- Heavy bleeding with no signs of remission or termination.
Method 2 of 2: Know When to Seek Medical Help
You can ignore mild bleeding. If the amount of blood is quite small (just a few drops), brown in color, and lasts no more than a day or 2, and doesn't cause pain or cramping, it's okay to ignore it. Usually, this is only bleeding caused by the fetus or the result of dilated blood vessels.
- No matter how mild the bleeding may be, avoid doing heavy work for a few days and carefully monitor the blood loss.
Seek medical help if you bleed a lot. Any major bleeding during pregnancy should be considered an emergency. Heavy bleeding means more blood loss than normal menstrual bleeding.
Pay attention to any pain or cramping you feel. Pain that comes and goes is a sign of uterine contraction, meaning the uterus is trying to remove the fetus. In the early stages of pregnancy, pain and cramps can be a sign of miscarriage and in the last 3 months of pregnancy it may be a sign of labor. So if you experience any pain or spasms, you should see your doctor right away.
- The real pain of labor will happen often and in intervals. Its level will increase gradually and are accompanied by "rupture of amniotic fluid" (a drop of mucus with blood).
Seek help if you feel dizzy or want to faint. Dizziness or fainting is a symptom of heavy blood loss.
Body temperature test. Bleeding associated with a fever is often a sign of an infection, such as an infection inside the uterus after spontaneous miscarriage or abortion. Therefore, you should see your doctor if you experience any signs of fever.
Seek help right away if your vagina is releasing a blood clot. This is a serious sign of a miscarriage. If this happens, you should see a doctor right away so the doctor can wash the uterus if needed and thereby help you manage the bleeding.
Follow your doctor's instructions to take care of yourself after treatment. Whatever the cause of your vaginal bleeding (whether it is due to miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, infection, labor), it puts considerable strain on your body. In most cases, your doctor will tell you to rest, not exercise too hard, abstain from sex for a while, and drink plenty of fluids. Remember to pay attention to the advice of your doctor to maximize the recovery process as well as prevent other complications. advertisement
Warning
- It is important to tell your doctor if you experience any bleeding if your blood type is Rh negative because you will likely need RhoGAM injection.